Chapter 6 Notes ws
advertisement

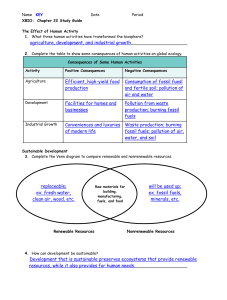
Name Class Date 6.1 A Changing Landscape The Effect of Human Activity Humans and other organisms change the environment when they obtain food, eliminate wastes, and prepare places to live. Because Earth is like an island, life is limited to the resources that are here. Humans affect regional and global environments through three major activities: _______________________, particularly ___________________________, which is the cultivation of a single crop _______________________________________________________, including conversion of farmland and destruction of habitats for other organisms _______________________________________, which consumes energy and emits pollutants Sustainable Development In economic terms, ecosystems are providers of goods and services (natural resources). Healthy ecosystems produce or replace ______________________________________. Humans must be careful about the use of _____________________________________________, such as _________________________, which cannot be replaced. _______________________________________________ provides for human needs while preserving the ecosystems that provide renewable resources. The Effect of Human Activity Consequences of Some Human Activities Activity Positive Consequences Agriculture Development Industrial Growth How is Earth like an island? Negative Consequences Sustainable Development coal marsh grass natural gas oil Renewable Resources 1. Sustainable development is the wise use of renewable resources nonrenewable resources pine tree wind Nonrenewable Resources . both renewable and nonrenewable resources 2. When fossil fuels are depleted, they are essentially gone for a little while forever 3. A renewable resource . cannot be produced within a reasonable amount of time. nonrenewable resource 4. Which of the following is an example of sustainable development? Circle the right answer. When building a new house, the builders leave many of the trees in place. After they paint a building, the painters dump the leftover paint in a nearby stream. A new highway goes through a wetland. 6.2 Using Resources Wisely Soil Resources Soil is a _________________________________, but it must be managed properly. ________________________________ is the wearing away of surface soil by water and wind. In dry climates, farming and overgrazing change farmland into deserts, a process called _________________________________. __________________________________ is loss of forests. Because healthy forests hold soil in place, deforestation increases erosion. Sustainable uses include leaving stems and roots of previous crops in place, __________________________, contour plowing, terracing, selectively harvesting mature trees, and __________________________. Freshwater Resources The amount of fresh water is limited, and some sources cannot be replaced. A __________________________ is a harmful material that can enter the biosphere. Water pollutants come from industrial chemicals, residential sewage, and other sources. Nonpoint pollution________________________________________________________ Point pollution________________________________________________________ Many chemical pollutants become concentrated in organisms at higher trophic levels of the food chain through ___________________________________________. Sustainable uses include conservation, pollution control, and watershed protection. Atmospheric Resources Clean air is important to human health and Earth’s climate. Pollution reduces air quality. __________________ is a mixture of chemicals formed from emissions from cars and industry. Burning fossil fuels releases compounds that join with water in air, forming ___________________. _______________________, such as ______________________ and ___________________, can cause global warming. Particulates are microscopic particles that cause health problems. One way of sustaining air quality is controlling automobile emissions. Soil Resources What is topsoil? How does it form? Sustainable Soil Use Examples What is a “dead zone,” and what is its cause? Atmospheric Resources 1. Which is the name for the mixture of chemicals that forms as a gray-brown haze in the atmosphere? A. dust C. ozone B. smog D. radiation 2. Which component of acid rain kills plants and harms soil? A. carbon dioxide and water C. nitric and sulfuric acids B. CFCs and fossil fuels D. ozone and particulates 3. Which is the name for the bits of ash and dust put into the air by certain kinds of diesel engines? A. particulates C. ozone layer B. precipitation D. greenhouse gases 4. Which is a pollutant of soil and water that is now dropping steadily due to laws that affected the automobile industry? A. carbon C. nitrogen B. lead D. ozone 5. Why is smog a problem? Biological Magnification The diagram below shows the biological magnification of the pollutant DDT. 1. Find the trophic level with the lowest concentration of DDT. Color it blue. 2. Find the trophic level with the highest concentration of DDT. Color it red. 3. Draw an arrow showing how the concentration of DDT increases in trophic levels. Use the diagram to answer the questions. 4. Circle the organism that has the most DDT in its body. zooplankton small fish 5. Think about your answer to item 4. Select the choice below that best explains the reasoning behind your answer. A. Zooplankton has DDT. Small fish eat lots of zooplankton. Therefore DDT builds up in the bodies of the small fish. B. Large fish eat small fish, and large fish have more DDT than small fish. Therefore small fish have the most DDT. Concept Map acid rain automobile emission standards crop rotation deforestation desertification drip irrigation greenhouse gases industrial chemicals nonpoint sources residential sewage smog Negative human impacts on the environment Water pollution Soil erosion Air pollution resulting from unwise handling of common forms are Gray-brown haze Loss of trees poor soil productivity CO2 acid precipitation DDT, etc. other sources nitrogen and phosphorous in Sustainable environmental practices Water conservation and water quality such as Soil conservation such as Air quality such as 6.3 Biodiversity The Value of Biodiversity The sum of all the genetic diversity among all the organisms in the biosphere is called __________________________. There are three general types of biodiversity: ____________________________________ is the variety of habitats, communities, and ecological processes in the biosphere. ______________________________________________ is the number of different species in an area or in the biosphere. ________________________________________ is the total of all genetic information carried in living things. Biodiversity benefits humans through its contributions to medicine and agriculture and through the provision of ecological goods and services. Threats to Biodiversity Human activities threaten biodiversity. Development splits ecosystems into pieces, resulting in ______________________________. The smaller the pieces of a habitat, the less likely that species in the habitat can survive. Other threats to biodiversity include hunting, introduced species, pollution, and climate change. Conserving Biodiversity Conservation efforts are focused on three things: ____________________________________________________________ is the focus of groups such as the Association of Zoos and Aquariums (AZA), which oversees species survival plans (SSPs). _______________________________________________________________________ is the main thrust of global efforts. Biologists are particularly concerned about __________________________________________, which are places where significant numbers of habitats and species are in immediate danger of extinction. _______________________________________________________________ is part of developing plans to replace harmful activities with ones that conserve environments and biodiversity. Threats to Biodiversity The current rate of species loss is ______________ times the typical rate of extinction. Habitat fragmentation __________________ the impact of hunting on endangered species. ______________________ species can become invasive and threaten biodiversity. The increased concentration of carbon dioxide in air is making oceans ____________________ and putting stress on coral reefs. What are five ways that human activity reduces biodiversity? Identify three reasons why endangered species are hunted. 6.4 Meeting Ecological Challenges Ecological Footprints The _____________________________________ of an individual or a population is the amount of land and water needed to provide resources, absorb wastes, and render the wastes harmless. Ecological Footprints Explain this statement: The average American has an ecological footprint more than four times larger than the global average. Ecology in Action Case Study 1: Atmospheric Ozone The ozone layer is a high concentration of ozone at about above Earth’s surface. The ozone layer is important to humans because it protects against exposure to _____________ from the sun. UV radiation causes __________________, damages eyes, and reduces resistance to disease. Case Study 2: North Atlantic Fisheries Technologies that have led to large increases in the mass of ocean fish caught include large boats and high-tech equipment. ______________________ caused the decline in fish catches since 1997. An alternative to commercial fishing is ______________________, which produces large amounts of food with minimal environmental damage if properly managed. Case Study 3: Climate Change How does the change in global temperature between 1850 and 2000 compare with the change that occurred between 1850 and 1880? List three factors that may have contributed to the trend shown in the graph. Suggest three possible effects of global warming on the future of the biosphere.