ENGR_25_Tutorial_MuPAD_Inflection_Point_Determination
advertisement

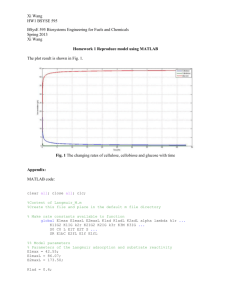
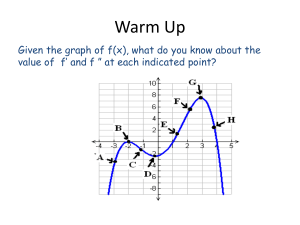
ENGINEERING-25 MuPAD Tutorial Problem The following function has exacly one INFLECTION point in the right-half of the Cartesian Plane: 𝐴 𝑦(𝑡) = 1 + (𝐵 + 7)𝑒 −𝑡⁄𝜏 Where, 𝐴, 𝐵, 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝜏are all POSITIVE Constants. For this situation find an Exact (that is, a SYMBOLIC) solution for the CoOrdinates of the inflection point location The Answer (𝑡𝑖𝑛𝑓𝑙 , 𝑦𝑖𝑛𝑓𝑙 ) → Quotient Rule If f(x) and g(x) are differentiable functions with g(x) ≠ 0, then d f x dx g x g x df dg f x dx dx 2 g x The HAND Solution 𝐴 𝑦(𝑡) = 1 + (𝐵 + 7)𝑒 −𝑡⁄𝜏 d f x dx g x g x df dg f x dx dx 2 g x The MuPAD NoteBook Bruce Mayer, PE ENGR25 • 28Nov13 ENGR25_Inflection_Point_Tutorial_1311.mn A, B, τ, and t are all POSITIVE so use the assume command • Either of the "assume" commands below insures positivevalue behavior assume(A, Type::Positive); assume(B > 0); assume(`τ` > 0); assume(t, Type::Positive) Check that `τ` was properly accepted by MuPAD getprop(`τ`) The function y := A/(1+(B+7)*E^(-t/`τ`)) When In Doubt...PLOT IT! • for the test-plot set A=1, B=2, τ=3 The Test Function z(u) z := 1/(1+(2+7)*E^(-u/3)) plot(z, u =-10..20, GridVisible = TRUE, LineWidth = 0.04*unit::inch, Width = 320*unit::mm, Height = 180*unit::mm, AxesTitleFont = ["sans-serif", 24], TicksLabelFont=["sans-serif", 16]) Looks like the inflection point is at about (6.6,0.5) for A=1, B=2, τ=3 Now The First Derivative dydt := diff(y, t) Also Plot the first Derivative, dy/dt = m. Look for where m is MAX or MIN m := subs(dydt, A=1, B=2, `τ`=3) plot(m, t =-10..20, GridVisible = TRUE, LineWidth = 0.04*unit::inch, Width = 320*unit::mm, Height = 180*unit::mm, AxesTitleFont = ["sans-serif", 24], TicksLabelFont=["sans-serif", 16]) The Second Derivative d2ydt2 := diff(dydt, t) Set the 2nd derivative to ZERO to find the location of the Inflection Point ti := solve(d2ydt2,t) tiS := Simplify(ti) Double Check solution using the simplified version of d2y/dt2 d2ydt2S := Simplify(d2ydt2) tsolS := solve(d2ydt2S,[t]) Checks OK. Now extract solution from SET NOTATION to back-sub into y(x) tiback := solvelib::getElement(tiS) Then the y-value of the inflection point yi := subs(y, t = tiback) Simplify yi yiS := Simplify(yi) Now that is REALLY Simple Finally the inflection Point Location. [tinfl,yinfl] := [tiback, yi] Check the test Case [titest,yitest] := [subs(tiback, B =2, `τ`=3), subs(yiS, A = 1)] float([titest,yitest])
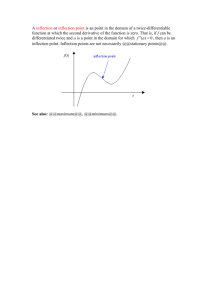

![Inflection points [4.2]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005711558_1-7e6caa30b78ed23b978b40c18112cd02-300x300.png)