Click here for Section 8.5 Study Guide
advertisement

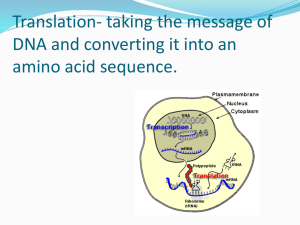
Study Guide 8.5: Translation Vocabulary Translation Codon Stop codon Start codon Anticodon Review Questions 1. What is translation? The process that converts a mRNA strand into a polypeptide or protein. 2. What is a codon? Sequences of three nucleotides that code for an amino acid. 3. Would the codons in the figure at the end of this study guide be found in a strand of DNA or RNA? RNA 4. What is a reading frame? It is the order in which nucleotides are read; they are read as a series of three, non-overlapping nucleotides called codons. 5. The codon is AGA. What is the amino acid (use the table at the end of this study guide)? Arginine (Arg) 6. The codon is UAG. What is the amino acid? Stop codon (there is no amino acid). 7. The codon is GGA. What is the amino acid? Glycine (Gly) 8. The amino acid is tryptophan. What the codon that codes for it? UGG 9. Ribosomes and tRNA molecules are the tools that help a cell translate an mRNA message into a polypeptide. 10. The small subunit of a ribosome holds onto the mRNA strand. 11. The large subunit of a ribosome has binding sites for tRNA. 12. A tRNA molecule is attached to an amino acid at one end and has an anticodon at the other end. 13. Draw a diagram showing the steps (there are 5) of translation. You can draw it on scratch paper on the table in the back of the room. The diagram should contain the following information: an exposed codon of mRNA, in the small subunit of the ribosome, attracts a complementary tRNA (pairing with its anticodon) bearing an amino acid. The ribosome forms a peptide bond between the amino acid whose tRNA molecule has paired up with the mRNA codon and the previous amino acid. The ribosome pulls the mRNA strand the length of one codon each time an amino acid is added to the growing polypeptide chain. Every time an amino acid is delivered, the empty (having given up its amino acid) tRNA molecule exits the ribosome, and another codon is exposed to be matched with another anticodon. 14. What are AGG, GCA, and GUU examples of? Codons 15. What is a set of three nucleotides on a tRNA molecule that is complementary to an mRNA codon? An anticodon 16. What do codons code for in addition to amino acids? Stop codons indicate where translation is to stop. Also, there is a start codon that also codes for the amino acid methionine. The genetic code matches each mRNA codon with its amino acid