MID-TEST/UTS (40%) - Departemen Ekonomi FEM IPB
advertisement
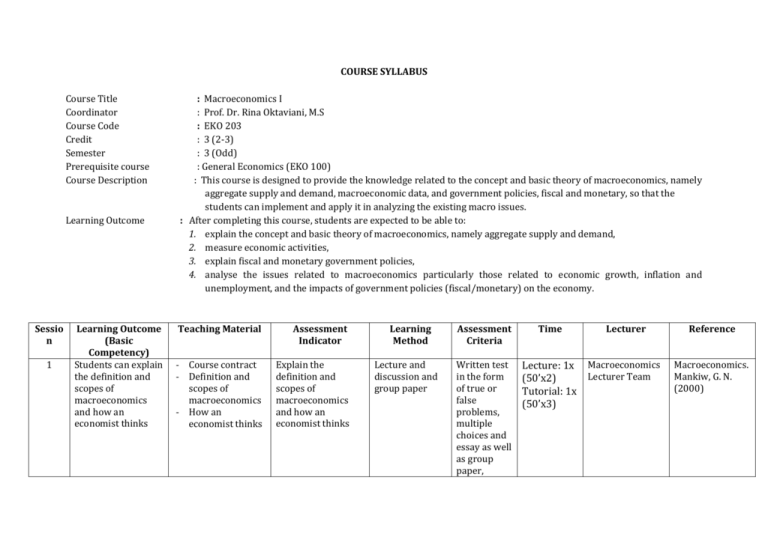
COURSE SYLLABUS Course Title Coordinator Course Code Credit Semester Prerequisite course Course Description Learning Outcome Sessio n 1 Learning Outcome (Basic Competency) Students can explain the definition and scopes of macroeconomics and how an economist thinks : Macroeconomics I : Prof. Dr. Rina Oktaviani, M.S : EKO 203 : 3 (2-3) : 3 (Odd) : General Economics (EKO 100) : This course is designed to provide the knowledge related to the concept and basic theory of macroeconomics, namely aggregate supply and demand, macroeconomic data, and government policies, fiscal and monetary, so that the students can implement and apply it in analyzing the existing macro issues. : After completing this course, students are expected to be able to: 1. explain the concept and basic theory of macroeconomics, namely aggregate supply and demand, 2. measure economic activities, 3. explain fiscal and monetary government policies, 4. analyse the issues related to macroeconomics particularly those related to economic growth, inflation and unemployment, and the impacts of government policies (fiscal/monetary) on the economy. Teaching Material Assessment Indicator - Course contract - Definition and scopes of macroeconomics - How an economist thinks Explain the definition and scopes of macroeconomics and how an economist thinks Learning Method Lecture and discussion and group paper Assessment Criteria Time Lecturer Reference Written test in the form of true or false problems, multiple choices and essay as well as group paper, Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) Macroeconomics Lecturer Team Macroeconomics. Mankiw, G. N. (2000) Sessio n Learning Outcome (Basic Competency) Teaching Material Assessment Indicator Learning Method 2 Student can measure economic activity value Measure economic activity value, living cost, unemployment rate, and relationship between economic variables Lecture and discussion and group paper 3 Students can explain the concept and determining factor of national income - Measure economic activity value: GDP - Measure living cost: CPI - Measure unemployment: unemployment rate - Relationship between GDP, CPI, and unemployment rate (Okun’s Law) - Factors that influence national income - National income distribution to factors of production - Factors that influence goods and service demand - Equilibrium condition of goods, service, and money market Explain the factors that determine national income and its distribution on factors of production, goods and service demand, and equilibrium condition of goods, service and money market Lecture and discussion and group paper Assessment Criteria Tutorial Written test in the form of true or false problems, multiple choices and essay, essay, and group paper, Tutorial Written test in the form of true or false problems, multiple choices and essay, essay, and group paper, Tutorial Time Lecturer Reference Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) Macroeconomics Lecturer Team Macroeconomics. Mankiw, G. N. (2000) Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) Macroeconomics Lecturer Team National Income: Mankiw, G. N. (2000) Sessio n Learning Outcome (Basic Competency) Teaching Material Assessment Indicator 4 Students can explain the concept and basic theory of money, relationship between inflation and interest rate Explain the basic theory of money, relationship between inflation and interest rate 5 Students can explain the concept and consequence of open economy - Money definition - Money quantity theory - Seigniorage - Inflation and nominal interest rate - Nominal interest rate and money demand - Inflation demand - Hyperinflation - International flow of capital and goods - Savings and investment in open economy - Exchange rate 6 Students can explain the concept, determining factor, and implication of unemployment - Unemployment, job seekers and natural unemployment rate - Job seeker and frictional Learning Method Assessment Criteria Time Lecturer Reference Lecture and discussion and group paper Written test in the form of true or false problems, multiple choices and essay, essay, and group paper, Tutorial Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) Macroeconomics Lecturer Team Macroeconomics. Mankiw, G. N. (2000) 1. Explain the concept of open economy and its relationship with international capital flow, savings and investment 2. Explain the concept of exchange rate Lecture and discussion and group paper Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) Macroeconomics Lecturer Team Macroeconomics. Mankiw, G. N. (2000) Explain the concept of unemployment and determining factors of unemployment Lecture and discussion and group paper Written test in the form of true or false problems, multiple choices and essay, essay, and group paper, Tutorial Written test in the form of true or false problems, multiple choices and Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) Macroeconomics Lecturer Team Unemployment: Mankiw, G. N. (2000) Sessio n Learning Outcome (Basic Competency) Teaching Material Assessment Indicator Learning Method unemployment - Rigid real wage and structural unemployment - Types of unemployment 7 Students can explain Solow growth theory 1 - Capital accumulation - Regulation on capital association - Population growth Assessment Criteria Time Lecturer Reference Macroeconomics Lecturer Team Macroeconomics. Mankiw, G. N. (2000) Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) Macroeconomics Lecturer Team Macroeconomics. Mankiw, G. N. (2000) Lecture: 1x Macroeconomics Macroeconomics. essay, essay, and group paper, Tutorial Explain Solow growth theory 1 (capital accumulation and population) Lecture and discussion and group paper Written test in the form of true or false problems, multiple choices and essay, essay, and group paper, Tutorial Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) MID-TEST/UTS (40%) 8 Students can explain Solow growth theory 2 - Technology growth in Solow model - Policy that promotes growth Explain Solow growth theory 2 (technology) Lecture and discussion and group paper 9 Students can explain - Macroeconomic Explain the Lecture and Written test in the form of true or false problems, multiple choices and essay, essay, and group paper, Tutorial Written test Sessio n 10-11 Learning Outcome (Basic Competency) the definition of aggregate supply and demand Students can explain the concept of IS and LM and Aggregate Demand (AD) Teaching Material Assessment Indicator time horizon - Aggregate demand - Aggregate supply - Stabilization policy definition of aggregate supply and demand discussion and group paper - Goods market and IS curve - Money market and LM curve 1. Explain the concept of IS and LM and their relationship with aggregate demand and economic fluctuation Lecture and discussion and group paper - Economic fluctuation with IS-LM model - IS-LM as aggregate demand theory - Great depression Learning Method Lecture and discussion and group paper Assessment Criteria Time Lecturer Reference in the form of true or false problems, multiple choices and essay, essay, and group paper, Tutorial Written test in the form of true or false problems, multiple choices and essay, essay, and group paper, Tutorial Written test in the form of true or false problems, multiple choices and essay, essay, and group paper, (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) Lecturer Team Mankiw, G. N. (2000) Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) Macroeconomics Lecturer Team Macroeconomics. Mankiw, G. N. (2000) Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) Macroeconomics Lecturer Team Macroeconomics. Mankiw, G. N. (2000) Sessio n Learning Outcome (Basic Competency) Teaching Material Assessment Indicator Learning Method 12 Students can explain Mundell Fleming model - Mundell-Fleming model - The impacts of Fiscal and monetary policies on Mundell Fleming model 1. Explain Mundell Fleming model 2. Explain the impacts of fiscal and monetary policies on Mundell Fleming model Lecture and discussion and group paper 13 Students can explain the concept of exchange rate systems and their impacts on the economy 1. Explain exchange rate systems (fixed and floating) and their impacts on the economy Lecture and discussion and group paper 14 Students can explain Aggregate Supply (AS) model - Small open economy under fixed and floating exchange rates - Differential interest rate - Floating exchange rate or fixed exchange rate - Mundell-Fleming model with various exchange rate - The three models of aggregate supply - Inflation, unemployment, 1. Explain aggregate Lecture and supply models discussion and 2. Explain the group paper relationship between inflation, Assessment Criteria Tutorial Written test in the form of true or false problems, multiple choices and essay, essay, and group paper, Tutorial Written test in the form of true or false problems, multiple choices and essay, essay, and group paper, Tutorial Written test in the form of true or false problems, Time Lecturer Reference Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) Macroeconomics Lecturer Team Macroeconomics. Mankiw, G. N. (2000) Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) Macroeconomics Lecturer Team Macroeconomics. Mankiw, G. N. (2000) Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) Macroeconomics Lecturer Team Macroeconomics. Mankiw, G. N. (2000) Sessio n Learning Outcome (Basic Competency) Teaching Material and Phillips curve Assessment Indicator Learning Method unemployment, and Phillips curve Assessment Criteria Time Lecturer Reference multiple choices and essay, essay, and group paper, Tutorial FINAL TEST/UAS (40%) TUTORIAL including ASSIGNMENT (20%) LITERATURE REFERENCE : Mankiw, G. Macroeconomics. LECTURER TEAM : (1) Prof. Rina Oktaviani; (2) Dr. Dedi Budiman Hakim; (3) Prof. Dr. Noer Azam Achsani, (4) Prof. Dr. M. Firdaus, (5) Prof. Dr. Bambang Juanda, (6) Dr. Yeti Lis Purnamadewi, (7) Dr. Lukytawati Anggraeni, (8) Dr. Tanti Novianti LEARNING METHODS : Lecture, Discussion and Group Paper ASSIGNMENT DESIGN : paper assignment is given one time in group, each group consists of 5-6 students. (1) Paper writing with topic related to macro materials and issues given for one semester ASSESSMENT FORMAT : Exam and Assignment Mid-test (UTS) Final test (UAS) Tutorial % Assignment (Paper) : 40 % : 40 % : 20 %









