DNA notes
advertisement
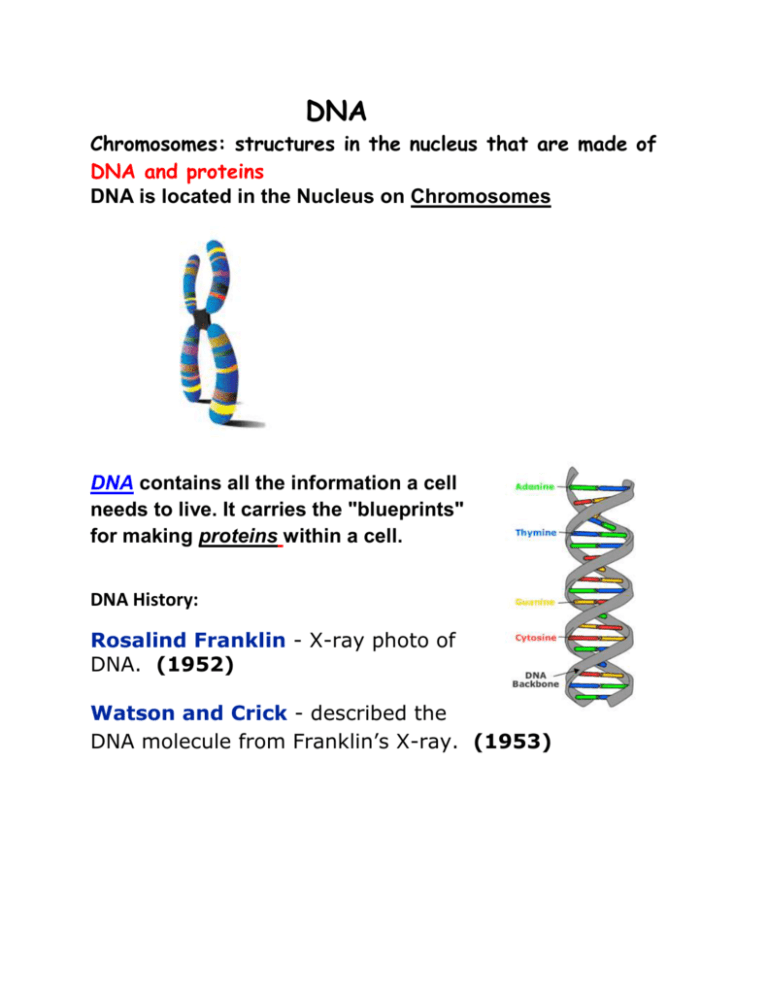
DNA Chromosomes: structures in the nucleus that are made of DNA and proteins DNA is located in the Nucleus on Chromosomes DNA contains all the information a cell needs to live. It carries the "blueprints" for making proteins within a cell. DNA History: Rosalind Franklin - X-ray photo of DNA. (1952) Watson and Crick - described the DNA molecule from Franklin’s X-ray. (1953) DNA: Double Helix made of a repeating unit called: Nucleotide 4 Nitrogenous Bases: Adenine Guanine Cytosine Thymine DNA: 2 long strands of nucleotides are arranged in a specific way called:“Complementary Rule”: (specific pairing between the nitrogen bases) DNA 1. 2. 3. ADENINE – THYMINE CYTOSINE - GUANINE Replication: DNA molecule uncoils and unzips. Each strand of the original DNA serve as a template for the new strands. 2 new IDENTICAL DNA molecules form. RNA: Ribonucleic Acid Single stranded molecule formed by a sequence of nucleotides Sugar molecule: Ribose. RNA Bases: Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, Uracil. (NO THYMINE IN RNA) 3 types of RNA: 1. messenger RNA (mRNA) 2. Transfer RNA (tRNA) 3. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) AIM: What is RNA synthesis? For a gene to make a protein it must first give the instructions to mRNA in a process called: DNA Transcription RNA Synthesis: DNA “unzip” itself and RNA nucleotides match up to the DNA strand. mRNA: copies the message from the DNA in the nucleus and carry the message to the ribosome. tRNA-Transfer: RNA brings the correct Amino Acid to the ribosome from the cytoplasm as it reads the mRNA. The assembly of the amino acids that takes place at the ribosome Protein Synthesis DNA provides the code to make RNA mRNA attaches to the ribosome tRNA read the message of mRNA Amino Acids are added to the growing protein Mutations: changes in the DNA sequence that affects genetic information. Most mutations are harmful, but some can be beneficial to the organism Chromosomal mutation: changes in the number or shape of chromosomes Gene mutation: random changes in the nucleotides. Many mutations are harmful to organisms, often causing their death. Some have no effect and some are beneficial Genetic Engineering: move sections of DNA (genes) from one organism to another so that it produces useful biological products. "Recombinant DNA" Gene Therapy: The potential of replacing a defective gene in a human with a normal functioning gene. Ex: cystic fibrosis.









