Ch 11 BV Money
advertisement

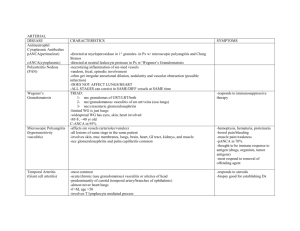
Aneurysms - intrinsic CT defects: o Marfan syndrome = fibrillin o Loeys-Dietz = elastin, collagen I & III o Ehlers-Danlos = collagen III o Scurvy = collagen cross-linking - 2 most important disorder predisposing to aortic aneurysms o atherosclerosis & HTN - abdominal aneurysm o males, increased age, smokers - thoracic aneurysm o most commonly assoc. w/ HTN o Marfan, Syphllis - aortic aneurysm o syphilitic aneurysms commonly affect the aortic arch Aortic dissection - occurs in o old men with HTN o younger men with CT disorder (Marfans) - MC preexisting lesion = cystic medial degeneration - initiates with intimal tear - can cause cardiac tamponade or double barreled aorta - Type A (MC) o DeBakey I & II o ascending aorta - Type B o DeBakey III o distal to subclavian - excruciating pain in anterior chest, radiates to back Vasculitis - immune complex deposition o drug hypersensitivity – serum sickness o viral infection – polyarteritis nodosa o pauci-immune - anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA) o MPO-ANCA (pANCA): microscopic polyangitis & Churg-strauss o PR3-ANCA (cANCA): Wegener granulomatosis - anti-endothelial cell antibodies o Kawasaki disease Giant cell (temporal) arteritis - MC vasculitis in elderly in US & Europe - granulomatous inflammation of arteries in head - facial pain - tender superficial temporal a. - ocular symptoms - segmental nodular intimal thickening - medial granulomatous inflammation - elastic lamina fragmentation - multinucleated giant cells - screening test = ESR Takayasu arteritis - pulseless disease - granulomatous vasculitis of medium/larger arteries - ocular disturbances - transmural fibrous thickening of aorta (aortic arch & great vessels) - severe luminal narrowing of great vessels - <50 = takayasu - >50 = giant-cell - initial symptoms - nonspecific Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN) - systemic; small/medium muscular arteries - renal & visceral but no pulmonary - 30% have chronic hepatitis B with HBsAg-HbsAb complexes in affected vessels - segmental transmural necrotizing inflammation - all stages of activity (early-late) coexist in diff. vessels or w/in same vessel (ongoing and recurrent insults) - malaise, fever, weight loss, HTN, abdominal pain, melena - diffuse muscular aches/pains, peripheral neuritis Kawasaki disease - aka mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome - leading cause of acquired <3 disease in children - affect large to medium sized & small vessels - coronary a. involvement (aneurysm, rupture, acute MI) - conjunctival & oral erythema and erosion - edema of hands/feet - erythema of palms & soles - desquamated rash - cervical lymph node enlargement - Tx: IV Ig therapy + aspirin Microscopic angiitis - necrotizing vasculitis affecting capillaries, arterioles, venules - MPO-ANCA - aka hypersensitivity or leukocytoclastic vasculitis - necrotizing GN in 90% - pulmonary capillaritis common - hemoptysis, hematuria, proteinuria, bowel pain, muscle pain, palpable cutaneous purpura Churg-Strauss syndrome - aka allergic granulomatosis and angiitis - small vessel necrotizing vasculitis assoc. w/ asthma, allergic rhinitis, lung infiltrates, peripheral eosinophilia, extravascular necrotizing granulomas - MPO-ANCA - cutaneous involvement (palpable purpura) - GI bleeding, renal disease - heart involvement in 60% Wegener granulomatosis - necrotizing vasculitis w/ triad: o acute necrotizing granuloma of URT o necrotizing vasculitis of lungs and URT o renal dz (crescentic GN) - PR3-ANCA Raynaud phenomenon - vasoconstriction of digital arteries and arterioles - red white blue changes [order matters, was a bonus] - primary – young women - secondary – SLE, Buerger, scleroderma Thrombophlebitis & phlebothrombosis - deep legs 90% - prolonged immobilization - systemic hypercoagulability predisposes - Trousseau sign – migratory thrombophlebitis in CA - Homan sign – pain w/ pressure over affected veins , squeezing calf muscles, or forces dorsiflexion of foot - PE serious complication Superior vena cava syndrome - usually caused by neoplasms that compress or invade the SVC leading to marked dilation of the veins of the head, neck, arms, and cyanosis - bronchogenic carcinoma - mediastinal lymphoma Inferior vena cava syndrome - neoplasms that invade or compress or by thrombus leading to marked LE edema, distension of the superficial collateral veins of the lower abdomen, massive proteinuria - HCC - RCC Lymphangitis - acute inflammation elicted when bacterial infection spreads to lymphatics - MC = GAS - red painful streaks, enlargement of lymph nodes Lymphedema - primary: congenital or Milroy disease - secondary: tumors, surgical, irradiation, filiarisis (MC in world), post radical mastectomy after losing axillary lymph nodes (MC in US) - Peau d’orange (brawny induration) - chylous ascities, thorax, pericardium from rupture Hemangioma - very common Buerger disease (thromboangitis obliterans) - increased amt of normal BVs filled with blood - segmental, thrombosing, acute & chronic inflammation of medium/small - regress spontaneously arteries - angiomatosis – form that involves large portions of body - affects tibial & radial arteries - majority are superficial lesions in head & neck - SMOKING - 1/3 found in the liver - superficial nodular phlebitis - rare malignant transformation - cold sensitivity of Raynaud - capillary hemangioma (MC) - instep claudication o skin, subQ tissues, mucous membranes, liver, spleen, kidney - severe pain at rest o strawberry type (juvenile) is very common in newborns; fades a 1- chronic ulceration of toes, feet, fingers 3 years and complete regression by 7 - cavernous hemangioma o large dilated channels o less circumscribed o can involve deep structures o assoc. w/ von Hippel-Lindau (involves cerebellum, brain stem, retina) o red-blue soft spongy mass 1-2 cm o large cavernous blood-filled vascular spaces - pyogenic granuloma o rapidly growing pedunculated red nodule o bleeds easily, often ulcerated o pregnancy tumor (in gingiva) o assoc. w/ trauma, proliferating capillaries, inflammation, exuberant granulation-like tissue Lymphangioma - simple (capillary) o head, neck, axillary, subQ tissue - cavernous (cystic hygromas) o neck and axilla of children o Turner syndrome Glomus tumor (glomangioma) - benign, very painful, modified smooth m. cells of the glomus body - distal portion of digits, esp. under the fingernails Vascular ectasia - nevus flammeus o birth mark o port wine stain o Sturge-Weber syndrome = port wine stain in trigeminal nerve distribution; mental retardation - spider telangiectasia o hyper-estrogenic states (pregnancy or cirrhosis) - hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu dz) o widely distributed throughout body o rupture can cause serious epistaxis, GI bleed, or hematuria Bacillary angiomatosis - vascular proliferation resulting from opportunistic infection - 1st seen in AIDS Kaposi sarcoma - HHV-8; sexually transmitted - requires cofactor for tumor progression - 4 forms: o chronic KS (classic or European) old men; Ashkenazi Jew, Mediterranean red to purple skin plaques in distal LE slowly increase in size and # patch plaque papule (neoplastic) o lymphadenopathic KS (African or endemic) prevalent in S. African Bantu children not assoc. w/ HIV skin lesions sparse pts present w/ lymphadenopathy if tumor involves viscera = extremely aggressive MC tumor in central Africa o transplant associated aggressive/fatal nodal, mucosal, visceral involvement o AIDS associated (epidemic) most prevalent malignancy in AIDS Angiosarcoma - malignant endothelial neoplasms - older adults more commonly affected; men=women - usually involve skin, soft tissue, breast, liver - hepatic angiosarcoma – assoc. w/ exposure to carcinogens (arsenic, Thorotrast, polyvinyl chloride) - can arise in setting of lymphedema in UE after radical mastectomy - can be radiation induced - all degrees of differentiation can be seen microscopically - locally invasive; metastasize readily, aggressive Angioplasty - abrupt reclosure may occur - long term can cause proliferative restenosis due to intimal thickening Vascular replacement - act like a vascular injury stenosis … etc.