review practice
advertisement
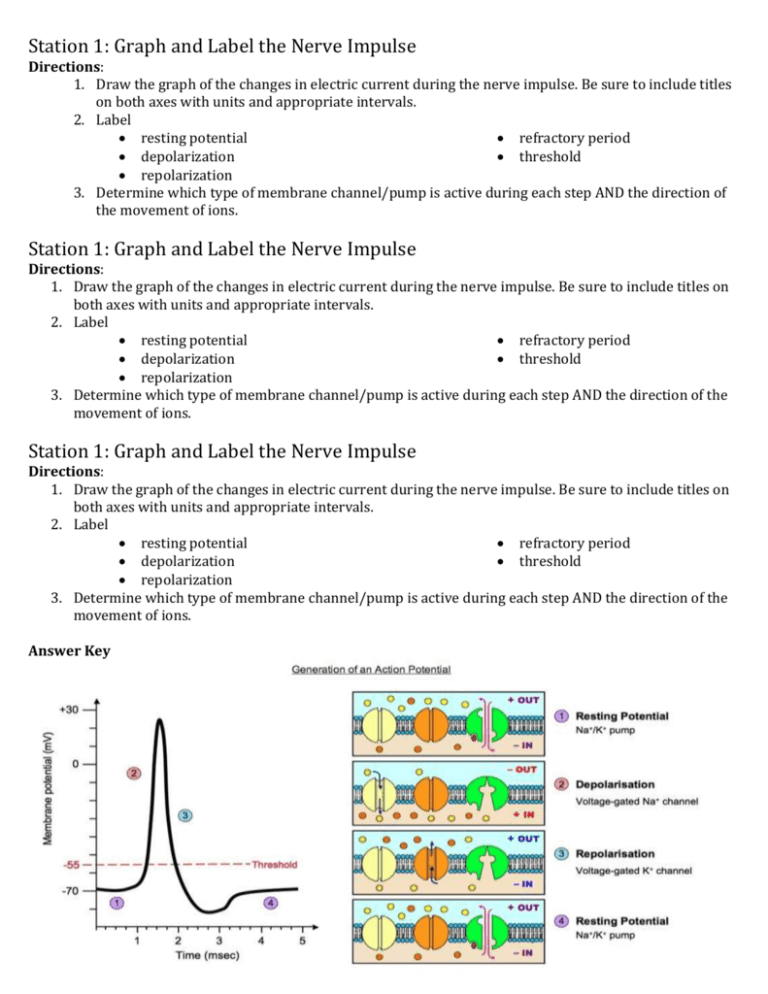
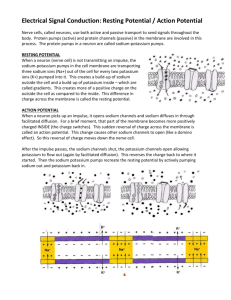
Station 1: Graph and Label the Nerve Impulse Directions: 1. Draw the graph of the changes in electric current during the nerve impulse. Be sure to include titles on both axes with units and appropriate intervals. 2. Label resting potential refractory period depolarization threshold repolarization 3. Determine which type of membrane channel/pump is active during each step AND the direction of the movement of ions. Station 1: Graph and Label the Nerve Impulse Directions: 1. Draw the graph of the changes in electric current during the nerve impulse. Be sure to include titles on both axes with units and appropriate intervals. 2. Label resting potential refractory period depolarization threshold repolarization 3. Determine which type of membrane channel/pump is active during each step AND the direction of the movement of ions. Station 1: Graph and Label the Nerve Impulse Directions: 1. Draw the graph of the changes in electric current during the nerve impulse. Be sure to include titles on both axes with units and appropriate intervals. 2. Label resting potential refractory period depolarization threshold repolarization 3. Determine which type of membrane channel/pump is active during each step AND the direction of the movement of ions. Answer Key Station 2: Draw & Label The Neuron Directions: 1. Draw a typical Neuron 2. Label Nucleus Axon Nodes of Ranvier Cell Body Dendrites 3. Show the direction the nerve impulse moves Motor End Plate or Axon Terminal Myelin Sheath Station 2: Draw & Label The Neuron Directions: 1. Draw a typical Neuron 2. Label Nucleus Axon Nodes of Ranvier Cell Body Dendrites 3. Show the direction the nerve impulse moves Motor End Plate or Axon Terminal Myelin Sheath Station 2: Draw & Label The Neuron Directions: 1. Draw a typical Neuron 2. Label Nucleus Axon Nodes of Ranvier Cell Body Dendrites 3. Show the direction the nerve impulse moves Answer Key Motor End Plate or Axon Terminal Myelin Sheath Station 3: Sequence the steps of the Nerve Impulse & the Synapse Directions: 1. Pick a set of cards (Nerve Impulse = Blue / Synapse = Green) and put them in order. 2. Try and remember the order without using the cards. resting membrane is polarized; interior is -70mV/negative relative to outside; more sodium ions outside than inside; more potassium ions inside than outside Disturbance of membrane Sodium channels open Sodium ions rush into cell Causes depolarization Sodium channels shut Potassium channels open Potassium ions rush out of cell Causes repolarization (helps restore polarized state of membrane Sodium-potassium pump restores resting potential and maintains polarity Process repeated along the length of the neuron resting membrane is polarized; interior is -70mV/negative relative to outside; more sodium ions outside than inside; more potassium ions inside than outside Disturbance of membrane Sodium channels open Sodium ions rush into cell Causes depolarization Sodium channels shut Potassium channels open Potassium ions rush out of cell Causes repolarization (helps restore polarized state of membrane Sodium-potassium pump restores resting potential and maintains polarity Process repeated along the length of the neuron Station 3: Sequence the steps of the Nerve Impulse & the Synapse Directions: 1. Pick a set of cards (Nerve Impulse = Blue / Synapse = Green) and put them in order. 2. Try and remember the order without using the cards. resting membrane is polarized; interior is -70mV/negative relative to outside; more sodium ions outside than inside; more potassium ions inside than outside Disturbance of membrane Sodium channels open Sodium ions rush into cell Causes depolarization Sodium channels shut Potassium channels open Potassium ions rush out of cell Causes repolarization (helps restore polarized state of membrane Sodium-potassium pump restores resting potential and maintains polarity Process repeated along the length of the neuron resting membrane is polarized; interior is -70mV/negative relative to outside; more sodium ions outside than inside; more potassium ions inside than outside Disturbance of membrane Sodium channels open Sodium ions rush into cell Causes depolarization Sodium channels shut Potassium channels open Potassium ions rush out of cell Causes repolarization (helps restore polarized state of membrane Sodium-potassium pump restores resting potential and maintains polarity Process repeated along the length of the neuron Action potential reaches axon terminal Calcium channels open Calcium causes vesicles to release neurotransmitter Neurotransmitter crosses synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter binds to neuroreceptors Triggers signal in post-synaptic neuron Action potential reaches axon terminal Calcium channels open Calcium causes vesicles to release neurotransmitter Neurotransmitter crosses synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter binds to neuroreceptors Triggers signal in post-synaptic neuron Action potential reaches axon terminal Calcium channels open Calcium causes vesicles to release neurotransmitter Neurotransmitter crosses synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter binds to neuroreceptors Triggers signal in post-synaptic neuron Action potential reaches axon terminal Calcium channels open Calcium causes vesicles to release neurotransmitter Neurotransmitter crosses synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter binds to neuroreceptors Triggers signal in post-synaptic neuron Action potential reaches axon terminal Calcium channels open Calcium causes vesicles to release neurotransmitter Neurotransmitter crosses synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter binds to neuroreceptors Triggers signal in post-synaptic neuron Answer Key The Nerve Impulse: The Synapse: