1412 Lab Final study guide Dr. Delgado I am going to select 25
advertisement
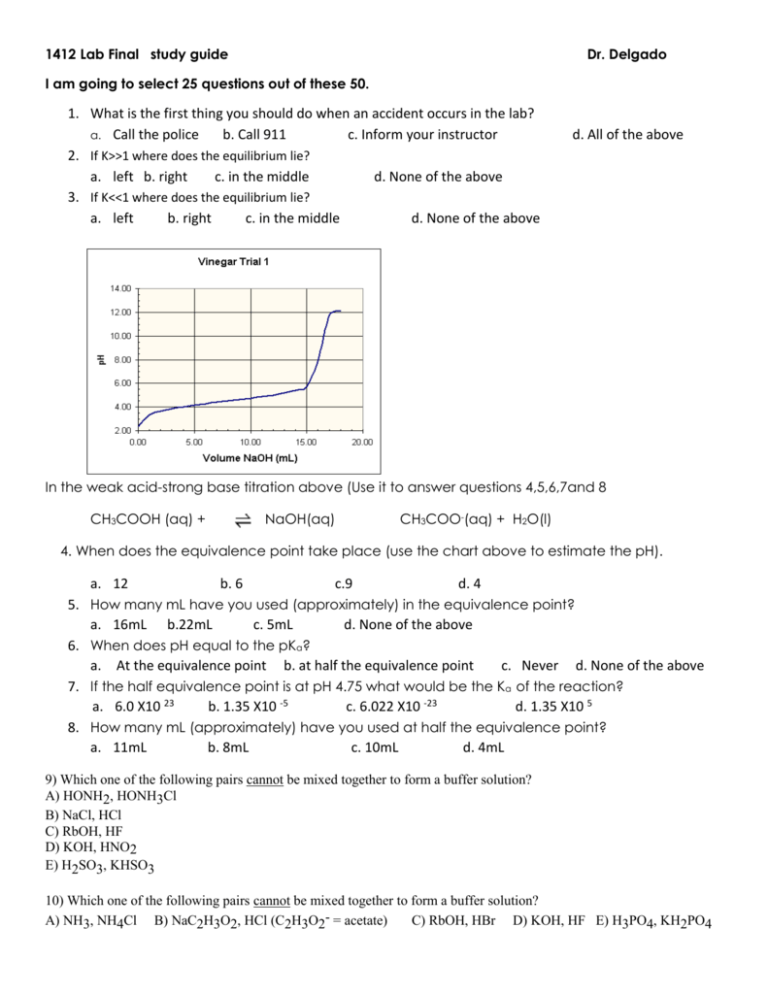
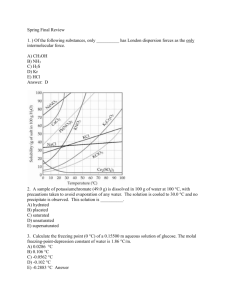
1412 Lab Final study guide Dr. Delgado I am going to select 25 questions out of these 50. 1. What is the first thing you should do when an accident occurs in the lab? a. Call the police b. Call 911 c. Inform your instructor 2. If K>>1 where does the equilibrium lie? a. left b. right c. in the middle d. None of the above 3. If K<<1 where does the equilibrium lie? a. left b. right c. in the middle d. None of the above d. All of the above In the weak acid-strong base titration above (Use it to answer questions 4,5,6,7and 8 CH3COOH (aq) + NaOH(aq) CH3COO-(aq) + H2O(l) 4. When does the equivalence point take place (use the chart above to estimate the pH). a. 12 b. 6 c.9 d. 4 5. How many mL have you used (approximately) in the equivalence point? a. 16mL b.22mL c. 5mL d. None of the above 6. When does pH equal to the pKa? a. At the equivalence point b. at half the equivalence point c. Never d. None of the above 7. If the half equivalence point is at pH 4.75 what would be the Ka of the reaction? a. 6.0 X10 23 b. 1.35 X10 -5 c. 6.022 X10 -23 d. 1.35 X10 5 8. How many mL (approximately) have you used at half the equivalence point? a. 11mL b. 8mL c. 10mL d. 4mL 9) Which one of the following pairs cannot be mixed together to form a buffer solution? A) HONH2, HONH3Cl B) NaCl, HCl C) RbOH, HF D) KOH, HNO2 E) H2SO3, KHSO3 10) Which one of the following pairs cannot be mixed together to form a buffer solution? A) NH3, NH4Cl B) NaC2H3O2, HCl (C2H3O2- = acetate) C) RbOH, HBr D) KOH, HF E) H3PO4, KH2PO4 11)The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is __________. base A) [H+] = Ka + acid base acid base C) pH = pKa + log acid acid D) pH = pKa + log base acid E) pH = log base B) pH = pKa - log 12) A 25.0 mL sample of a solution of an unknown compound is titrated with a 0.115 M NaOH solution. The titration curve above was obtained. The unknown compound is __________. A) a strong acid B) a strong base C) a weak acid D) a weak base E) neither an acid nor a base 13)) What substance is oxidized in the following reaction? Cr2O7 2– + 3 SO3 2– + 8 H+ 2 Cr3+ + 3 SO4 2– + 4 H2O a) Cr2O7 2– b) SO3 2– c) H+ d) SO4 2– 14) The gain of electrons in a reaction is called e) none of the above a) reduction b) oxidation c) reducing agent 15) What is the oxidation state of P in the phosphate ion, PO43– ? a) +2 b) +3 c) +5 d) emf e)SHE d) +6 16) What is the strongest type of intermolecular force present in CH3Cl? a. ion-dipole b. London-dispersion c. hydrogen bonding d. dipole-dipole e. none of the above 17) Choose the molecule or compound that exhibits London dispersion forces as its strongest intermolecular force. a. Cl2 b. C2H6 c. HF d. HCl e.CCl4 18) Which of the following compounds will be most soluble in pentane (C5H12)? a. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2 b. C6H6 c. KBr d. HCl e. none of these compounds should be soluble in pentane 19) Which one is not a colligative property? a. vapor pressure lowering b. osmotic pressure c. freezing point depression 20) Commercial grade HCl solution are typically 39.0% (by mass) HCl in water. Determine the molality of the HCl, if the solution has a density of 1.20 g/mL a. 39.0m b. 17.5m c. 6.39m d. 10.7m e. 9.44m 21) Determine the freezing point depression of a solution that contains 30.7 g of glycerin (C3H8O3) in 376 g water. For water Kf=1.86 C/m a. 0.887 C b. 1.65C c. 3.33 C d. 3.85 C e. 0.654 C 22) A lab assistant needs to prepare 2000 mL of 0.15 M NaCl. How many grams of NaCl are required to prepare this solution? a. 18 g b. 17g c. 15g d. 19g e. 20g 23 The type of compound that is most likely to contain an ionic bond is a) b) c) d) one that is composed of a metal and a nonmetal a solid metal one that is composed of only nonmetals one that is nonpolar 24. What type of intermolecular force occurs between water molecules? a) ion-dipole b) dipole-dipole c) London dispersion d) covalent 25. In the gas phase reaction below, if the rate of formation of NO2 is 8.24 X 10–4 M s–1, what is the rate of disappearance of O2? 4 NH3 + 7 O2 –––> 4 NO2 + 6 H2O a. 1.44 X 10 +3 b. 8.24 x 10 -4 c. 1.44 X 10 -3 d.8.24 x 10 +4 26.Use the table of data shown below to calculate the value of the rate constant k. The reaction is first order. time (s) [A] (M) 0 0.124 10.0 0.102 20.0 0.0831 30.0 0.0681 40.0 0.0557 a. 0.0244 b. 0.0200 c. 0.200 d.0.0300 27. The correct units for the rate constant k in the rate law Rate = k[A]2[B] are a) M s–1 b) M–1 s–1 c) M–2 s–1 d) M–1 s–2 28. The rate law for the aqueous reaction H2SeO3 + 6 I– + 4 H+ –––> Se + 2 I3+ 3 H2O is Rate = k[H2SeO3][I–]3[H+]2. By what factor will the rate increase if we double the concentrations ofall three reactants? a) 8 b) 32 c) 64 d) 128 29. Given the rate data below for the reaction 2A + 3B–––> Products, what is the rate law for this reaction? Exp. [A], 1 0.100 2 0.200 3 0.100 M [B], 0.100 0.100 0.200 a) Rate = k[A][B] M Rate, M sec–1 4.0 X 10–5 1.6 X 10–4 8.0 X 10–5 b) Rate = k[A]2[B] c) Rate = k[A]2[B]2 d) Rate = k[A][B]2 30. The equilibrium constant Kp for reaction (1) has a value of 0.112. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for reaction (2) ? (1) SO2 (g) + 1/2 O2(g) SO3 (g) Kp = 0.112 (2) 2 SO3 (g) 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g) Kp = ? a) 0.512 b) 2.24 c) 44.2 d) 79.7 31. Write the equilibrium constant expression for the reaction 3 Fe (s) + 4 H2O (g) a) Keq = [CO (g)] / [CO2 (g)][H2 (g)] c) Keq = [O2 (g)]6 / [CO2 (g)]6 Fe3O4 (s) + 4 H2 (g) b) Keq = [CO2 (g)]2 / [CO (g)]2 d) Keq = [H2 (g)]4 / [H2O (g)]4 32. Assuming that the following apply to elementary reactions, what is the molecularity of ? A + B –––> C a. Uni-molecular b. bimolecular c. termolecular d. multi-molecular 33. Assuming that the following apply to elementary reactions, what is the molecularity of ? Rate = k[A][B]2 a. Uni-molecular b. bimolecular c. termolecular d. multi-molecular 34. Knowing that Ka for acetic acid = 1.8 X 10-5, calculate Go for the dissociation of this substance in aqueous solution at 25oC. a) 27.1 J/mole b) -27.1 kJ/mol c)27.1 kJ/mole d) -27.1 J/mole e) none of the above 35. Ammonia is a __________. A) weak acid B) strong base C) weak base D) strong acid E) salt 36. What is the conjugate acid of NH3? A) NH3 B) NH2+ C) NH3+ D) NH4+ E) NH4OH 37. What is the conjugate acid of CO3-2? A) CO2-2 B) HCO2-2 C) H2CO3 D) HCO3E) none of the above 38) The conjugate base of HSO4- is __________. A) OHB) H2SO4 C) SO42D) HSO4+ E) H3SO4+ 39)Which is a conjugate pair? a) LiF and NaF b) HF and HCl c) HF and KF 40)Which of the following is a strong base? a) KOH b) KF c) KC2H3O2 d) HNO3 d) HNO2 and HNO3 41)Which of the following is a strong acid? a) HClO2 c) HNO2 c) HClO4 d) H2SO3 42) Which of the following is a strong base? a) KOH b) KF c) KC2H3O2 d) HNO3 43) An unknown solution of H3PO4 was titrated with 0.100 M NaOH. If 50.0 mL of the acid solution required 27.5 mL of the NaOH solution to reach the end point, what is the molarity of the H3PO4 solution? a) 0.0183 M b) 0.0183 moles c) 1.0183 M. d) 1.0183 moles 44) A solution of 0.15 M in NH3 and 0.25 M in ammonium chloride, NH4Cl. What is the pH of the solution? Ka for ammonium ion is 5.6 X 10–10. a) 8.03 b) 9.03 c) 7.03 d) 11.03 45)Calculate the hydrogen concentration in a rainwater sample with a pH of 6.3. a) 5.01 X 10+7 M b) 5.01 X 10–7 M c) 6.01 X 10–7 M d) 6.01 X 10+7 M 46) Calculate the hydrogen concentration in an ammonia solution with a pH of 13.4 a) 3.98 X 10-4 M b) 3.98 X 10-14 M c) 3.98 X 10+14 M d) 3.98 X 10+4 M 47) Calculate the hydrogen ion concentration a solution of NaOH with pOH = 1.5 a)3.16 X 10–13 M b) 3.16 X 10–3 M c) 3.16 X 10+13 M d) 3.16 X 10+3 M 48) What is the pH of a 0.100 M solution of the weak acid phenol, C6H5OH? Ka for phenol is 1.3 X 10–10. a) 5.44 b) 3.44 c) 2.44 d) 6.44 49) Which one of the following is the weakest acid? A) HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10-4) B) HClO (Ka = 3.0 × 10-8) C) HNO2 (Ka = 4.5 × 10-4) D) HCN (Ka = 4.9 × 10-10) E) Acetic acid (Ka = 1.8 × 10-5) 50) The solubility of slightly soluble salts containing basic anions is proportional to the pH of the solution. A) FALSE B) TRUE