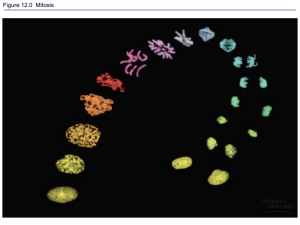
Different Stages of Mitosis and Meiosis
advertisement
TABLE 2 READING ACTIVITY COMPARING MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Contents 1 Process Differences 1.1 Different Stages of Mitosis and Meiosis 2 Differences in Purpose 2.1 Significance 3 Occurrence 4 History 5 Evolution 6 Chromosomal pattern comparison 7 Videos explaining the difference Process Differences Mitosis is a method of reproduction for single celled organisms that reproduce asexually. An identical version of the organism is created through splitting of the cell in two. Meiosis may result in millions of spermazoa and egg cells with unique genetic patterns. The mating of the two cells formed by meiosis results in a unique genetic offspring of the same species. Meiosis is a major factor in evolution, natural selection, and biodiversity. The processes of cellular division shown in mitosis and meiosis are present in all manner of life forms including humans, animals, plants, fungi, and single celled organisms and species. Essentially any cell based organism of which all organic life is based will exhibit some form of mitosis and meiosis for growth and reproduction of the individual and species. Cell division is the process by which a multicellular organism grows, repairs, maintains and reproduces itself. Most cells have a nucleus which is the controlling centre directing a cells activity. The instructions for these activities are contained in the chromosomes, which are composed of proteins and DNA. DNA contains the coded chemical instructions, which direct the growth, differentiation and functioning of a cell. Mitosis is a type of cell division that results in the production of daughter cells, which are identical to the original parent cell. It is referred to as division for growth and repair. Mitosis occurs in all body cells. The number and type of chromosomes produced are exactly the same as the original parent cell. The parent cell duplicates its DNA by duplicating the chromosomes, the chromosomes then separate to either end of the cell and the cell eventually divides into two daughter cells. Meiosis is a type of cell division that forms cells with half the number of chromosomes normally found in cells of the species. If they did not, on fertilization, the chromosome number would be doubled in the new generation. Meiosis is referred to as division for reproduction. Chromosomes can be matched into pairs, which are similar – homologous chromosomes. Each pair is made up of one chromosome contributed by each parent and carries information about the same inherited characteristics. During the process of meiosis, the homologous chromosomes are divided between the separate gametes. In this way, meiosis produces haploid cells, which show variation. This variation has been produced by the random segregation or assortment of chromosomes pairs, or by crossing over where the chromosomes get tangled up when they separate. Different Stages of Mitosis and Meiosis The different phases of meiosis are: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase. An overview of the process and phases of meiosis The stages of mitosis are: Interphase, Preprophase, Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase and Cytokinesis. An overview of the process of mitosis. Differences in Purpose Both Meiosis and Mitosis are found in complex organisms which reproduce sexually. Mitosis may be used for human growth, the replenishment of depleted organs and tissues, healing, and sustenance of the body. Identical versions of cells can be created to form tissues through Mitosis. Meiosis is a special process reserved for the creation of the egg and sperm cells. The same patterns may be found in many species of plant and animal cell reproduction. Significance The importance of mitosis is the maintenance of the chromosomal set; each cell formed receives chromosomes that are alike in composition and equal in number to the chromosomes of the parent cell. Occurrence Meiosis is found to occur in humans, animals and plants while mitosis is found in single-cell species as well. History Meiosis was discovered and described for the first time in sea urchin eggs in 1876, by noted German biologist Oscar Hertwig. Walther Flemming discovered the process of Mitosis in 1882. Evolution Mitosis as a form of reproduction for single-cell organisms originated with life itself (around 4 billion years ago). Meiosis is thought to have appeared 1.4 billion years ago. Chromosomal pattern comparison In mitosis, each daughter cell ends up with two complete sets of chromosomes while in meiosis, each daughter cell ends up with one set of chromosomes. Both mitosis and meiosis are studied by scientists generally by using a microscope to identify and classify chromosomal patterns and relationships within the cell’s structure. An understanding of the way cells synthesize chromosomes for reproduction can be applied in bio-machines and nano-technology. Transplantation of genes and chromosomes through injection and implantation is used to experiment with bio-engineering and cloning. Understanding the process through which cells replicate also has application in medicine and the study of health and disease. Videos explaining the difference Here are two videos (the first one short and the second is longer, more in-depth) that explain the process of mitosis and meiosis. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sJCWVTnFf5o http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mr0oiws9ZvM