heredity study guide
advertisement

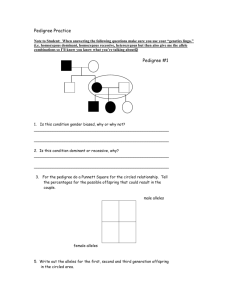
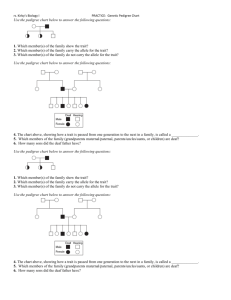
Name:___________________________________________________ Date:____________________ Pd:______ Heredity (Chapter 5) Study Guide Part I: Vocabulary. Using the word bank below, match each word to its correct definition. alleles dominant genetic engineering recombinant DNA genetics genotype heredity heterozygous homozygous incomplete dominance phenotype polygenic inheritance Punnett square recessive sex-linked gene Gregor Mendel 1. The allele for hemophilia is on the X chromosome and is considered a ___________________________. 2. ______________________________ is the passing of traits from one generation to another. 3. The different forms a gene may have for a trait are called _____________________________. 4. In ______________________________ both alleles are expressed in offspring. 5. ______________________________ is known as “The Father of Genetics”. 6. A ______________________________ trait covers up other traits. 7. In a Punnett square, a small letter (t) stands for a ______________________________ allele. 8. A tool used to predict the possible offspring of a mating is called a ______________________________. 9. The genetic makeup of an organism is called its ______________________________. 10. ______________________________ is the way an organism looks and behaves a result of its genotype. 11. The study of how traits are inherited through the interactions of alleles is ______________________________. 12. Through ______________________________ scientists are experimenting to change the arrangement of DNA in a gene. 13. An organism with two alleles that are exactly the same is _____________________________. 14. ______________________________ occurs when a group of gene pairs acts together to produce a single trait (Examples include height and skin color). 15. An organism that has two different alleles for a trait is ______________________________. 16. A type of genetic engineering where a useful gene is inserted into a bacterium is known as __________________________________________. Part II: Punnett Square Practice Problems. For each problem below you must write down your “cross” and a punnett square. Box or circle the final answer. 17. In silkworms, the dominant allele for cocoon color is yellow (Y), and the recessive allele is white cocoon (y). If white cocoon silk worm is crossed with a homozygous dominant yellow cocoon silk worm, what will be all the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring? 18. In mice, the dominant allele for eye color is black (B), and the recessive allele is red eyes (b). If two heterozygous parents are crossed, what will be the probability of the offspring having red eyes? 19. A widow’s peak (W) hairline is dominant to straight hairline (w). A straight hairline person is crossed with another person who is heterozygous for the trait. What is the probability of the offspring having a widow’s peak? 20. Sex-Linked Punnett Square. Colorblindness is inherited as a sex-linked recessive disease. An affected male marries a heterozygous female. Use b for color blindness, and use B for normal. What is the genotype of the male (remember you put the genes on top of the X chromosome): ____________ What is the genotype of the female: ________________ Draw and complete the punnett square below: What is the probability that the daughters will be color blind? _____________________ What is the probability that the sons will be color blind? ______________________ Part III: Short Answer. Respond to each question/prompt completely in the space provided. 21. The pedigree below shows how color-blindness (a sex-linked disorder) is spread through this family. Use this pedigree to answer the questions. a. How many individuals in the pedigree are affected with color blindness? ____________________________ b. How many individuals in the pedigree are male? _________________________________ c. How many individuals in the pedigree are female? ______________________________ d. How many females are affected with color blindness?________________________________ e. All of the carriers are which sex? Why is that the case? __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 22. How is incomplete dominance different from the patterns observed by Mendel? __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 23. Genetic counselors help individuals determine the risk of passing a disease on to their offspring. What would a pedigree be a useful tool for a genetic counselor? __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 24. Do you agree with genetic testing for diseases? Use specific evidence from class discussions, the video, or class readings to support your answer. __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________