File
advertisement

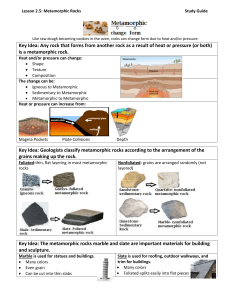
Earth Materials Unit: Metamorphic Rocks and Processes Text: Chapters 7 Lab: Laboratory 7 Name________________________________ Geology 12: Metamorphic Rocks Page 1 Metamorphic Rocks and Processes Purpose: To classify metamorphic rocks and features by their physical and chemical properties. -By the end of this unit, students are expected to be able to: 1. Relate the types and characteristics of metamorphic rocks to: a) Parent Rock b) Temperature c) Pressure d) Chemical Conditions 2. Describe the features of, and identify, the following sedimentary rocks: Slate Phyllite Quartzite Marble Schist Gneiss Metaconglomerate 3. Contrast the two major categories of metamorphic rocks: a) Foliated b) Non-foliated 4. Contrast the two types of metamorphism: a) Contact b) Regional 5. Describe changes that occur in country rock and in the intrusion at a contact region. 6. Relate metamorphic rock type to the concept of metamorphic grade. Geology 12: Metamorphic Rocks Page 2 Geology 12: Metamorphic Rocks and Processes Part A: What is a Metamorphic Rock? Rocks that have changed from one form to another through the addition of intense heat, pressure or fluid activity. Part B: Agents Metamorphism The chemical composition of a metamorphic rock is determined by its parent rock (protolith), but its texture and mineral makeup depends on the agents of metamorphism that acted on it. Heat Heat can be added to rocks by: a) ________________________________________________________ b) ______________________________________________________ Heat causes recrystallization (not melting!) to form equigranular crystals, like marble. Heat changes the distribution of the chemical components of the rock. *Remember that minerals are stable at different temperatures! Pressure (Stress) a) Confining Pressure __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ Increases with burial at depth and can cause mineral grains to compact together. This forms a harder/denser rock, but has little impact on the internal structure of the rock. b) Directed Pressure ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ There are three types of directional pressure: i) Compression: Pushing together; ii) Tension: Pulling apart; iii) Shear Parallel forces Geology 12: Metamorphic Rocks Page 3 At high enough temperatures where rocks are ductile, highly folded strata and foliation can be produced. Foliation: ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ Chemically Active Fluids Water and other volatiles become reactive when heated and act as catalysts to cause metamorphism. Heated fluids dissolve ions from minerals from regions of high stress and deposit them in regions of low stress. This allows minerals to grow longer in the direction perpendicular to compressional stress (produces foliation). Heated fluids can cause chemical changes in porous rocks and also transport chemicals from one area to another where they can produce more minerals. Will metamorphic rocks altered by fluids have the same chemical composition as their parent rocks? _____________________________________________________________________________________ Metamorphic Grade Metamorphic Grade is the amount of metamorphism (heat, pressure, fluid activity) a rock has undergone. Metamorphic grade can be indicated by index minerals which only form at specific temperatures. What grade did a rock containing garnet form? _____________________________________________________________________________________ The amount of heat and pressure put onto a rock varies depending on the scale of metamorphism: Burial Metamorphism Alteration of rock by an increase in temperature (geothermal gradient) and confining pressure caused by the weight of overlying sediment/volcanic layers. Mild metamorphism, rock becomes denser but previous features are preserved (e.g. bedding, grain size) Geology 12: Metamorphic Rocks Page 4 Contact Metamorphism Igneous intrusion bakes the immediately surrounding rocks, forming aureoles (altered zone around the intrusion). Usually only a small (km’s) area is affected. The addition of heat without pressure creates unfoliated rocks with random crystal orientation. Heat decreases with distance from the intrusion, creating rocks with high metamorphic grade next to the pluton and then lower grades as you move outwards. What type of rocks are often formed closest to the igneous intrusion? (Lab page 156) _____________________________________________________________________________________ Regional Metamorphism Metamorphism on a large scale, caused by pressure, heat and fluid activity. It is the most common type of metamorphism and is associated with convergent plate boundaries. Index minerals, foliation and changes in texture are common. Metamorphic Rock Textures Metamorphic rocks are divided into two groups: a) Foliated -Folaited rocks vary in their characteristics depending on the degree of metamorphism they underwent. Define the foliated textures below using pages 159-161. Slaty Rock Cleavage ___________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Phyllite ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Geology 12: Metamorphic Rocks Page 5 Schistosity ___________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Gneissic Banding______________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ b) Non-Foliated -Nonfoliated rocks do not have obvious layering, but can be distinguished by other characteristics (Lab pages 161-162): Crystalline ___________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Microcrystalline _______________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Sandy _______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Glassy _______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ c) Some textures are common to both foliated and nonfoliated rocks. Define the following terms using lab text page161-164: Stretched Grains _______________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Geology 12: Metamorphic Rocks Page 6 Porphyroblastic _______________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Hydrothermal Veins ____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Folds _______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Lineations ____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ *Complete Activity 7.1, 7.2 and 7.3 Geology 12: Metamorphic Rocks Page 7