ECOLOGY REVIEW (PART II): What is an ecosystem? Define
advertisement

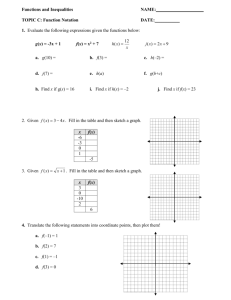
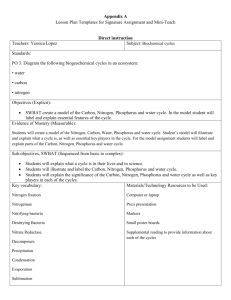
NAME _________________________ PER _______ ECOLOGY REVIEW (PART II): 1. What is an ecosystem? 2. Define biochemical process. 3. a) Name the three processes in which water cycles in the environment. b) Circle the process(es) in which water enters the atmosphere. 4. a) Name the three processes in which carbon cycles through the environment. b) Circle the process(es) in which energy is released. 5. a) Name the five processes in which nitrogen cycles through the environment. b) In which process does atmospheric nitrogen gas become usable form? c) What process takes ammonia to make “fertilizers” that plants can use? d) What do decomposers do? e) In what process does nitrogen gas return to the atmosphere? 6. Define population. 7. What are the three properties of a population? 8. List the three types of dispersion. Provide an example of each type of dispersion. a) b) c) NAME _________________________ PER _______ ECOLOGY REVIEW (PART II): 1. What is an ecosystem? 2. Define biochemical process. 3. a) Name the three processes in which water cycles in the environment. b) Circle the process(es) in which water enters the atmosphere. 4. a) Name the three processes in which carbon cycles through the environment. b) Circle the process(es) in which energy is released. 5. a) Name the five processes in which nitrogen cycles through the environment. b) In which process does atmospheric nitrogen gas become usable form? c) What process takes ammonia to make “fertilizers” that plants can use? d) What do decomposers do? e) In what process does nitrogen gas return to the atmosphere? 6. Define population. 7. What are the three properties of a population? 8. List the three types of dispersion. Provide an example of each type of dispersion. a) b) c) 9. Sketch all three types of survivorship curves in one graph. Be sure to label what each is. Star the type that would represent a population that produces a lot of offspring, but most die early on. 10. How is a density-independent factor different from a density dependent factor? 11. What is a limiting factor? 12. A. Sketch i) an exponential model and ii) identify that limits this type of growth. B. Sketch i) a logisitic model, ii) label the carrying capacity and iii) identify what limits this type of growth. 13. a) What does it mean when a population reaches carrying capacity? b) What does it mean when a population has zero population growth? 14. In a population of 200 guppies, 25 are born in one month and 75 die. a) Calculate the growth rate. b) Is the population growing or declining? c) Determine what the population will be the next month. 15. As of right now, what type of growth model represents the human population? 16. In the beginning, what factor led to human population growth? 17. In the past few hundred years, what factors have led to the jump in human population growth? 9. Sketch all three types of survivorship curves in one graph. Be sure to label what each is. Star the type that would represent a population that produces a lot of offspring, but most die early on. 10. How is a density-independent factor different from a density dependent factor? 11. What is a limiting factor? 12. A. Sketch i) an exponential model and ii) identify that limits this type of growth. B. Sketch i) a logisitic model, ii) label the carrying capacity and iii) identify what limits this type of growth. 13. a) What does it mean when a population reaches carrying capacity? b) What does it mean when a population has zero population growth? 14. In a population of 200 guppies, 25 are born in one month and 75 die. a) Calculate the growth rate. b) Is the population growing or declining? c) Determine what the population will be the next month. 15. As of right now, what type of growth model represents the human population? 16. In the beginning, what factor led to human population growth? 17. In the past few hundred years, what factors have led to the jump in human population growth?