59.7 KB - K-10 Outline
advertisement
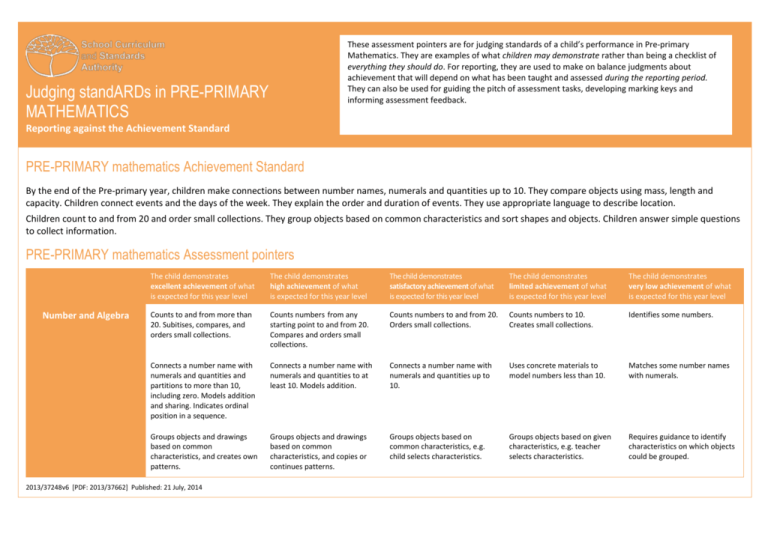
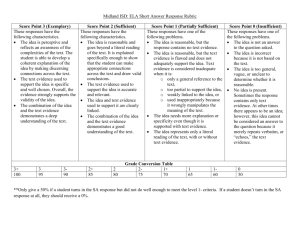
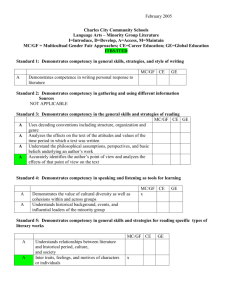
These assessment pointers are for judging standards of a child’s performance in Pre-primary Mathematics. They are examples of what children may demonstrate rather than being a checklist of everything they should do. For reporting, they are used to make on balance judgments about achievement that will depend on what has been taught and assessed during the reporting period. They can also be used for guiding the pitch of assessment tasks, developing marking keys and informing assessment feedback. Judging standARDs in PRE-PRIMARY MATHEMATICS Reporting against the Achievement Standard PRE-PRIMARY mathematics Achievement Standard By the end of the Pre-primary year, children make connections between number names, numerals and quantities up to 10. They compare objects using mass, length and capacity. Children connect events and the days of the week. They explain the order and duration of events. They use appropriate language to describe location. Children count to and from 20 and order small collections. They group objects based on common characteristics and sort shapes and objects. Children answer simple questions to collect information. PRE-PRIMARY mathematics Assessment pointers Number and Algebra The child demonstrates excellent achievement of what is expected for this year level The child demonstrates high achievement of what is expected for this year level The child demonstrates satisfactory achievement of what is expected for this year level The child demonstrates limited achievement of what is expected for this year level The child demonstrates very low achievement of what is expected for this year level Counts to and from more than 20. Subitises, compares, and orders small collections. Counts numbers from any starting point to and from 20. Compares and orders small collections. Counts numbers to and from 20. Orders small collections. Counts numbers to 10. Creates small collections. Identifies some numbers. Connects a number name with numerals and quantities and partitions to more than 10, including zero. Models addition and sharing. Indicates ordinal position in a sequence. Connects a number name with numerals and quantities to at least 10. Models addition. Connects a number name with numerals and quantities up to 10. Uses concrete materials to model numbers less than 10. Matches some number names with numerals. Groups objects and drawings based on common characteristics, and creates own patterns. Groups objects and drawings based on common characteristics, and copies or continues patterns. Groups objects based on common characteristics, e.g. child selects characteristics. Groups objects based on given characteristics, e.g. teacher selects characteristics. Requires guidance to identify characteristics on which objects could be grouped. 2013/37248v6 [PDF: 2013/37662] Published: 21 July, 2014 Measurement and Geometry Statistics and Probability The child demonstrates excellent achievement of what is expected for this year level The child demonstrates high achievement of what is expected for this year level The child demonstrates satisfactory achievement of what is expected for this year level The child demonstrates limited achievement of what is expected for this year level The child demonstrates very low achievement of what is expected for this year level Uses direct and indirect comparisons to order objects by length, mass and capacity and uses everyday language to explain results, e.g. shortest or longest, lightest or heaviest, holds more or less. Uses direct and indirect comparisons to order objects by length, mass and capacity. Compares length, mass and capacity. Correctly compares objects only when their differences are obvious. Identifies objects as ‘big’ or ‘little’, but does not make comparisons. Names and orders the days of the week and identifies the relationship between yesterday, today and tomorrow. Provides details of familiar events occurring on specific days of the week. Sequences events and uses the everyday language of time when explaining and comparing duration. Names and orders the days of the week, connecting familiar events to specific days. Sequences events and compares duration, e.g. it takes longer to walk to school than it does to drive in the car. Connects events and the days of the week. Orders familiar everyday events, using their start and finish points to explain duration, e.g. short time or long time. Connects some events with days of the week. Orders some familiar everyday events. Names some days of the week and, with prompting, identifies some familiar everyday events. Sorts, names and describes familiar two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional objects. Sorts and names familiar twodimensional shapes and threedimensional objects. Sorts familiar two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional objects. Sorts familiar two-dimensional shapes. Requires prompting to sort familiar two-dimensional shapes. Gives and follows simple instructions, using the language of location and direction, to describe position and movement. Follows simple instructions using the language of location and direction, e.g. goes towards, stands next to, climbs over. Uses appropriate language to describe location, e.g. between, on, under. Responds to simple positional language, e.g. in, out, up and down. Requires prompting to respond to simple positional language. Asks own simple questions to collect information and displays data. Responds to simple questions to collect information and completes data displays, e.g. contributes to a class data display by drawing own favourite fruit. Responds to simple questions to collect information, e.g. do you like bananas? With prompting, provides relevant responses to simple questions to collect information. Does not provide relevant responses to simple questions to collect information.