Earthquake test study guide
advertisement

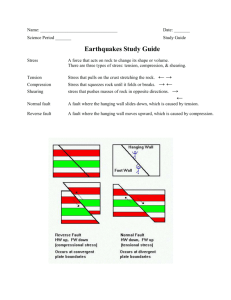
Earthquake Test Study Guide Short answer: 1. 2. List the three types of stress that can occur in Earth’s crust, and describe how each stress can affect rock. Compare and contrast the different types of seismic waves. 10. Do all earthquakes with the same magnitude also have the same intensity? Explain why or why not. 11. During a reverse fault, what happens to the hanging wall? 12. During a normal fault, what happens to the hanging wall? 3. List the two types of body waves and the two types of surface waves. 13. Where is the earthquake’s epicenter located? 14. How do geologists determine where the epicenter of an earthquake is located? 4. In what order do the waves arrive at a seismograph location? (First, second, last). 5. Which seismic waves cause the most damage? 6. Where do seismic waves originate? In what direction do they travel? 15. When can aftershocks occur? 16. What is the biggest danger during earthquakes? 17. What U.S. State is most likely to have major earthquakes? 7. 8. What happens to the distance between P waves and S waves as you travel farther away from the epicenter? 18. Where do most earthquakes occur on Earth (what natural feature)? How are fault-block mountains created? 19. The San Andreas Fault is an example of what type of fault? 9. Compare and contrast the three different types of earthquake scales. 20. Draw a picture (side view) of a fault in the Earth’s crust. Label the fault, focus, epicenter, hanging wall, and footwall. 21. Complete the chart below. Picture Fault types Type of stress Similar to what type of Plate Boundary Vocabulary: Match the following terms with the correct definition. _____1. focus A. seismic waves that produce the most severe ground movements _____2. epicenter B. measurement of the effects of an EQ _____3. seismic waves C. structure designed to reduce or withstand EQ damage _____4. P-waves D. smaller EQ the occurs after the main EQ in the same area _____5. S-waves E. device used to measure the ground movements caused by an EQ _____6. surface waves F. any change in the volume or shape of rock _____7. seismograph G. violent shaking caused by moving rock _____8. magnitude H. seismic waves that move up and down and side to side _____9.intensity I. scale that measures the magnitude of ALL EQs _____10. Mercalli Scale J. huge wave caused by underwater EQ _____11. Richter scale K. the spot where rock breaks and causes an earthquake _____12. Moment Magnitude Scale L. when vibrations turn soil into mud _____13. liquefaction M. cracks in the Earth’s crust where rock moves past other rock _____14. aftershock N. scale that measures the magnitude of small and nearby EQs _____15. tsunami O. measurement of the energy released during an EQ _____16. base-isolated building P. seismic waves that compress and expand like an accordian _____17. stress Q. the point on Earth’s surface where seismic waves reach first _____18. deformation R. vibrations that carry energy released during an earthquake _____19. earthquake S. scale that measures intensity _____20. fault T. the forces that can change rock