Chemistry of Life notes
advertisement
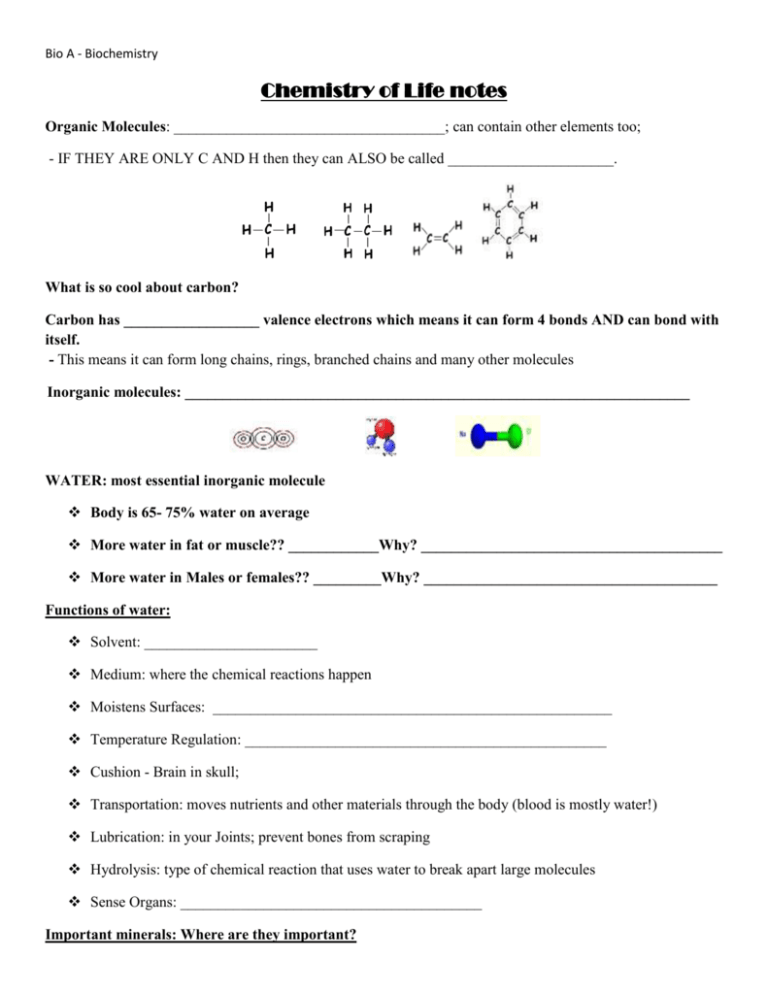
Bio A - Biochemistry Chemistry of Life notes Organic Molecules: ____________________________________; can contain other elements too; - IF THEY ARE ONLY C AND H then they can ALSO be called ______________________. What is so cool about carbon? Carbon has __________________ valence electrons which means it can form 4 bonds AND can bond with itself. - This means it can form long chains, rings, branched chains and many other molecules Inorganic molecules: ___________________________________________________________________ WATER: most essential inorganic molecule Body is 65- 75% water on average More water in fat or muscle?? ____________Why? ________________________________________ More water in Males or females?? _________Why? _______________________________________ Functions of water: Solvent: _______________________ Medium: where the chemical reactions happen Moistens Surfaces: _____________________________________________________ Temperature Regulation: ________________________________________________ Cushion - Brain in skull; Transportation: moves nutrients and other materials through the body (blood is mostly water!) Lubrication: in your Joints; prevent bones from scraping Hydrolysis: type of chemical reaction that uses water to break apart large molecules Sense Organs: ________________________________________ Important minerals: Where are they important? Bio A - Biochemistry Iron: Calcium and phosphorous: Sodium, potassium and Chlorine: Iodine: Function of minerals: _________________________________________________ o act as a pH buffer o aid in structure of cells and the body The organic molecules we will study are known as _______________________________ Macro means _____________ - made up of many small molecules linked together to form one big molecule - _____________________________________________________ - _____________________________________________________ Nutritional Compounds: These Macromolecules are what provide us with ENERGY AND NUTRIENTS __________________________________________________________ Calorie (in chemistry) is the amount of energy it takes to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water 1 degree Celsius; 1 food calorie = 1000 chemistry calories = 1 kilocalorie So if we eat 100 calories, it means our body gets 100 kCal of energy from that food! We will study the four major classes of macromolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins and Nucleic acids CARBOHYDRATES: The monomer of a carbohydrate is called a _________________________________ What elements are carbohydrates made of? ___________________________________ What shape do these molecules have? _______________________________________ Define: Dissaccharide: _____________________________________________________________ Bio A - Biochemistry Polysaccharide: ____________________________________________________________ Dehydration synthesis: A chemical reaction that _____________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ - 2H’s and an O have to be removed from the reactants to connect them. These atoms then become __________________. This same reaction will be used to build carbs, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids Below is the dehydration synthesis reaction that connects two monosaccharides into a disaccharide. - Highlight the atoms that become the water molecule Hydrolysis: a chemical reaction that _______________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ - Requires the addition of ONE water molecule. - this same reaction will be used to break down carbs, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids - Hydrolysis is the exact reverse of dehydration synthesis shown above! What do Carbs do for us? Function Examples: Instant energy Monosaccharides (simple sugars) like glucose, fructose Short term energy storage Polysaccharides like glycogen (in animals) and starch (in plants) Cell structure (plant cell walls) Polysaccharides like cellulose (becomes fiber in our diet when we eat plants!) What do the formal names of carbs all have in common? LIPIDS: Bio A - Biochemistry One type of lipid molecule is made of __________________________________________________ This type of lipid molecule is called a _________________________________________________ Do lipids have a true monomer? ___________ why? What reaction puts a triglyceride together? ____________________________ What reaction breaks apart a triglyceride? _____________________________ Highlight the atoms that become the water molecules. Then fill in how many waters are made H + H + __H2O H Three Fatty Acids 1 Triglyceride Lipids are made of the following elements: _________________________________ Some examples of lipids include: __________________________________________________________ The major functions of lipids are: 1. _______________________________________________________________________________ 2. ________________________________________________________________________________ 3. _______________________________________________________________________________ 4. _______________________________________________________________________________ PROTEIN: The monomer of a protein is called an ____________________________ What reaction builds proteins by linking amino acids? _____________________________ What reaction breaks down proteins into amino acids? _____________________________ Below is a dehydration synthesis reaction of two amino acids: - highlight the atoms that become the water molecule Bio A - Biochemistry - label the amino and carboxyl ends of AA 1 label the “variable R” group label the peptide bond + + H2O How many different types of Amino acids exist? _________ The __________________________ is different in each amino acid while the amino group and carboxyl group are the same. Proteins are made of the following elements_________________________________ Once amino acids are linked in a chain, they are called a polypeptide. What has to happen to the polypeptide before it becomes a functional protein? Functions of Proteins and examples Function Examples Structure Chemical Messengers Speed up chemical reactions Fight disease NUCLEIC ACIDS: Nucleic acids are made up of the monomer called ____________________________ Draw the structure of one monomer and label the THREE parts; include the variations: Nucleic acids are made of the elements_________________________________ Bio A - Biochemistry What is the general role for all nucleic acids: ___________________________________________________ Compare and contrast RNA and DNA, the two types of nucleic acids. RNA Full Name Ribonucleic Acid DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Name of the sugar Possible nitrogen Bases How many chains or strands does it have? Function - Contains the directions to make 1 protein; temporary copy DNA is the master copy of all our information. Stored in the nucleus of the cell Nucleic acid analogy: Nucleic acids are information molecules that teach our cells how to make proteins. Use this analogy to help understand. DNA is an ENTIRE COOKBOOK of recipes that contains the information to make EVERY protein your body needs. - But let’s say you want to make cookies. Do you need the pot roast recipe in the same cookbook? Do you need all the pie recipes? No! - So… we can copy the cookie recipe onto an index card and follow ONLY those directions. Likewise, the cell can copy a single protein recipe from the DNA into RNA. - If you follow the cookie recipe you will end up with one batch of tasty cookies. Likewise, if your cells follow the directions on the RNA it will make a single protein - After finishing the cookies, we can throw out the index card because we still have that recipe in the cookbook. Likewise, after making the protein, the temporary copy of the recipe (RNA) can be destroyed because there is still a master copy in the DNA! - Each protein recipe in the DNA is called a Gene