Biology
advertisement

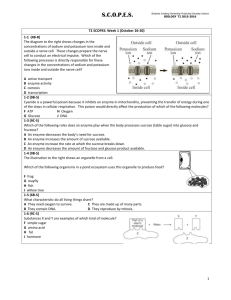
Biology First Six Weeks Student Expectations (TEKS) 9A Compare the structures (what it looks like) and functions (what it does) of different biomolecules. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, monomer, polymer, reactant, product, dehydration synthesis, hydrolysis 1. What are the functions of each biomolecule? 2. What are the structures of each biomolecule? 3. What are the monomers of each biomolecule? 4. List several examples of each biomolecule. 5. What are the polymers of each biomolecule? 6. Describe how a polymer is formed. 7. Describe how a polymer is broken down into a monomer. 8. What is the difference between dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis? 9. What are the reactants and products of dehydration synthesis? 10. What are the reactants and products of hydrolysis? 9C Identify and investigate the role of enzymes. Enzyme, substrate, catalyst, reaction 1. Predict how enzymes affect the rate of reaction. 2. What are the effects of temperature, pH, and substrate concentration on enzymes? 3. Illustrate the effects of temperature, pH, and substrate concentration on enzymes using graphs. 4. What is the structure of an enzyme? How is this structure related to its function? 4A Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryote, eukaryote, organelle, cytoplasm, nuclear envelope (membrane), ribosome, endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi apparatus, lysosome, vacuole, mitochondria(ion), chloroplast, centriole, cell membrane, cell wall, chromosome, lipid bilayer 1. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 2. List at least 3 examples of prokaryotic organisms. 3. List at least 3 examples of eukaryotic organisms. 4. List each organelle found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and explain its function. 5. What organelles are found only in plant cells? 4B Examine and explain cellular processes. Equilibrium, diffusion, osmosis, isotonic, hypertonic, hypotonic, facilitated diffusion, active transport, endocytosis, exocytosis, phagocytosis, pinocytosis 1. How does the concentration gradient determine the direction solutes and water move across a membrane? 2. How do large amounts of solutes or solutions enter or exit a cell? 3. How do the structure and chemical properties of the lipid bilayer determine what can diffuse across? 4. What happens to a cell in a Hypertonic solution? Hypotonic solution? Isotonic solution? 4C Compare the structure of viruses to cells, describe viral reproduction and the role of viruses in causing diseases. Virus, lytic cycle, lysogenic cycle, capsid, retrovirus, influenza, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) 1. What is the structure of a virus? 2. How does the structure of a virus compare to the structure of a cell? 3. Describe the lytic reproduction cycle. 4. Describe the lysogenic reproduction cycle. 5. How does a virus cause a disease like influenza and HIV? 5A Describe the cell cycle, including DNA replication. Cell division, cell cycle, mitosis, cytokinesis, chromatid, chromatin, replication, spindle fiber, centromere, interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, homologous, diploid, haploid, meiosis, crossing-over, nucleotide, base-pairing rule, DNA polymerase 1. Draw and explain the cell cycle. 2. Draw and explain the stages of cell division. 3. Why is DNA replicated in the S phase? 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Why do eukaryotic cells undergo cell division? Why do prokaryotic cells undergo cell division? List the steps of DNA replication. What are the complementary base pairs for each nitrogenous base? Why does DNA replicate? Explain how the order of DNA codes determines the traits of the organism. 5C Describe the role of DNA, RNA and environmental factors (ex: proteins & signaling molecules) Differentiation, stem cells 1. What is a stem cell? 2. What is differentiation? 3. DO all cells in the body have the same DNA? 4. How do muscle cells become muscle cells? 5D Recognize the disruptions in the cell cycle lead to diseases such as cancer. Cancer, cell division, mitosis, checkpoint 1. What is cancer? 2. What causes cancer? 3. When working on treatments to inhibit cancer, what process must be inhibited? 4. How do checkpoints play a role in regulating cell cycle? 5. What happens when these checkpoints fail? Unit 1 Exam 9A,9C Unit 2 Exam 4A,4B,4C Unit 3 Exam 5A,5C,5D