Chapter 1 Test Review Packet
advertisement

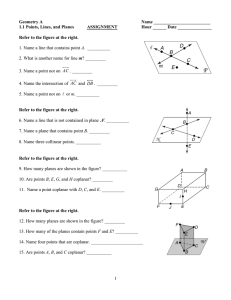
Name: Ms. D’Amato Date: Block: Essentials of Geometry Test Review Part I: Matching. A. has no dimension; it is usually represented as a dot For questions #1 – 30, match each term on the left with its definition on the right. B. a rule that is accepted without proof 1. Undefined terms D. the real number that corresponds to a point on a line 2. Collinear points E. points that lie on the same line 3. Coplanar points 4. Defined terms 5. Line segment 6. Ray 7. Opposite rays 8. Intersection 9. Postulate/axiom 10. Coordinate 11. Distance C. a point that divides, or bisects, a segment into two congruent segments F. the set of points that two or more geometric figures have in common G. has two dimensions; it is usually represented by a shape that looks like a floor or a wall, it extends without end H. terms that can be described using known words I. points that lie on the same plane J. part of a line that consists of a point called an endpoint and all points on the line that extend in one direction K. the absolute value of the difference of the coordinates of the points L. has one dimension; it is usually represented by a straight line with two arrowheads to indicate that it extends without end in two directions 12. Between 13. Congruent segments 14. Midpoint 15. Segment bisector N. when three points lie on a line, you can say that one point is between the other two 16. Point O. line segments that have the same length 17. Line P. a word that does not have a formal definition, but there is agreement about what the word means 18. Plane M. a point, ray, line, segment, or plane that intersects a segment at its midpoint Q. part of a line that consists of two points, called endpoints, and all points on the line that are in between R. rays that have the same endpoint but go in opposite directions 19. Complementary Angles 20. Supplementary Angles 21. Acute Angle 22. Obtuse Angle 23. Right Angle S. an angle that measures 180° T. adjacent angles whose sum is 180° U. an angle measuring between 90° and 180° V. an angle that measures 90° W. angles that have a sum of 90° X. an angle that measure between 0° and 90° Y. angles that have a sum of 180° 24. Straight Angle 25. Linear Pair Angles 26. ⃡ 𝐴𝐵 A. line segment AB 27. 𝐴𝐵 B. distance of AB 28. ̅̅̅̅ 𝐴𝐵 C. ray AB 29. 𝐴𝐵 D. congruent to 30. ≅ E. line AB Part II: Identify Points, Line and Planes. For questions #31 – 34, use the diagram to the right. 31.] Name the sets of collinear points. 32.] What is the intersection of line m and line l? 33.] What is the intersection of plane S and plane R? 34.] What is another name for plane R? for plane S? For questions #35 – 42, use the diagram to the right. 35.] Name the intersection of ⃡𝑃𝑅 and ⃡𝐻𝑅. 36.] Name the intersection of plane EFG and plane FGS. 37.] Name the intersection of plane PQS and plane HGS. 38.] Are points P, Q, and F collinear? Are they coplanar? 39.] Are points P and G collinear? Are they coplanar? 40.] Name three planes that intersect at point E. 41.] Identify, if any, a point that is coplanar with points P, E, and R. 42.] Identify, if any, three points that are collinear. Part III: Use Segments and Congruence 43.] In the diagram of collinear points, GK = 24, HJ = 10 and GH = HI = IJ. Find the indicated lengths. G H I J K A] HI = B] IJ = C] GH = D] JK = E] IG = F] IK = For questions #44 – 45, find the indicated length. 44.] Find BC. 45.] 46.] ̅̅̅̅. Use the given information to write an equation in terms of Point S is between R and T on 𝑅𝑇 x. Solve the equation. Then find RS, ST and RT. Draw a picture! RS = x – 5 Find RT. ST = 3x + 2 RT = 6x – 23 Part IV: Use Midpoint and Distance Formulas For questions #47 – 48, M is the midpoint of the segment. Find the indicated length. 47.] Find MF. 48.] Find LN. For questions #49 – 50, find the coordinates of the midpoint of the segment with the given endpoints. 49.] C(-4, 4) and D(7, 2) 50.] G(7, -6) and H(5, -8) ̅̅̅̅ to find the For questions #51 – 52, use the given endpoint R and midpoint M of 𝑹𝑺 coordinates of the other endpoint S. 51.] R(0, 5), M(3, 3) 52.] R(-1, -3), M(5, 9) For questions #53 – 54, find the length of the segment with the following points. 53.] (-2, -4) and (3, 8) 54.] (-5, 8) and (-10, 14) For questions #55 – 56, the endpoints of two segments are given. Find each segment length. Tell whether the segments are congruent. 55.] ̅̅̅̅ 𝐴𝐵 : A(1, 1), B(0, 5) ̅̅̅̅: C(1, 1), D(-3, 2) 𝐶𝐷 56.] ̅̅̅ 𝐽𝐾 : J(4, 3), K(-1, 6) ̅̅̅̅: L(2, -3), M(-2, 0) 𝐿𝑀 Part V: Measure and Classify Angles 57.] Given mADC = 118°, find mADB. 58.] Given mEHG = 77°, find mFHG. For questions #59 – 61, 𝑩𝑫 bisects ABC. Find mABC. 59.] 61.] 60.] Careful with this one! mABC = 15x – 21 mDBC = 6x + 3 Part VI: Describe Angle Pair Relationships 62.] The measure of one angle is three times the measure of its complement. Find the measure of each angle. Draw a picture. 63.] Two angles form a linear pair. The measure of one angle is 15 times the measure of the other angle. Find the measure of each angle. Draw a picture. For questions #64 – 68, find the values of x and y. Then find the measure of each angle. 64.] 65.] 66.] 67.] 68.] 69.] A and B are complementary angles. Find mA and mB. mA = (4x – 18)° mB = (6x – 18)° 70.] A and B are supplementary angles Find mA and mB. mA = (x + 50)° mB = (x + 100)°