Click here for Section 6.1 Study Guide
advertisement

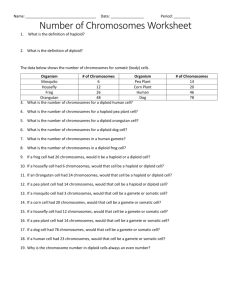
Section 6.1 Study Guide – Chromosomes and Meiosis Vocabulary • Somatic cell • Gamete • Homologous chromosome • Autosome • Sex chromosome • Sexual reproduction • Fertilization • Diploid • Haploid • Meiosis Review Questions 1. What is a somatic cell and where are they found? Somatic cells are also called body cells and make up most of your body tissues and organs. DNA in your body cells is not passed on to offspring from the parents. 2. What is a gamete (also referred to as sex cells) and where are they found? Gametes are sex cells and they are found in testes (in males) and ovaries (females). DNA in your gametes can be passed on to offspring from the parents. 3. What are the differences between a gamete and a somatic cell? Please compare and contrast – including the vocabulary words “haploid” and “diploid” in your answer. A gamete is a haploid sex cell found only in an organism’s reproductive organs (ovaries in females and testes in males). A somatic cell is a diploid cell found in the tissues and organs of an organism’s body. DNA is passed on from parent to offspring through the haploid gametes; the DNA in somatic cells is not passed on. 4. Which cell type makes up the brain? Somatic (body) cells 5. Are homologous chromosomes identical to each other? Explain. Homologous chromosomes are two chromosomes (one from the mother, the other from the father) that have the same length and general appearance. They have copies of the same genes; however, the copies may differ. 6. What is the difference between an autosome and a sex chromosome? Autosomes are chromosomes that contain characteristics not directly related to the sex of an organism. Sex chromosomes directly control the development of sexual characteristics. 7. Why is it important that gametes are haploid cells? Changes to chromosome number are typically very harmful. Therefore, the fact gametes are haploid means that the correct number of chromosomes will be maintained – becoming diploid when the gametes are brought together at fertilization. 8. Is the cell that results from fertilization (also known as a zygote) a haploid or diploid cell? Explain your answer. Diploid. In humans, the combination of 23 chromosomes from the mother and 23 from the father restores the diploid number of chromosomes (46). 9. Using the figures at the end of the study guide, please explain how the process of meiosis differs from mitosis. Meiosis produces genetically unique, haploid sex cells – involved in sexual reproduction. Mitosis produces genetically identical, diploid body cells – involved in asexual reproduction. 10. Does mitosis or meiosis occur more frequently in your body? Explain your answer. Mitosis occurs a lot more frequently since it occurs throughout an individual’s body (with the exception of the sex cells) and lifetime. Meiosis only occurs at certain times and only in the reproductive organs. 11. Explain the difference between the X chromosome and the Y chromosome. Do you think the Y chromosome contains genes that are critical for an organism’s survival? Explain your reasoning. The Y chromosome does not contain genes that are critical for an organism’s survival. This is evident by the fact females do not have a Y chromosome and they are absolutely fine. 12. (Challenge question) The ends of DNA molecules form telomeres that help keep the ends of chromosomes from sticking to each other. Why might this be especially important in germ cells, which go through meiosis and make haploid gametes? If the ends of two chromosomes stick together, the chromosomes will not separate correctly during meiosis. One of the resulting gametes will have an extra chromosome, and the other will be missing a chromosome.