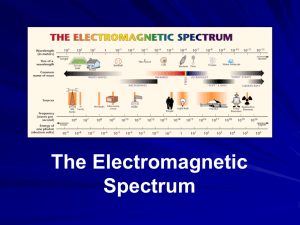
The amount of energy in a photon of light is proportional to the

Name: ____________________ Date: _______________ Per: ___________
Sound & Light Review
1.
The rate at which light energy flows through a given area of space is referred to as its a. b. speed. wavelength. c. d. intensity.
energy.
2.
Which type of electromagnetic waves has slightly longer wavelengths than red light? a. yellow light b. infrared light c. d. ultraviolet light green light
3.
Which type of electromagnetic waves has the highest frequency? a. gamma rays c. infrared b. ultraviolet light d. microwaves
4.
When light rays reflect off a rough surface, they a.
scatter in many different directions. b.
c.
d.
converge toward the normal. diverge away from the normal. decrease their speed and change their angle.
5.
An orange looks orange because it a.
reflects orange light and absorbs other colours. b.
c.
d.
absorbs orange light and reflects other colours. reflects red and yellow light only. absorbs red and yellow light only.
6.
You look at a red tulip, with green leaves, under green light. What do you see? a.
b.
a green flower with green leaves a black flower with green leaves c. d. a yellow flower with black leaves a black flower with black leaves
7.
Light rays that pass through a lens change direction because a.
of internal reflection. b.
c.
d.
they are refracted. light is broken up into many different colours. virtual images always appear slightly larger than real images.
8.
The effect in which white light separates into different colours is called a. magnification. c. reflection. b. refraction. d. dispersion.
9.
White light breaks up into different colours when it passes through a prism because of a. differences in wave speed. b. total internal dispersion. d. c. reflection. droplets in the air.
Short Answer
10.
Sound waves with frequencies higher than 20 000 Hz are referred to as
____ ultrasonic _____________ waves.
11.
In a vacuum, all light travels at the same speed, which is ___ 300,000,000 m/s (or 300,000 km/s; or 180,000 miles/s) __________.
12.
All possible kinds of light, at all energies, frequencies, and wavelengths, make up the ___ electromagnetic spectrum ___________.
13.
The electromagnetic waves with the highest energy and shortest wavelengths are classified as __ gamma rays ______________.
14.
_____ Microwaves _________ are used for cooking as well as for communication.
15.
A(n) __ infrared _____________ sensor can be used to measure the heat that objects radiate.
16.
A lens that bends light inward is called a(n) __ convergent _______ lens.
17.
Describe the sound of a car whose horn is stuck as it approaches you and then passes you.
The horn has a higher pitch as the car comes towards you (due to a compression of the sound waves) and has a lower pitch when travelling away (stretching out the sound waves).
18.
Are the wavelengths of radio and television signals longer or shorter than those detectable by the human eye?
Radio waves (which includes both radio and television signals) have a longer wavelength than what people can see.
19.
Compare a regular and a diffuse reflection.
A regular reflection occurs when all the rays of light reflect exactly the same off of a smooth surface.
Diffuse reflections occur with rough surfaces, and the light rays reflect in many different directions.
20.
What are the three primary colours of light?
The three primary colours of light are red, green, and blue. No yellow!!
21.
Describe why you see a rose as red.
The rose absorbs all colours of light except for red, which reflects off of the rose.
22.
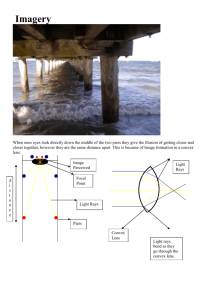
Describe/show the difference in how a convergent lens and a divergent lens affect the light rays that pass through them.
A convergent lens focuses the light rays that pass through it onto a single focal point.
A divergent lens sends the light rays away from a focal point on the opposite side of the lens.
23.
What are the colours of the visible light spectrum?
ROYGBIV!! Red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet
24.
Identify two uses we have for microwaves.
Microwave ovens, cell phones, radar.
25.
What are the positives and negatives of ultraviolet (UV) light?
Positive – creates Vitamin D in the melanin of the skin, can be used in forensics.
Negative – can cause mutations, cancer, sunburns.
26.
Identify two uses we have for sound waves (besides music and speech).
Sonar, ultrasound, warnings/sirens
27.
Which colour of visible light has the longest wavelength? The shortest?
Longest – Red
Shortest - Violet
28.
Draw a wave diagram to illustrate each of the following sounds: a.
high pitched and loud b.
low pitched and soft c.
low pitched and loud