chapter 7 powerpoint ol
advertisement

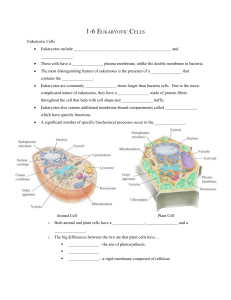
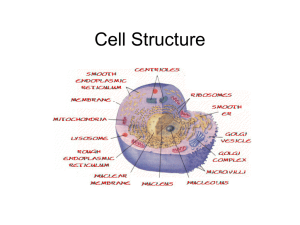
BIOLOGY: CHAPTER 7 CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Powerpoint Outline 25pts Chapter 7: Structure and Function of the Cell What is a Cell? How Big are they? What are they made of? Developing the Cell Theory 7.1 Contributors to The Cell Theory Robert Hooke Cells first seen with microscope in 1665 Observed honeycomb of empty compartments in cork (called them cells) Antoine Van Leeuwenhoek First observance of living microscopic singlecelled organisms in water Called organisms "animalcules" NAME______________________________ Matthias _________________________ Observed plant tissues All plants aggregates of separate cells Theodor Schwann All animals are made of cells Rudolph Virchow All cells come from pre-existing cells Introduction to Microscopy The Major parts of the Microscope include: Ocular or ______________________ Lens Light Source Objective lenses Diaphragm Stage Neck & Base Coarse & Fine Focus Total Magnification = Ocular x Objective Magnification Q1. If the magnification of the ocular lens is 10x and the objective lens is 40x what is total magnification? The Cell Theory From the Observations of Schleiden, Schwann &Virchow 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells 2. The Cell is the basic unit of living things 3. All Cells arise from other cells Q2. What was Rudolph Virchow’s contribution to the cell theory? The Limitations to Cell Size Cells must not exceed a certain size Molecules pass faster through small cells Communication is more efficient An Increase in size = Decrease in ______________________________________ /Volume Ratio (that’s bad!!!!) Interactions with outside only occurs at surface Q3. Which cell has the greater surface area/volume ratio, an ovum or a cheek epithelial cell? Q4. Calculate the surface area to volume ratio for 2 cubes. The first cube has a length of 2cm, and the second 4cm. Which has the greatest surface area/volume ratio? Some Typical Human Cells:Vary in size, Vary in shape, Measured in micrometers Q5. Answer the following using the Factor label method. If a human ovum is 140m, how many mm? EUKARYOTES vs PROKARYOTES PROKARYOTES All are bacteria Either Archae or _______________________________ No membrane bound organelles DNA is CCC (Covalently closed and circular) Q6. Is a plant prokaryotic or eukaryotic? EUKARYOTES Protista, Fungi Plantae, & Animalia Have Multiple membrane bound organelles Have a Nucleus, with DNA in Chromosomes Eukaryotes are More Complex Than Prokaryote The Key to Cell Organization is Compartmentalization Possess internal membrane-bound organelles Golgi complex and lysosomes created by folding ER Mitochondria and chloroplasts associated with cellular energy THE STRUCTURE OF EUKARYOTIC CELLS AN OVERVIEW OF CELL STRUCTURE The Plasma Membrane: Surrounds the Cell- ____________________________ bilayer contains embedded protein The Nucleus: Central Portion of the Cell Contains DNA Prokaryotes-Single, Circular molecule of DNA Eukaryotes- Chromosomes The Cytoplasm – Cytosol: cell fluid (H2O) Organelles Q7. Draw the structural diagram of a phospholipid. Identify the hydrophobic fatty acids. CELLULAR ORGANELLES THE NUCLEUS: Information center for the cell The Nuclear Envelope: Double layer of membranes, Outer layer is continuous with ____________________________ Nucleolus: Dense Collection of RNA and Proteins, Site of Ribosome Production Chromatin: DNA &Proteins, Stores Information for Synthesis of Proteins Chromosomes are Complex, Contain hereditary information, associated with histone protein Q8. What is chromatin made of? Q9. What is the function of the nucleolus? ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM: Connected, Membrane-bound Sacs, Canals, and Vesicles, Transport System Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER): Studded with Ribosomes, Protein and Lipid Synthesis Smooth ER (SER):Lipid Synthesis, Break Down of Drugs Ribosomes:Free Floating Or Connected To ER, Site of Protein Synthesis, Made of _____________________________ Q10. What are ribosomes made of, and what is their function? THE GOLGI APPARATUS: Delivery System Of The Cell Molecular Collection, Packaging, & Distribution Q11. What is the function of the Golgi Apparatus? Flattened Stacks of Membranes, Abundant in glandular ________________________ cells LYSOSOMES: Digestive Enzymes For The Cell Contain Hydrolytic Enzymes Breakdown of macromolecules within cell Q12. What do hydrolytic enzymes do? Digest worn-out _______________________ components Eliminate Other Substances Including Whole Cells Digest pathogens engulfed by white blood cells MITOCHONDRIA: The Cell's Chemical Furnaces Bounded by double membrane Makes ATP through Cellular Respiration Inner membrane is folded into ____________________ Possesses own genome (DNA) Divides into inner matrix and outer compartment Q13. Write the equation that describes cellular respiration CHLOROPLASTS: Where Photosynthesis Occurs Photosynthetic pigments on thylakoid surface Found in Photosynthesizers: plants and algae Stack of thylakoids called ______________________ Internal membranes form disk-shaped thylakoids Possess own genome Q13. Write the equation that describes photosynthesis FLAGELLA & CILIA: Motility For The Cell Eukaryotic Flagella 9+2 structure of microtubules Long tail-like projection Provides motility to ____________________________ Q14. Which cells in humans are ciliated and why? CENTRIOLES: Microtubular Assembly Plants Present in animal cells, NOT plant cells Occur in pairs near nucleus THE CYTOSKELETON: Interior Framework Of The Cell Network of 3 types of Fibers Microfilament: Thin, made of ____________________ Intermediate Filament: found in animal cells Microtubule: Hollow tube of Tubulin Q15. What are Tubulin and Actin made of? Cilia and Centrioles Also Show 9+2 Arrangement Short hair-like projections Propel substances on cell surface Form the ______________________________ Assemble and organize microtubules Form basal bodies that anchor flagella and cilia Provide Mechanical Support for Cell Actin fibers determine cell shape Rapid changes in filament length changes cell shape quickly Plant versus Animal Cells Animal Cells: Plant Cell: Cell Membrane Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Irregular Shape 1 Large Central Vacuole Small Vacuoles __________________________________ Centrioles Fixed shape often rectangular Q16. Give 3 structures Plant cell possess that Animal Cells do not SYMBIOSIS AND THE ORIGIN OF EUKARYOTES Eukaryotes Have Radically Different Cell Structure Possess organelles that resemble bacteria Endosymbiont Theory Symbionts Provided Metabolic Advantage to Host Mitochondria are energy factories Chloroplasts photosynthesize Evidence Supporting The Endo-Symbiont Theory Mitochondria and chloroplasts surrounded by double membrane Mitochondria and bacteria have similar size Mitochondrial ribosomes resemble bacterial ribosomes Mitochondria and chloroplast DNA circular like bacteria Mitochondria divide by simple _____________________________ Q17. What is the significance of the fact that both Chloroplasts and Photosynthesis have their own DNA? Use The Following Terms To Label The Diagrams Plant Cell Animal Cell Lysosome Nucleolus Central Vacuole Chromosome Golgi Apparatus Smooth Er Rough Er Ribosomes Mitochondria Chloroplast Cell Membrane Cell Wall Nuclear Membrane DNA Cytoplasm ____________________