K-2 Science Topics* KG 1st 2nd EARTH SCIENCE NON
advertisement
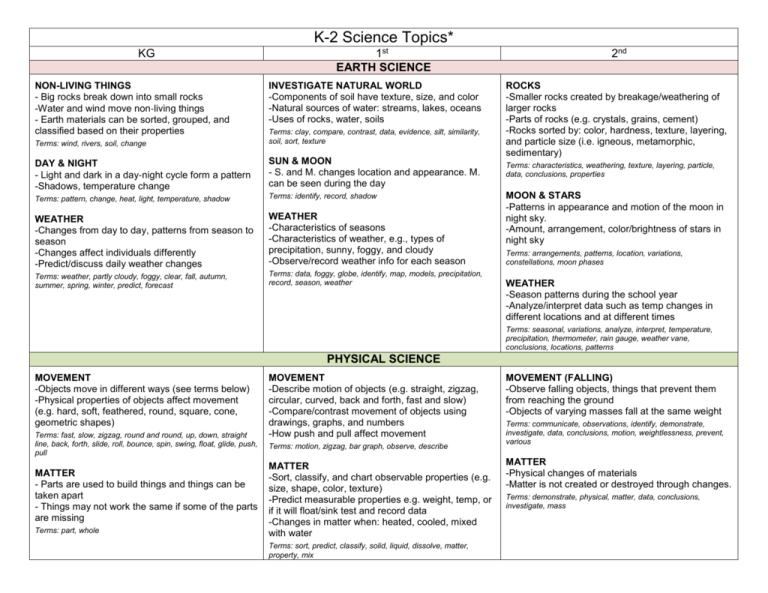
K-2 Science Topics* KG NON-LIVING THINGS - Big rocks break down into small rocks -Water and wind move non‐living things - Earth materials can be sorted, grouped, and classified based on their properties 1st EARTH SCIENCE INVESTIGATE NATURAL WORLD -Components of soil have texture, size, and color -Natural sources of water: streams, lakes, oceans -Uses of rocks, water, soils Terms: wind, rivers, soil, change Terms: clay, compare, contrast, data, evidence, silt, similarity, soil, sort, texture DAY & NIGHT - Light and dark in a day‐night cycle form a pattern -Shadows, temperature change SUN & MOON - S. and M. changes location and appearance. M. can be seen during the day Terms: pattern, change, heat, light, temperature, shadow Terms: identify, record, shadow WEATHER -Changes from day to day, patterns from season to season -Changes affect individuals differently -Predict/discuss daily weather changes WEATHER -Characteristics of seasons -Characteristics of weather, e.g., types of precipitation, sunny, foggy, and cloudy -Observe/record weather info for each season Terms: weather, partly cloudy, foggy, clear, fall, autumn, summer, spring, winter, predict, forecast Terms: data, foggy, globe, identify, map, models, precipitation, record, season, weather 2nd ROCKS -Smaller rocks created by breakage/weathering of larger rocks -Parts of rocks (e.g. crystals, grains, cement) -Rocks sorted by: color, hardness, texture, layering, and particle size (i.e. igneous, metamorphic, sedimentary) Terms: characteristics, weathering, texture, layering, particle, data, conclusions, properties MOON & STARS -Patterns in appearance and motion of the moon in night sky. -Amount, arrangement, color/brightness of stars in night sky Terms: arrangements, patterns, location, variations, constellations, moon phases WEATHER -Season patterns during the school year -Analyze/interpret data such as temp changes in different locations and at different times Terms: seasonal, variations, analyze, interpret, temperature, precipitation, thermometer, rain gauge, weather vane, conclusions, locations, patterns PHYSICAL SCIENCE MOVEMENT -Objects move in different ways (see terms below) -Physical properties of objects affect movement (e.g. hard, soft, feathered, round, square, cone, geometric shapes) Terms: fast, slow, zigzag, round and round, up, down, straight line, back, forth, slide, roll, bounce, spin, swing, float, glide, push, pull MATTER - Parts are used to build things and things can be taken apart - Things may not work the same if some of the parts are missing Terms: part, whole MOVEMENT -Describe motion of objects (e.g. straight, zigzag, circular, curved, back and forth, fast and slow) -Compare/contrast movement of objects using drawings, graphs, and numbers -How push and pull affect movement Terms: motion, zigzag, bar graph, observe, describe MATTER -Sort, classify, and chart observable properties (e.g. size, shape, color, texture) -Predict measurable properties e.g. weight, temp, or if it will float/sink test and record data -Changes in matter when: heated, cooled, mixed with water Terms: sort, predict, classify, solid, liquid, dissolve, matter, property, mix MOVEMENT (FALLING) -Observe falling objects, things that prevent them from reaching the ground -Objects of varying masses fall at the same weight Terms: communicate, observations, identify, demonstrate, investigate, data, conclusions, motion, weightlessness, prevent, various MATTER -Physical changes of materials -Matter is not created or destroyed through changes. Terms: demonstrate, physical, matter, data, conclusions, investigate, mass LIFE SCIENCE LIVING THINGS -Compare/contrast young plants and animals with their parents -Fast or slow changes in plants and animals that are hard to see LIVING THINGS -Plants and animals resemble their parents -Similarities and differences within/across larger groups Terms: populations, similarities, differences Terms: living vs. non-living things, change, grow PARTS OF LIVING THINGS -Difference between body parts and the five senses -Main parts of plants, e.g., roots, stem, leaf, flower, trunk, branches -Parts of different animals, e.g., skin, fur, feathers, scales, hand, winds, flippers, fins LIVING THINGS & THEIR ENVIRONMENT -Observe living things and environment with the five senses -Earth materials sustain plant and animal life (e.g. food, water, air, light, space) -Life cycles Terms: life cycle, offspring, need, environment, investigate Term: living vs. non-living things, senses, sight, taste, touch, smell, sound, bitter, sweet, salty LIVING THINGS -Characteristics of living things in different habitats -Why a habitat is/isn’t suitable for a specific organism -Why some animals extinct and similar ones not Terms: characteristics, environments, habitats, justify, compare, contrast, extinct, desert, ocean, rainforest, tundra BASIC NEEDS OF LIVING THINGS -Physical characteristics, behaviors, and reactions of living things help them meet their basic needs -Behaviors and reactions of living things in response to changes in the environment including seasonal changes in temp and precipitation Terms: physical characteristics, behaviors, reaction, environment, seasonal, temperature, precipitation, migration, hibernation, dormancy 3-6 Science Topics* 3rd EARTH & MOON -Spherical shape -Sun is source of light that lights moon -Physical appearance of Earth and moon from space -Motions of earth (i.e. rotation [spinning] of Earth on its axis, revolution [orbit] of Earth around sun) -Lunar cycle chart -Earth rotates on axis every 24 hrs creating night and day -Use model to show why it appears that sun, planets, and stars move across the sky Terms: model, orbit, sphere, moon, axis, rotation, revolution, appearance LIVING/NONLIVING -Organisms depend on living and nonliving things -Characteristics of both living and nonliving -Describe interactions between living 4th WATER CYCLE -Relationship between heat energy, evaporation, and condensation -Describe the water cycle -Locations of water during the cycle, e.g., oceans, atmosphere -Water cycle in relation to your community water supply Terms: vapor, precipitation, evaporation, clouds, dew, condensation, temperature, water cycles WEATHER -Observing elements of weather -Predicting weather based on recorded observation and measurement -Cloud types (i.e. cumulus, cirrus, stratus) -Evidence that air is substance -Weather patterns -Wind affects on weather -Weather prediction and tools of meteorology 5th 6th MATTER -Chemical and physical changes -Matter not created or destroyed just changed -Weight of matter before and after change -Physical properties of matter (hard, soft), appearance before and after physical change -Evidence of chemical reactions, chemical reactions in daily life -Chemical reaction vs. physical change LUNAR CYCLE -Changes in appearance and pattern of the moon -Movement of moon around Earth -Positions of Earth, moon, and sun create appearance of moon phases -Rotating on an axis vs. revolving in orbit -Objects in the sky change in relative position over course of day or night Terms: heat, substance, chemical change, dissolve, physical change, matter, product, reactants, solid, liquid, weight SEASONS -Tilt of Earth’s axis and revolution around the sun -Earth’s position to the sun during each season -How the angle of the sun’s rays strike the Earth’s surface in the Northern Hemisphere during: summer, fall, winter, spring -Seasons reversed in Northern and Southern Hemispheres. EARTH’S CHANGING SURFACE -Processes/forces that weather and erode -Relationship of time and geological changes -Volcanoes, earthquakes, and uplift -Landforms related to above -Process of building up and breaking down of Earth’s surface over time -Appearance of Earth’s surface if there was no uplift, weathering, or erosion Terms: Earth’s tilt, seasons, axis of rotation, orbits, phases of the moon, revolution, reflection and nonliving in a small environment -Predict effects of changes in an environment on a living organism -Small-scale vs larger environment Terms: environment, interaction, living, nonliving, organism, survive, observe, terrarium, aquarium, temperature, moisture, small-scale FORCE & MOTION and GRAVITY -Forces cause change in speed or direction of objects -Objects at rest stay at rest…… -Pushing vs. pulling -Simple machines and forces -Compare effects of forces on objects (varying strength of force and varying the objects) -Objects near Earth are pulled to it by gravity -Describe effects of gravity on the motion of an object Terms: distance, force, gravity, weight, motion, speed, direction, simple machine SUN/HEAT -Main source of heat and light for living things -Rubbing objects together can produce heat -Demonstrate mechanical and electrical machines produce heat and sometimes light Terms: mechanical, electrical, temperature, degrees, lubricated, misconception, heat source, machine Terms: atmosphere, meteorologist, freezing, cumulus, stratus, cirrus, air pressure, thermometer, air temperature, wind speed, forecast, severe phenomena, precipitation, seasonal, accuracy, barometer, rain gauge, components ROCKS/SOILS -Basic properties of rocks and minerals (differences) -Sort by appearance the 3 basic types of rock: igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic -Utah rocks -Weathering vs. erosion -Basic components of soil -Relationship between plants and soil Terms: mineral, weathering, erosion, sedimentary, igneous, metamorphic, topsoil, subsoil, bedrock, organism, freeze, thaw, profile, nonliving, structural support, nutrients FOSSILS -Formation -Where found in Utah -How they can be used to infer Terms: infer, environments, climate, dinosaur, preserved, extinct, extinction, impression, fossil, prehistoric, mineral, organism, replacement, trilobite, sedimentary, tropical UTAH HABITATS -Physical characteristics of wetlands, forests, and deserts -Plants and animals in Utah, how they adapt to their environment -Effect of elevation on habitats -Endangered Utah plants and animals -Classify Utah plants and animals -Utah spiders and insects Terms: wetland, forest, desert, adaptation, deciduous, coniferous, invertebrate, vertebrate, bird, amphibian, reptile, fish, mammal, insect, hibernation, migration Common plants: sagebrush, pinyon pine, Utah juniper, spruce, fir, oak brush, quaking aspen, cottonwood, cattail, bulrush, prickly Terms: earthquakes, erode, erosion, faults, uplift, volcanoes, weathering, buttes, arches, glaciers, geological, deposition MAGNETISM/ELECTRICITY -Types of magnets -Attract/repel, permanent magnets vs. electromagnetism -Earth’s magnetic field -Features of static and current electricity -Electrical circuit components -Conductors, insulators Terms: battery, complete circuit, incomplete circuit, current, conductor, insulator, pathway, power source, attract, compass, electromagnetism, magnetic force, magnetic field, natural magnet, permanent magnet, properties, repel, static electricity, temporary magnet, switch, load HEREDITY/TRAITS -Parent to offspring -Inherited traits can help or hinder survival -Inherited traits vs. traits and behaviors that are learned or induced by the environment -Characteristics can give a survival advantage Terms: inherited, environment, species, offspring, traits, variations, survival, instincts, population, specialized structure, organism, life cycle, parent organism, learned behavior SOLAR SYSTEM -Planet names and locations relative to the sun -Physical properties and sizes of objects in solar system -Characteristics of comets, asteroids, and meteors -Manmade satellites -Technology used to observe and explore the solar system -Forces holding objects in orbit; mass of objects and gravitational force -Role of gravity in the solar system -Compare size/distance of objects within the: solar system, galaxy, universe -Appearance and motion of stars, how various cultures have understood and used them Terms: asteroids, celestial object, comets, galaxy, planets, satellites, star, distance, force, gravity, gravitational force, mass, scale, solar system, constellation, Milky Way galaxy, speed of light, telescope, universe, sun, light years MICROORGANISMS -Size, shape, and structure of organisms -Common characteristics of organisms and their function -Plan/conduct experiments to determine microorganisms requirements -Positive/negative effects of microorganisms; decomposers, food production, etc. -Helpful uses and role of science that led to positive uses (i.e., Pasteur established the existence, growth, and control of bacteria; Fleming isolated and developed penicillin) -Diseases caused by microorganisms (e.g. athlete’s footfungi, streptococcus throat-bacteria, giardia-protozoa) -Harmful effects on food (e.g., pear cactus Common animals: jackrabbit, cottontail rabbit, red fox, coyote, mule deer, elk, moose, cougar, bobcat, deer mouse, kangaroo rat, muskrat, beaver, gopher snake, rattlesnake, lizard, tortoise, frog, salamander, red-tailed hawk, barn owl, lark, robin, pinyon jay, magpie, crow, trout, catfish, carp, grasshopper, ant, moth, butterfly, housefly, bee, wasp, pill bug, millipede causes fruits and vegetables to rot, destroys food bearing plants, makes milk sour) Terms: algae, fungi, microorganism, decomposer, single-celled, organism, bacteria, protozoan, producer, hypothesis, experiment, investigation, variable, control, culture HEAT, LIGHT, SOUND -Heat transfer: conduction, convection, radiation -Heat from the sun -Various sources of light -Light can be produced, reflected, refracted, and separated -Sounds and vibrations -Relationship between size and shape of object and it’s pitch -Volume as related to energy used to create the vibration Terms: angle of incidence, angle of reflection, absorption, conduction, conductor, convection, medium, pitch, prism, radiation, reflection, refraction, spectrum, vibration *Information about the core was taken from the uen.org, the topics have been edited and paraphrased but the terms are listed the same as what shows on the website. http://www.uen.org/core/science/index.shtml








