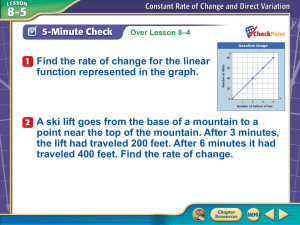
04 CCM7 Unit 2 PARCC info

Common Core 7
Unit 2: Ratios and Proportional Relationships
PARCC Exam Notes
Unit 2: Assessment Clarifications
Standard M/S/A PBA/
EOY?
Calc? MP
7.RP.A.1 Major PBA
Yes
Yes
Yes
EOY
Yes
7.RP.A.2a Major PBA
Yes
EOY
Yes
7.RP.A.2b Major PBA
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Notes
6
2, 5, 8
2, 3, 5,
2, 5
2, 3, 5,
6
2, 3, 6
2, 6, 4
2, 3, 5,
6
Compute unit rates associated with ratios of fractions, including ratios of lengths, areas and other quantities measured in like or different units. i) Tasks have a context.
Connected to Evidence Statement 7.C.4
Base explanations/reasoning on a coordinate plane diagram (whether provided in the prompt or constructed by the student in her response).
Content Scope: Knowledge and skills articulated in 7.RP.A
2, 6, 4 Compute unit rates associated with ratios of fractions, including ratios of lengths, areas and other quantities measured in like or different units. i) Tasks have a context.
2, 5
Recognize and represent proportional relationships between quantities. a. Decide whether two quantities are in a proportional relationship, e.g., by testing for equivalent ratios in a table or graphing on a coordinate plane and observing whether the graph is a straight line through the origin. i) Tasks have “thin context” or no context. ii) Tasks may offer opportunities for students to investigate a relationship by constructing graphs or tables; however, students can opt not to use these tools. iii) Tasks are not limited to ratios of whole numbers.
Connected to Evidence Statement 7.C.4
Base explanations/reasoning on a coordinate plane diagram (whether provided in the prompt or constructed by the student in her response).
Content Scope: Knowledge and skills articulated in 7.RP.A
Connected to Evidence Statement 7.C.6.1
Construct, autonomously, chains of reasoning that will justify or refute propositions or conjectures. Content Scope: Knowledge and skills articulated in 7.RP.2
Recognize and represent proportional relationships between quantities. a. Decide whether two quantities are in a proportional relationship, e.g., by testing for equivalent ratios in a table or graphing on a coordinate plane and observing whether the graph is a straight line through the origin. i) Tasks have “thin context” or no context. ii) Tasks may offer opportunities for students to investigate a relationship by constructing graphs or tables; however, students can opt not to use these tools. iii) Tasks are not limited to ratios of whole numbers.
Recognize and represent proportional relationships between quantities. b. Identify the constant of proportionality (unit rate) in tables, graphs, equations, diagrams, and verbal descriptions of proportional relationships. i) Pool should contain tasks with and without context. ii) Tasks sample equally across the listed representations (graphs, equations, diagrams, and verbal descriptions).
Connected to Evidence Statement 7.C.4
Base explanations/reasoning on a coordinate plane diagram (whether provided in the prompt or constructed by the student in her response).
Content Scope: Knowledge and skills articulated in 7.RP.A
7.RP.A.2c
7.RP.A.2d
7.RP.A.3
Major
Major
EOY
Yes
PBA
Yes
EOY
Yes
PBA
Yes
(for
Sub-C)
EOY
Yes
Major PBA
Yes
(for
Sub-C)
EOY
Yes
Yes
No
No
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
2, 8
2, 3, 5,
6
2, 3, 6
2, 3, 6 Connected to Evidence Statement 7.C.6.1
Construct, autonomously, chains of reasoning that will justify or refute propositions or conjectures. Content Scope: Knowledge and skills articulated in 7.RP.2
2, 8 ,5 Recognize and represent proportional relationships between quantities. b. Identify the constant of proportionality (unit rate) in tables, graphs, equations, diagrams, and verbal descriptions of proportional relationships. i) Pool should contain tasks with and without context. ii) Tasks sample equally across the listed representations (graphs, equations, diagrams, and verbal descriptions).
2, 8
Recognize and represent proportional relationships between quantities. c. Represent proportional relationships by equations. i) Tasks have a context.
Connected to Evidence Statement 7.C.4
Base explanations/reasoning on a coordinate plane diagram (whether provided in the prompt or constructed by the student in her response).
Content Scope: Knowledge and skills articulated in 7.RP.A
Connected to Evidence Statement 7.C.6.1
Construct, autonomously, chains of reasoning that will justify or refute propositions or conjectures. Content Scope: Knowledge and skills articulated in 7.RP.2
Recognize and represent proportional relationships between quantities. c. Represent proportional relationships by equations. i) Tasks have a context.
2, 3, 5,
6
2, 3, 6
2, 4
2, 3, 5,
6
1, 3, 6,
7, 8
1, 2, 6
1, 2, 5,
6
Connected to Evidence Statement 7.C.4
Base explanations/reasoning on a coordinate plane diagram (whether provided in the prompt or constructed by the student in her response).
Content Scope: Knowledge and skills articulated in 7.RP.A
Connected to Evidence Statement 7.C.6.1
Construct, autonomously, chains of reasoning that will justify or refute propositions or conjectures. Content Scope: Knowledge and skills articulated in 7.RP.2
Recognize and represent proportional relationships between quantities. d. Explain what a point ( x , y ) on the graph of a proportional relationship means in terms of the situation, with special attention to the points
(0,0) and (1, r ) where r is the unit rate. i) Tasks require students to interpret a point ( x , y ) on the graph of a proportional relationship in terms of the situation, with special attention to the points (0,0) and (1, r ) where r is the unit rate.
Connected to Evidence Statement 7.C.4
Base explanations/reasoning on a coordinate plane diagram (whether provided in the prompt or constructed by the student in her response).
Content Scope: Knowledge and skills articulated in 7.RP.A
Connected to Evidence Statement 7.C.7.1
Present solutions to multi-step problems in the form of valid chains of reasoning, using symbols such as equal signs appropriately (for example, rubrics award less than full credit for the presence of nonsense statements such as 1+4 = 5+7 = 12, even if the final answer is correct), or identify or describe errors in solutions to multi-step problems and present corrected solutions.
Content Scope: Knowledge and skills articulated in 7.RP.3
Use proportional relationships to solve multi-step ratio problems.
Use proportional relationships to solve multi-step percent problems. Examples: simple interest, markups and markdowns, gratuities and commissions, fees, percent increase and decrease, percent error.
7.G.A.1
7.D.1
Addtl PBA
No
EOY
Yes
N/A
Yes
N/A
2, 5
N/A
Other Integrative Tasks that may be linked to Unit 2
Evidence
Statement
Reach
Back?
PBA/
EOY?
Calc? MP Notes
N/A PBA Yes 4, 1, 2,
5, 7
Solve problems involving scale drawings of geometric figures, including computing actual lengths and areas from a scale drawing and reproducing a scale drawing at a different scale. i) Pool should contain tasks with and without contexts.
7.D.2
7.D.3
6.RP.A PBA
N/A PBA
Yes
Yes
4, 1, 2,
5, 7
4, 1, 2,
5, 7
Solve multi-step contextual word problems with degree of difficulty appropriate to grade 7, requiring application of the grade 7 knowledge and skills articulated in the Evidence Statements on the PBA (excludes the Reasoning Evidence Statements which are those that start with
7.C).
Tasks may have scaffolding if necessary in order to yield a degree of difficulty appropriate to grade 7.
Solve multi-step contextual problems with degree of difficulty appropriate to grade 7, requiring application of knowledge and skills articulated in 6.RP.A, 6.EE.C, and 6.G
Tasks may have scaffolding if necessary in order to yield a degree of difficulty appropriate to grade 7.
Micro-models: Autonomously apply a technique from pure mathematics to a real-world situation in which the technique yields valuable results even though it is obviously not applicable in a strict mathematical sense (e.g., profitably applying proportional relationships to a phenomenon that is obviously nonlinear or statistical in nature). Content Scope: Grade 7 knowledge and skills articulated in the Evidence
Statements on the PBA (excludes the Reasoning Evidence Statements which are those that start with 7.C).
Tasks may have scaffolding if necessary in order to yield a degree of difficulty appropriate to grade 7.
7.D.4 N/A PBA Yes 4, 1, 2,
5, 7
Reasoned estimates: Use reasonable estimates of known quantities in a chain of reasoning that yields an estimate of an unknown quantity.
Content Scope: Grade 7 knowledge and skills articulated in the Evidence Statements on the PBA (excludes the Reasoning Evidence
Statements which are those that start with 7.C).
Tasks may have scaffolding if necessary in order to yield a degree of difficulty appropriate to grade 7.
Grade 7 Sub-Claim A and B Performance Level Descriptors applicable to Unit 2
Proportional
Relationships
7.RP.1
7.RP.2a
7.RP.2b
7.RP.2c
7.RP.2d
7.RP.3-1
7.RP.3-2
Grade 7 Math: Sub-Claim A
The student solves problems involving the Major Content for the grade/course with connections to the Standards for Math Practice.
Level 5: Distinguished Command
Analyzes and uses proportional relationships to solve real-world and mathematical problems, including multistep ratio/percent problems.
Computes unit rates of quantities associated with ratios of fractions.
Decides whether two quantities are in a proportional relationship and identifies the constant of proportionality (unit rate) in tables, equations, diagrams, verbal descriptions and graphs.
Interprets a point ( x , y ) on the graph of a proportional relationship in terms of the situation, with special attention to the points (0, 0) and (1, r ) where r is the unit
Level 4: Strong Command
Analyzes and uses proportional relationships to solve real-world and mathematical problems, including multistep ratio/percent problems.
Computes unit rates of quantities associated with ratios of fractions.
Decides whether two quantities are in a proportional relationship and identifies the constant of proportionality (unit rate) in tables, equations, diagrams, verbal descriptions and graphs.
Interprets a point ( x , y ) on the graph of a proportional relationship in terms of the situation, with special attention to the points (0, 0) and (1, r ) where r is the unit
Level 3: Moderate Command
Analyzes and uses proportional relationships to solve real-world and mathematical problems, including simple ratio/percent problems.
Computes unit rates of quantities associated with ratios of fractions.
Decides whether two quantities are in a proportional relationship and identifies the constant of proportionality (unit rate) in tables, equations, diagrams, verbal descriptions and graphs.
Interprets a point ( x , y ) on the graph of a proportional relationship in terms of the situation, with special attention to the points (0, 0) and (1, r ) where r is the unit
Level 2: Partial Command
Uses proportional relationships to solve real-world and mathematical problems, including simple ratio/percent problems.
Computes unit rates of quantities associated with ratios of fractions.
Decides whether two quantities are in a proportional relationship and identifies the constant of proportionality (unit rate) in tables, equations, diagrams, verbal descriptions and graphs.
Uses equations representing a proportional relationship to solve simple mathematical and real-world problems, including simple ratio and percent problems.
rate.
Represents proportional relationships by equations and uses them to solve mathematical and real-world problems, including multi-step ratio and percent problems.
Compares proportional relationships given in different forms (tables, equations, diagrams, verbal, graphs).
Determines when it is appropriate to use unit rate and understands when it has its limitations. rate.
Represents proportional relationships by equations and uses them to solve mathematical and real-world problems, including multi-step ratio and percent problems. rate.
Represents proportional relationships by equations and uses them to solve mathematical and real-world problems, including simple ratio and percent problems.
Grade 7 Math: Sub-Claim B
The student solves problems involving the Additional and Supporting Content for grade/course with connections to the Standards for Mathematical Practice.
Level 5: Distinguished Command Level 4: Strong Command Level 3: Moderate Command Level 2: Partial Command
Drawings and
Measurement
7.G.1
7.G.4-1
7.G.4-2
7.G.5
7.G.6
Solves mathematical and real-world problems involving circumference, area, surface area and volume of two- and three-dimensional objects, including composite objects.
Solves problems involving scale drawings of geometric figures, including reproducing a scale drawing at a different scale.
Represents angle relationships using equations to solve for unknown angles.
Identifies or produces a logical conclusion about the relationship between the circumference and area of a circle.
Solves mathematical and real-world problems involving circumference, area, surface area and volume of two- and three-dimensional objects, including composite objects.
different scale.
Solves problems involving scale drawings of geometric figures, including reproducing a scale drawing at a
Represents angle relationships using equations to solve for unknown angles.
PARCC Abbreviation Key:
PBA: Performance-Based Assessment
EOY: End of Year Assessment
M/S/A: Indicates whether this standard is considered Major content, Supporting Content, or Additional Content
MP: Standards for Mathematical Practice
* Indicates a modeling standard
PARCC Sub-Claims:
Sub-Claim A: Information on how PARCC will assess major content
Sub-Claim B: Information on how PARCC will assess additional and supporting content
Sub-Claim C: Information on how PARCC will assess reasoning
Sub-Claim D: Information on how PARCC will assess modeling
Solves mathematical and real-world three-dimensional objects.
Solves problems involving scale reproducing a scale drawing at a different scale. problems involving circumference, area, surface area and volume of two- and drawings of geometric figures, including
Represents angle relationships using equations to solve for unknown angles.
Solves mathematical problems involving circumference, area, surface area and volume of two- and three-dimensional objects.
Solves problems involving scale drawings of geometric figures.
Uses facts about angle relationships to determine the measure of unknown angles.