Name: PRACTICE TEST – Unit 2: Geology, Mineral Resources
advertisement

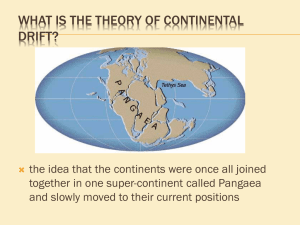
Name: _________________________ PRACTICE TEST – Unit 2: Geology, Mineral Resources & Mining AP Environmental Science – October 1, 2013 Directions: Choose the letter of the best answer and darken its bubble. Questions 1-4 refer to the following answers. Select the one lettered choice that best fits each statement. (A) Igneous rocks (B) Metamorphic rocks (C) Sedimentary rocks (D) All of the above (E) None of the above 1. This type of rock is susceptible to chemical and mechanical weathering. 2. This type of rock is created by the cooling of magma within the lithosphere. 3. This type of rock is produced when small particles, transported by erosion, settle on top of each other and become compressed. 4. Marble is an example of this type of rock. Questions 5-8 refer to the following answers: Select the one lettered choice that best fits each statement. (A) Divergent boundary (B) Convergent boundary with oceanic and continental plates (C) Convergent boundary with two oceanic plates (D) Convergent boundary with two continental plates (E) Transform boundary 5. The San Andreas Fault between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate in California is an example. 6. The Himalayas were formed from this type of boundary. 7. This type of boundary created the Marianas Trench. 8. The mid-Atlantic rift forms this type of boundary. 10. Which of the following set of characteristics would best characterize a continental-oceanic convergent plate boundary? (A) island arc, earthquakes, mountain ranges (B) offshore trench, coastal volcanic mountain range (C) broad, gently sloping continental shelf with sporadic volcanoes (D) visible fault in the ocean floor, earthquakes, relatively new sea floor becoming older farther offshore (E) deep marine sediments located at the high altitudes in on shore mountain ranges, small, frequent earthquakes 11. Heap leach extraction is the process that is used to refine which of the following from ore? (A) Uranium (B) Gold (C) Aluminum (D) Halite (E) Gravel 12. Which of the following is an example of an extrusive igneous rock? (A) limestone (B) sandstone (C) granite (D) basalt (E) shale 13. When a continental plate collides with another continental plate,… (A) a subduction zone will be created. (B) the two plates will push each other up into a mountain range. (C) an island arc will be formed. (D) a rift valley will be formed. (E) a deep submarine trench will be formed. 14. The evidence that Alfred Wegner cited when he originally proposed the theory of continental drift was… 9. Which of the following layers of the Earth would be the warmest solid layer? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) crust upper mantle lower mantle outer core inner core (A) the changes in magnetic polarity within iron ore that occurred equidistant from the mid-Atlantic rift (B) the earthquakes that occurred along the edges of tectonic plates (C) the subduction zones, where one plate dives underneath another (D) the way coastlines fit together like a puzzle and similar fossils occur on both sides of an ocean. (E) the location of mountain ranges, which occur where continental plates collide. 15. Which of the following would NOT occur as part of the rock cycle? (A) Extrusive igneous rocks could be converted into sediments. (B) Compressed sediments subjected to intense heat and pressures become metamorphic rocks. (C) Metamorphic rocks are subducted, melted, and returned to the lithosphere as intrusive igneous rocks. (D) Intrusive igneous rocks are converted into extrusive igneous rocks by weathering processes. (E) Sedimentary rocks are weathered and eroded to form different sedimentary rocks. 16. A seismically active arc of islands, such as Alaska’s Aleutian Island chain, is an indicator of… (A) the convergence of oceanic and continental plates. (B) a mid-plate hotspot. (C) the convergence of two oceanic plates. (D) a divergent boundary. (E) a mid-oceanic rift. 17. Most volcanism in the world is associated with (A) plate boundaries (B) midcontinental hot spots (C) faulting (D) aquifer depletion (E) desertification 18. Which of the following elements constitutes the highest percentage of mass in the Earth’s crust? (A) Oxygen (B) Aluminum (C) Carbon (D) Potassium (E) Nitrogen 19. Radioisotopes decay at different rates than nonradioactive isotopes primarily because they have differing numbers of (A) protons (B) neutrons (C) electrons (D) quarks (E) atoms 20. Which of the following is NOT a unique property of water that supports life? (A) Cohesion (B) High heat capacity for its molecular size (C) Very low melting point (D) Universal solvent (E) Becomes less dense as it freezes 21. Which of the following substances would have a pH greater than 7? (A) Seawater (B) Lemon juice (C) Battery acid (D) Normal rainwater (E) Acid rain 22. Which of the following organic compounds is responsible for conveying an organism’s hereditary information? (A) carbohydrates (B) proteins (C) phospholipids (D) nucleic acids (E) hydrocarbon 23. Which of the following possesses the highest kinetic energy? (A) superheated water trapped under the Earth’s crust (B) a geyser (C) a large high-altitude lake (D) a raindrop hanging from a leaf tip (E) an aquifer 24. Which of the follow represents the summary equation for the process of photosynthesis? (A) C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + sunlight 6H2O + 6CO2 (B) C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6H2O + 6CO2 + energy (C) CO2 + 4H2S + O2 -> CH20 + 4S + 3H2O (D) 6H2O + 6CO2 + sunlight C6H12O6 + 6 O2 (E) 6CO2 + 6 H2O + 3H2S C6H12O6 + 3H2SO4 25. Of the following, the most common fuel for nuclear fission is… (A) radium. (B) magnesium. (C) hydrogen. (D) sodium. (E) uranium. 26. Which of the following natural hazards is least associated with the ‘Ring of Fire?’ (A) active volcanoes (B) earthquakes (C) tsunamis (D) landslides (E) wildfires 27. A resource that is too expensive to extract is said to be (A) perpetual. (B) economically depleted. (C) ecologically depleted. (D) environmentally depleted. (E) limited. 28. Which of the following is NOT a method for extracting coal? (A) Contour strip mining (B) Subsurface mining (C) Area strip mining (D) In situ leach mining/injection wells (E) Mountain top removal 29. Coal continues to be used in the United States partially because… (A) the country has large reserves of coal. (B) the quality of coal in the United States is very consistent from deposit to deposit. (C) coal causes almost no air pollution when burned. (D) coal deposits in the United States lie very close to the surface and are easily extracted. (E) coal contains very few impurities, which cause problems in petroleum and natural gas. 30. Which of the following is NOT an environmental hazard of coal use? (A) leaching of acid materials into waterways (B) lung disease and high accident rates in mine workers (C) widespread scarring of the landscape (D) high CO2 and other air pollutants such as soot, mercury, and radioactive particles (E) all of the above are environmental hazards of coal use 31. The theory of plate tectonics suggests that Earth’s crust is made up of a series of plates that float on a more fluid layer of the upper mantle called the… (A) lithosphere (B) mesosphere (C) asthenosphere (D) hydrosphere (E) core 32. Which of the following terms refers to the desired material in a mining operation? (A) tailings (B) ore (C) spoils (D) overburden (E) gangue 33. Which of these is a non-metallic mineral resource? (A) aluminum (B) gold (C) sand (D) oil (E) copper 34. Which of the following is NOT a provision of the Surface Mining Control and Reclamation Act of 1977? (A) Companies are required to obtain a permit before they can begin surface mining operations. (B) Government is given the authority to inspect mining operations and levy fines for unsafe or polluting practices. (C) Companies must restore the land when they are finished mining, often referred to as reclamation. (D) A bond must be posted by the company which is held by the government until it is satisfied that reclamation has been completed. (E) Surface mining is permitted on certain lands such as national parks and wilderness areas. 35. When it comes to nonrenewable mineral resources recycling is a sustainable option because it reduces all of the following except: (A) air pollution (B) water pollution (C) toxics released to the environment (D) energy consumption (E) demand for mineral resources ANSWER KEY 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. D A C B E D B A E B B D B D D C A A B C 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. A D B D E E B D A E C B C E E