Sedimentary Rocks
advertisement
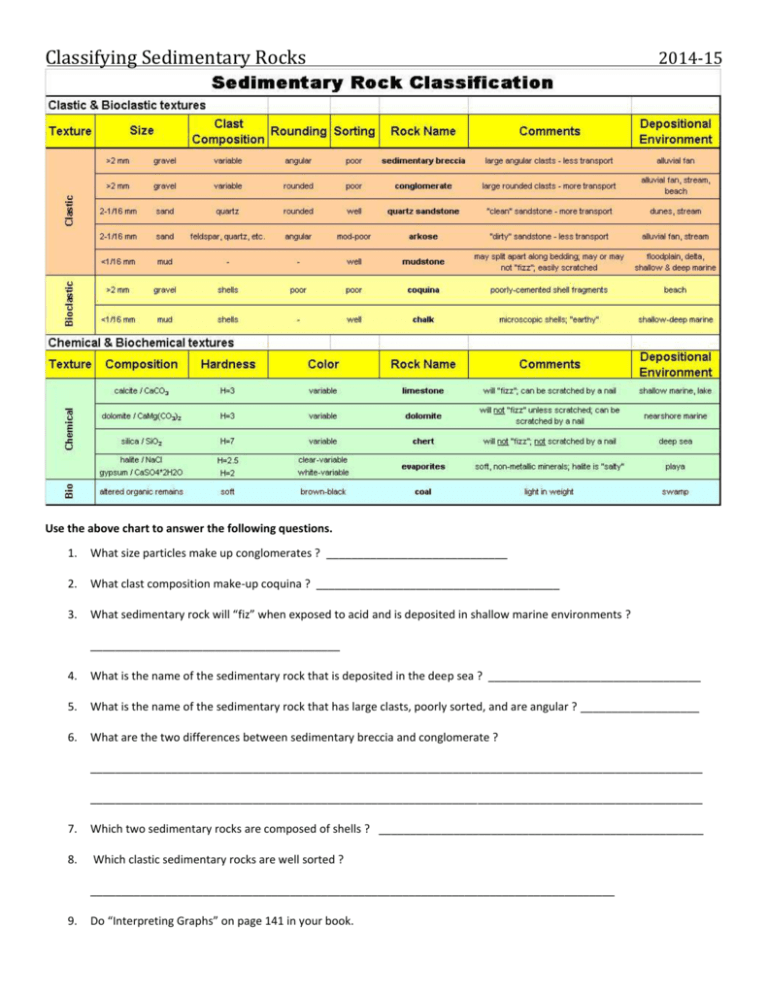
Classifying Sedimentary Rocks 2014-15 Use the above chart to answer the following questions. 1. What size particles make up conglomerates ? _____________________________ 2. What clast composition make-up coquina ? _______________________________________ 3. What sedimentary rock will “fiz” when exposed to acid and is deposited in shallow marine environments ? ________________________________________ 4. What is the name of the sedimentary rock that is deposited in the deep sea ? __________________________________ 5. What is the name of the sedimentary rock that has large clasts, poorly sorted, and are angular ? ___________________ 6. What are the two differences between sedimentary breccia and conglomerate ? __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Which two sedimentary rocks are composed of shells ? ____________________________________________________ 8. Which clastic sedimentary rocks are well sorted ? ____________________________________________________________________________________ 9. Do “Interpreting Graphs” on page 141 in your book. Classifying Sedimentary Rocks 2014-15 • 75% of the earth’s surface rocks are sedimentary rocks. Sedimentary rocks are formed when sediments (weathered material and/or organic material) are compacted and cemented together or when precipitates harden out of solution. They are generally associated with water, the #1 agent of erosion. There are 3 categories of sedimentary rocks: clastic, chemical, and organic. • Clastic sedimentary rocks are a type of sedimentary rock that is composed of “broken” bits of rock or organic matter that are compacted and cemented together (sandstones may form when sand-sized deposits pile on top of each other so that there is enough weight). • Chemical sedimentary rocks are composed of the precipitates that harden out of solution. When bodies of saltwater evaporate the remains may form halite (rock salt). • Organic sedimentary rocks may form when there is a large enough accumulation of organic matter like sea shells. In this case limestone may form. In swampy areas decaying plants may be buried and undergo chemical changes creating coal after long periods of time. • Look at the examples of sedimentary rocks. Can you make any guesses as to whether they are clastic, chemical, and organic ? Which ones ? Explain. S-1 _________________________ S-3 _________________________ S-2 _________________________ S-4 _________________________ S-5 _________________________ S-6 _________________________










