Chpt. 10A-Molecular Biology of the Gene - TJ
advertisement
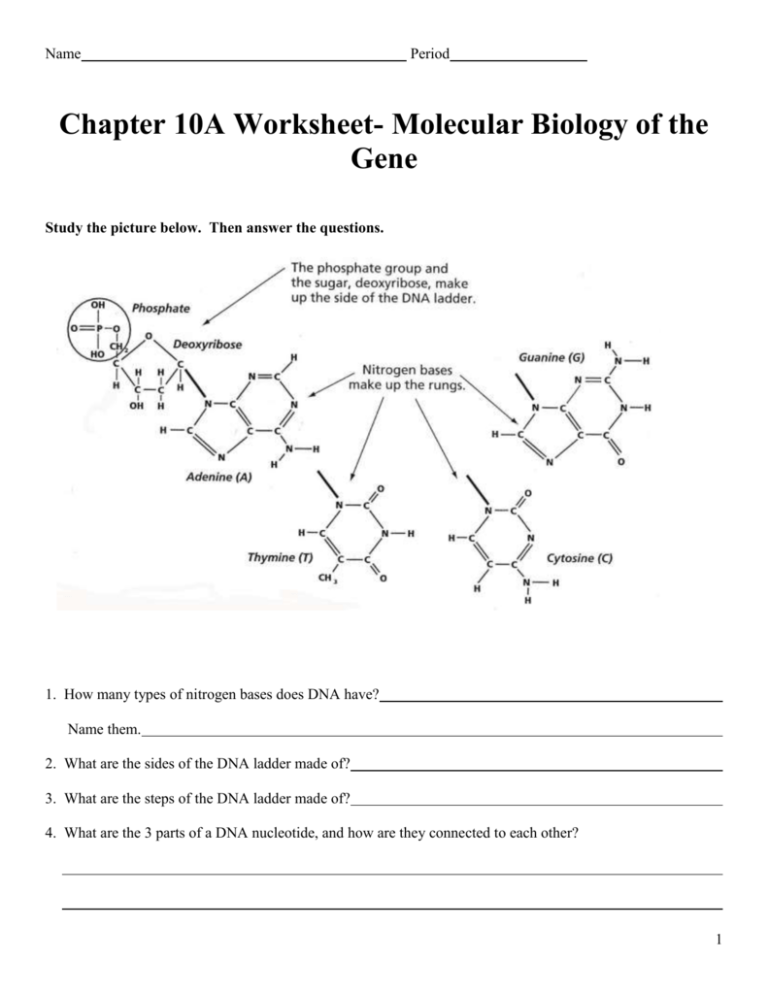
Name Period Chapter 10A Worksheet- Molecular Biology of the Gene Study the picture below. Then answer the questions. 1. How many types of nitrogen bases does DNA have? Name them. 2. What are the sides of the DNA ladder made of? 3. What are the steps of the DNA ladder made of? 4. What are the 3 parts of a DNA nucleotide, and how are they connected to each other? 1 5. Why is it important that exact copies of DNA are produced during replication? 6. Why is it advantageous to have weak hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs and strong covalent bonds between phosphate and deoxyribose groups in a DNA molecule? 7. If 15% of the nucleotides in a DNA molecule contain guanine, what percentage of the nucleotides contain each of the other three bases? Explain your reasoning. Label each part of the figure in the spaces provided. The diagram below shows two nucleotide base pairs in a segment of a DNA molecule. 2 The diagram below shows and unzipped strand of DNA. Write the letters (A, T, C, & G) of the bases that will pair with the bases on the strand. Some of the bases have been paired for you. True or false. Making use of the diagram above answer the following questions. If the answer is true write true, if the answer is false correct the statements so that is becomes true. 8. True or False? Nucleotide bases already attached to proteins form the copied side of the DNA ladder. 9. True or False? The process of DNA replication results in a copy of the original strand of DNA. 10. True or False? Sugar and phosphates provide energy for DNA replication. 11. True or False? The final result of DNA replication is two copies of the original DNA strand. 3 DNA: Its Structure and Replication 1. On the double helix in figure 1 of a DNA molecule, in the boxes label the part that represents deoxyribosephosphate chains and the part that represents the base. 2. Using A for adenine, C for cytosine, G for guanine, and T for thymine, complete the labeling of the bases in figure 2. 3. In figure 2, circle a single nucleotide. 4. Alongside each half of the separated portion of the DNA molecule in figure 1, label the sequence of nucleotides that might become attached to it creating a complimentary strand and thus form a duplicate off the original 4 Multiple Choice Write the correct letter in the blank provided. 1. The primary function of DNA in cells is to a. serve as a storage form for unused nucleotides b. occupy space in the nucleus to keep the nucleus from collapsing c. store information that tells the cells which proteins to make d. serve as a template for making long, spiral carbohydrates 2. The two stands of a DNA molecule are held together by a. ionic bonds b. covalent bonds c. peptide bonds d. hydrogen bonds 3. According to the base-pairing rules, guanine binds with a. cytosine b. adenine c. thymine d. guanine 4. During DNA replication, the enzyme DNA polymerase a. separates the two nucleotide chains in a DNA molecule b. constructs new nucleotide chains that are complementary to the chains in the original DNA molecule c. breaks down the original DNA molecule into individual nucleotides d. joins two DNA molecules into a single molecule 5. If the sequence of nucleotides in one chain of a DNA molecule is T-C-A-A-G-C, a new nucleotide chain will be produced during replication with the complementary sequence a. T-C-A-A-G-C b. A-G-T-T-C-G c. C-T-G-G-A-T d. G-A-C-C-T-A Use the vocabulary words below and match the word with the appropriate definitions in the space provided. a. b. c. d. e. DNA polymerase Replication Nucleotide Watson & Crick Replication fork f. Semiconservative model g. Franklin h. Helicase i. Origin of replication j. Polynucleotide 1. An enzyme that assembles DNA nucleotides into polynucleotides using a preexisting strand of DNA as a template. 2. An organic monomer consisting of a five-carbon sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group. The building blocks of nucleic acids. 3. Type of DNA replication in which the replicated double helix consists of one old strand, derived from the old molecule, and one newly made strand. 4. The process of coping DNA. 5. Credited with the discovery of DNA structure. 5









