new opioid charts
advertisement

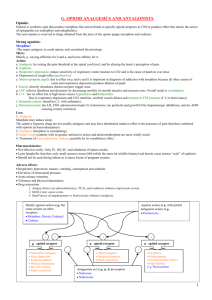
Meperidine Receptor Mu Kappa Structure Phenylpiperidine derivative Clinical Use Post op pain Post op shivering Primarily for labor pain Fentanyl Sufentanil Alfentanil Selective Mu receptor agonist Phenylpiperidine derivative Analgesia Adjunct to IA Blunt circulatory response: Laryngoscopy Sudden change in surg. stimulation Analogue of fentanyl Analogue of fentanyl Greater receptor affinity Structurally unique – ester linkage susceptible to hydrolysis by non-specific plasma and tissue esterases **fastest elimination** Potency 5-10 > fentanyl 1/5 – 1/10 potency of fentanyl **most potent** Potency = fentanyl Analgesia Induction Heart room Blunt response to brief single stimulus: Intubation Retrobulbar block Blunt response to brief single stimulus Intubation dose = 15 mcg/kg Analgesic infusion during GA = 0.05 – 2.0 mcg/kg/min Blunt circ response to high Des. = 10-20 mcg/kg Blunt catechol = 30 mcg/kg Pharmacokinetics 1/10th as potent as morphine 75x more potent that MSO4 100 mg = 10 mg morphine Onset IV = 10 min DOA = 2-4 hrs Similar to atropine and possesses some antispasmodic qualities Remifentanil Onset = 30 sec Effect-site equil time = 6.8 min Short DOA d/t rapid redistribution to inactive tissue sites >potency and rapid onset d/t > lipid solubility Lungs = large inactive storage site,1st pass Pulm uptake – 75% of initial dose E1/2 x > than any other opioid; context sensitive ½ x increases w/duration 12xs more potent than fentanyl Sufenta 5mcg = Fent 50 mcg Rapid redistribution to inactive tissue sites High tissue affinity d/t > lipid solubility Alfentanil 500 mcg = Fentanyl 50 mcg = Sufentanil 5 mcg Onset = rapid; redistributes to inactive tissue sites Need long acting opioids before infusion is stopped Fastest elimination d/t rapid metabolism by blood nonspec. esterases Accumulates less than other opioids Highly non-ionized at physiological pH Effect site equil time = 1.1 min Effect-site equil time =1.4 min E ½ x = 6 min Renal Fail. Does not alter E ½ x or clearance Small Vd Effect-site equil time = 6.2 min 1st pass pulm uptake = 60% Longer E ½ x in Elderly & obese Short E ½ x = 1.5 hrs Longer E ½ x w/Cirrhosis Highly protein bound 92.5% Highly protein bound 92% Small Vd Longer E1/2 x in Elderly Induction dose= 1 mcg/kg Small Vd = low lipid sol Highly Protein bound 79-97% Large Vd **Potency from least to greatest: Demerol < Morphine<Alfentanil <Fentanyl = Remifentanil < Sufentanil** Meperidine Metabolism Extensive Hepatic metabolism 90% demethylated to active metabolite Normeperidine Normeperidine -hydrolyzed to an acid and excreted in urine Normeperidine E ½ x = 15 hrs *Seizure Activity* Fentanyl Extensively Metabolized by: N-demethylation Inactive metabolite = norfentanyl Excreted by kidneys Detected in urine 72 hrs after single dose Sufentanil Rapidly metabolized by: N-dealkylation O-demethylation Inactive and active metabolites formed <1% unchanged in urine Alfentanil 2 independent Pathways: Noralfentanil major metabolite Efficiently cleared by liver metabolism within 60 min Redistributes to inactive tissue sites Remifentanil Unique among the opioids – rapid metabolism Not affected by Pseudocholinesterase Deficiency Can be used in renal and hepatic disease High lipid solubility -> max renal tubular reabsorption E ½ x of Meperidine = 3-5 hrs Clearance sensitive to hepatic blood flow 60% Protein Bound Use Cautiously in Elderly and Renal Disease Side Effects Causes Histamine Release No Histamine release No Histamine release No Histamine release No Histamine release Orthostatic ↓ BP Marked Bradycardia Hypotension Hypotension Hypotension ↑ HR and Mydriasis- modest atropine like effect Possible seizure activity Bradycardia Bradycardia Bradycardia ↓ Myocardial contractility w/large doses Chest wall and skeletal muscle rigidity Itchy nose Delirium and Seizures ***Life threatening interaction w/MAOIs = Serotonin Syndome*** Type I Rxn: Hypertension Agitation Skeletal Muscle Rigidity Headache Hyperpyrexia Type II Reaction: Hypotension Respiratory Depression Coma Acute Opioid tolerance Skeletal muscle rigidity with large doses Codeine Hydromorphone Methadone Heroin Structure Made from Morphine Derivative of Morphine Synthetic Opioid with prolonged duration of action (24 hrs) Synthetic Opioid produced by Acetylation of Morphine= Diacetylmorphine Pharmacokinetics E ½ x with PO = 3.5 hrs Onset IV almost immediate E ½ x = 35 hrs Rapid penetration into the brain Peak = 5 – 20 min DOA = 2-5 hours 5x as potent as Morphine 2 mg = 10 mg Morphine Uses Effective antitussive at 15 mg PO Same as morphine Heroin addiction Good for mod to severe pain Side Effects Histamine Release with IV dosing No histamine release Similar SE to morphine Same SE as morphine Metabolism Limited 1st pass hepatic metabolism – effective when given PO Demethylated to: Morphine and Norcodeine Shorter DOA than morphine 4-5 hours Lack nausea Great potention for physical dependency Metabolized in Liver to inactive metabolites Hydrolyzed in brain to active metabolites Opioid Agonists-Antagonists drugs ∙ Pentazocine (TTalwin) ∙ Butorphanol (SStadol) ∙ Nalbuphine (N Nubain) ∙ Buprenorphine (BBuprenex) receptor effects side effects ∙ Bind to MU receptors and act as a partial Agonist OR Antagonist ∙ Provide weaker analgesia than opioid agonists – good for mild – moderate pain ∙ Produce analgesia without respiratory depression ∙ Antagonist quality creates a “C CEILING” effect for analgesia (only first dose effective) ∙ Low potential for physical dependence ∙ Side effects similar to Opioids ∙ May cause Dysphoric Reactions Opioid Agonists-Antagonists Pentazocine (Talwin) Butorphanol (Stadol) Nalbuphine (Nubain ) Buprenorphine (Buprenex) ∙ Opioid agonist ∙ Weak antagonist ∙ Similar to - Pentazocine ∙ Related to - Oxymorphone - Naloxone ∙ Derived from Opioid Alkaloid: - Thebaine ? Delta ? Kappa ∙ MU low affinity ∙ Kappa moderate affinity ∙ Sigma minimal affinity ∙ MU Antagonist effects ∙ MU high affinity 50x > MSO4 - Slow dissociation = action - Resistant to Antagonism of Naloxone (Narcan) ∙ Agonist effects Antagonized by Naloxone (Narcan) ∙ Antagonist effects Withdrawal ∙ Agonist effects 20 x > than Pentazocine ∙ Antagonist effects 10 - 30 times greater ∙ Equal potency Analgesia to MSO4 ∙ Analgesia Onset and Duration - Similar to Morphine (MSO4) - Nubain 10mg IM ? Very Potent - 0.3mg IM = 10mg Morphine uses Treatment of: ∙ Chronic Pain ∙ Relieves Moderate Pain ∙ Good for: - Acute Pain rather than Chronic ∙ 10-20mg IV reverses the respiratory depression of Fentanyl postop - But maintains Analgesia ∙ Good for: - Moderate to Severe Pain dose ∙ Dose 10-30mg IV or 50mg PO ∙ 50mg PO = 60mg Codeine ∙ Available in parenteral form ∙ 2 -3 mg IM = 10mg Morphine ∙ > 30mg “C CEILING EFFECT” d/t antagonist activity ∙ ∙ Extensive 1st-Pass Hepatic Metabolism ∙ Metabolized to an inactive metabolite ∙ Excreted in Urine ∙ E ½ x = 2- 3 hours ∙ Hepatic metabolism to inactive metabolites ∙ Excreted in Urine ∙ E ½ x = 2.5 - 3.5 hours ∙ Rapidly &Completely absorbed after IM ∙ Metabolized in the Liver ∙ Morphine-like Drugs Inactive ∙ E ½ x = 3 - 6 hours ∙ Onset = 30 min ∙ Duration 8-10 hours ∙ Highly Lipid Soluble Sedation Diaphoresis Dizziness Dysphoria Crosses the Placenta Fetal Depression ∙ Catecholamines - HR - BP - PAP - LVEDP ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ Abuse potential LOW ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ moa receptors effects pharm.kinetics and metabolism side effects ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ Sedation Diaphoresis Nausea Respiratory Depression Attenuates Opioid Agonist Activity** ? Does NOT cause - HR - BP - PAP Opioid Antagonists Drowsiness Incidences of Pulmonary Edema Nausea/Vomiting Respiratory Depression structure ∙ Minor changes in structure of Opioid Agonist changes the Drug to an ANTAGONIST ∙ Substitute an Alkyl Group for a Methyl Group receptor ∙ Displaces Opioid agonist from the MU receptors ∙ Pure Antagonist DOES NOT activate the receptor Antagonism Naloxone (Narcan) receptor pharm.kinetics ∙ ANTAGONIZES Mu Receptors *** ∙ Short Duration of Action = 30 - 45 min dose ∙ 1 - 4mcg/kg Reverses Opioid-induced Respiratory Depression and Analgesia uses ∙ Detect suspected physical dependence ∙ To avoid abrupt reversal of analgesia give 40 mcg (0.1 mL) ∙ Used as continuous infusion to prevent respiratory depression and itching from neuraxial opioids ∙ Neonatal Depression - Given at Delivery (this is with moms that are NOT addicts) ∙ Opioid-Induced Depression of Ventilation ∙ Treatment of deliberate opioid overdose metabolism ∙ Metabolized in the liver side effects ∙ Side effects are due to reversal of analgesia and sudden perception of pain: ∙ E ½ x = 60 -90 minutes ∙ Nausea / Vomiting ∙ Increased SNS activity - Tachycardia - Pulmonary Edema - HTN - Cardiac Arrhythmias (VF) ∙ Crosses Placenta Acute Withdrawal of neonate of Opioid-Dependent mom (can lead to baby’s demise)