Barron`s Vocab Ch 8 Jerry
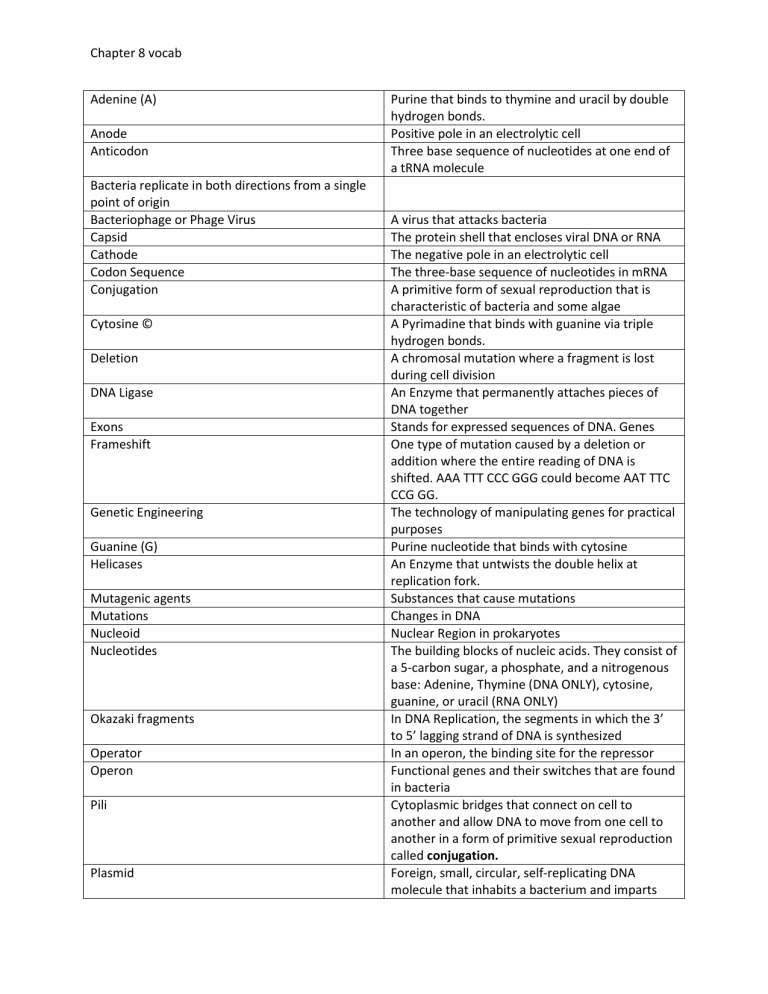
Chapter 8 vocab
Adenine (A)
Anode
Anticodon
Bacteria replicate in both directions from a single point of origin
Bacteriophage or Phage Virus
Capsid
Cathode
Codon Sequence
Conjugation
Cytosine ©
Deletion
DNA Ligase
Exons
Frameshift
Genetic Engineering
Guanine (G)
Helicases
Mutagenic agents
Mutations
Nucleoid
Nucleotides
Okazaki fragments
Operator
Operon
Pili
Plasmid
Purine that binds to thymine and uracil by double hydrogen bonds.
Positive pole in an electrolytic cell
Three base sequence of nucleotides at one end of a tRNA molecule
A virus that attacks bacteria
The protein shell that encloses viral DNA or RNA
The negative pole in an electrolytic cell
The three-base sequence of nucleotides in mRNA
A primitive form of sexual reproduction that is characteristic of bacteria and some algae
A Pyrimadine that binds with guanine via triple hydrogen bonds.
A chromosal mutation where a fragment is lost during cell division
An Enzyme that permanently attaches pieces of
DNA together
Stands for expressed sequences of DNA. Genes
One type of mutation caused by a deletion or addition where the entire reading of DNA is shifted. AAA TTT CCC GGG could become AAT TTC
CCG GG.
The technology of manipulating genes for practical purposes
Purine nucleotide that binds with cytosine
An Enzyme that untwists the double helix at replication fork.
Substances that cause mutations
Changes in DNA
Nuclear Region in prokaryotes
The building blocks of nucleic acids. They consist of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base: Adenine, Thymine (DNA ONLY), cytosine, guanine, or uracil (RNA ONLY)
In DNA Replication, the segments in which the 3’ to 5’ lagging strand of DNA is synthesized
In an operon, the binding site for the repressor
Functional genes and their switches that are found in bacteria
Cytoplasmic bridges that connect on cell to another and allow DNA to move from one cell to another in a form of primitive sexual reproduction called conjugation.
Foreign, small, circular, self-replicating DNA molecule that inhabits a bacterium and imparts
Chapter 8 vocab
Point mutation
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
Primase
Prions
Promoter
Prophage
Purines
Pyrimidines
Recognition sequences/sites
Replication bubbles
Replication fork
Repressor
Restriction Enzymes
Restriction fragment length polymorphisms
(RFLPs)
Restriction fragments
Reverse transcriptase
RNA polymerase
RNA primer
Semiconservative replication
Single-stranded binding proteins characteristics to the bacterium such as resistance to antibiotics.
A change in one nucleotide in DNA.
A cell-free, automated technique by which a piece of DNA can be rapidly copied or amplified
An Enzyme that joins RNA nucleotides to make the primer.
Infectious proteins that cause several brain diseases: scrapie in sheep, mad cow in cattle, and
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in humans.
The binding site of RNA polymerase in an operon.
A Phage genome that has been inserted into a specific site in a bacterial chromosome.
A Class of nucleotides that includes adenine and guanine
A class of nucleotides that includes cytosine, thymine, and uracil
A specific sequence of nucleotides at which a restriction enzyme cleaves a DNA molecule,
There are thousands of replication bubbles along the DNA molecule that speed u the process of replication
A Y-shaped region where the new strands of DNA are elongating,
Binds to the operator of an operon and prevents
RNA polymerase from binding to the promoter, thus blocking transcription,
Enzymes , naturally occurring in bacteria, that cut
DNA at certain specific recognition sites.
Noncoding regions of human DNA that vary from perso to person. They can be used to identify a single individual. Pronounced “riflips”
Fragments of DNA that result from the cuts made by restriction enzymes.
An enzyme found in retroviruses that facilitates the production of DNA from RNA
The enzyme that binds to the promoter in DNA and that begins transcription.
An already existing chain of RNA attatched to DNA to which DNA polymerase adds nucleotides during
DNA synthesis.
The way DNA replicates, each double helix separates and forms two new strands of DNA.
Each new molecule of DNA consists of one old and one new strand.
Proteins that act as scaffolding, holding two DNA strands apart during replication.
Chapter 8 vocab
Small Nuclear Ribonucleoproteins snRNPs
Somatic
Splicesomes
Taq polymerase
Telomerase
Telomeres
Thymine (T)
Transcription
Transduction
Transformation
Translation
Uracil (U)
Wobble
Help to process RNA after it is formed and before it moves to the ribosome.
A body cell.
Enzymes that (along with snRNPs) help process
RNA after it is formed and before it moves to the ribosome.
A heat-stable form of DNA polymerase extracted from bacteria that live in hot environments, such as hot springs, that is used during PCR technique.
An ezyme that catalyses the lengthening of the telomeres at the end of eukaryotic chromosomes.
The protective ends of eukaryotic chromosomes.
A nucleotide that binds with adenine. Pyrimidine and is not present in RNA.
The process by which DNA makes RNA
Transfer of bacterial DNA by phages from one bacterium to another.
The transfer of genes from one bacterium to another
The process by which the codons of an mRNA sequence are changed into an amino acid sequence.
A nucleotide in only RNA that binds with adenine.
Pyrimidine
Refers to translation of mRNA to protein. The
Relaxation of base-pairing rules where the pairing rules for the third base of a codon are not as strict as they are for the first two bases. E.g. UUU and
UUA both code for the amino acid phenylalanine









