8-2.P.2- Energy Conservation and Transfer - NHCS
advertisement
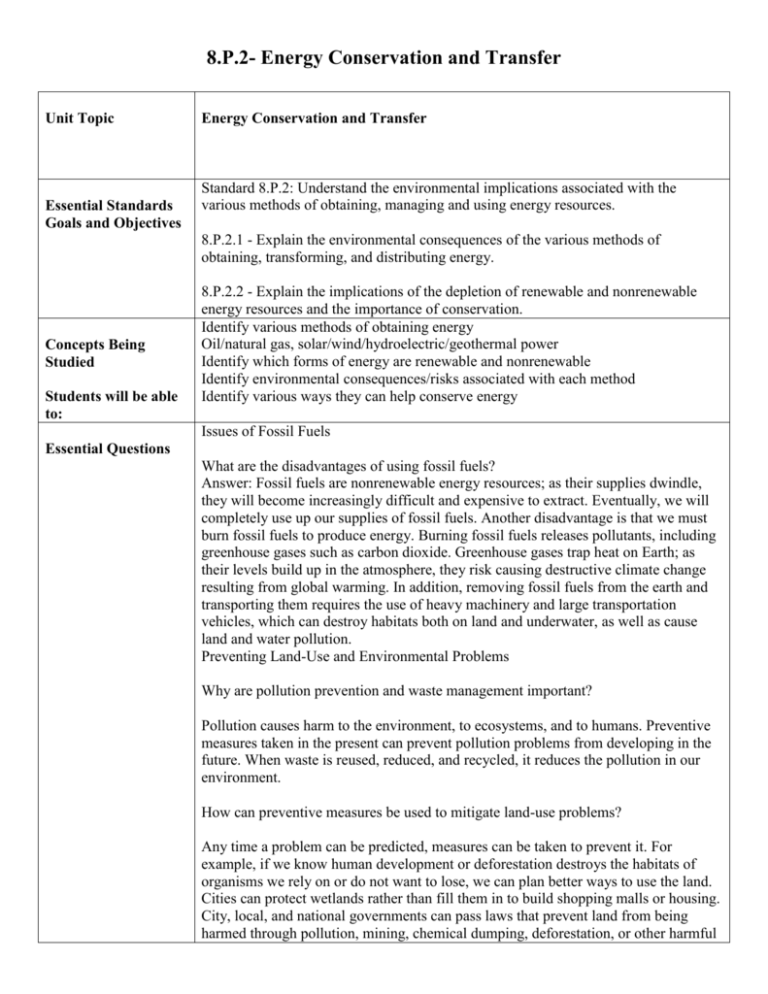
8.P.2- Energy Conservation and Transfer Unit Topic Essential Standards Goals and Objectives Energy Conservation and Transfer Standard 8.P.2: Understand the environmental implications associated with the various methods of obtaining, managing and using energy resources. 8.P.2.1 - Explain the environmental consequences of the various methods of obtaining, transforming, and distributing energy. Concepts Being Studied Students will be able to: 8.P.2.2 - Explain the implications of the depletion of renewable and nonrenewable energy resources and the importance of conservation. Identify various methods of obtaining energy Oil/natural gas, solar/wind/hydroelectric/geothermal power Identify which forms of energy are renewable and nonrenewable Identify environmental consequences/risks associated with each method Identify various ways they can help conserve energy Issues of Fossil Fuels Essential Questions What are the disadvantages of using fossil fuels? Answer: Fossil fuels are nonrenewable energy resources; as their supplies dwindle, they will become increasingly difficult and expensive to extract. Eventually, we will completely use up our supplies of fossil fuels. Another disadvantage is that we must burn fossil fuels to produce energy. Burning fossil fuels releases pollutants, including greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide. Greenhouse gases trap heat on Earth; as their levels build up in the atmosphere, they risk causing destructive climate change resulting from global warming. In addition, removing fossil fuels from the earth and transporting them requires the use of heavy machinery and large transportation vehicles, which can destroy habitats both on land and underwater, as well as cause land and water pollution. Preventing Land-Use and Environmental Problems Why are pollution prevention and waste management important? Pollution causes harm to the environment, to ecosystems, and to humans. Preventive measures taken in the present can prevent pollution problems from developing in the future. When waste is reused, reduced, and recycled, it reduces the pollution in our environment. How can preventive measures be used to mitigate land-use problems? Any time a problem can be predicted, measures can be taken to prevent it. For example, if we know human development or deforestation destroys the habitats of organisms we rely on or do not want to lose, we can plan better ways to use the land. Cities can protect wetlands rather than fill them in to build shopping malls or housing. City, local, and national governments can pass laws that prevent land from being harmed through pollution, mining, chemical dumping, deforestation, or other harmful procedures. How are remote sensing and ground truthing methods useful? Remote sensing methods, such as satellite analysis of Earth’s surface, help scientists understand land use on a global scale. Satellites allow scientists to capture images of the same places over long periods of time, enabling them to observe how the land is changing. This helps them see potential problems and try to prevent them. Ground truthing is a way of verifying what remote sensing methods tell us. Resource Management What are some resource-use choices that can be made at home, and how do the costs and benefits of these choices compare? We make choices every day about resource use. For example, in class our teacher illustrated the choice of using a paper cup. She threw it away when she was done. She could have chosen to use a reusable cup, and she wouldn’t have needed to throw it away. Or she could have utilized a water fountain instead, and not used a cup at all. This way there would be fewer non-biodegradable plastic cups that would eventually make their way to a landfill. There are costs and benefits that come with every choice, such as financial cost, how easy it is to get the item, whether or not we really need it, what it’s made from, and so on. We need to weigh these costs and benefits with all of our choices. What are the costs and benefits of using nonrenewable resources? The costs of using nonrenewable resources include: we might someday run out of them, they often create more pollution, and they can cause human health problems. Some byproducts of nonrenewable resources, like nuclear waste and air pollution, can be hazardous and difficult to manage in the waste stream. Some benefits include: These resources power many of our modern conveniences and make many of the products we use everyday. We have technologies in place to obtain these resources, and many of them are relatively affordable. What are the costs and benefits of using renewable resources? Some of the costs of using renewable resources include: We can degrade or pollute resources by using them, even if they are renewable (like soil or coastal resources). We can limit the supply, and make a renewable resource hard to get and more expensive. Sometimes obtaining, preparing, and cleansing renewable resources after use has a high hidden cost in nonrenewable resources. Some renewable resources, like solar power, are still more expensive than using nonrenewable resources for the same purpose. Benefits include the fact that these resources, like wood products, can regrow and will likely be here forever if we implement plans to protect and preserve them. Many of these resources, like water, are cheap and readily available in some parts of the world. Essential Information 8.P.2.1 Different ways of obtaining, transforming, and distributing energy have different environmental consequences. Different types of fuels have different environmental impacts. Some have longer lasting impacts on the environment than others. Transformations and transfers of energy within a system usually result in some energy escaping into its surrounding environment. Some systems transfer less energy to their environment than others during these transformations and transfers. Whenever energy appears in one place, it must have moved from another. Whenever energy appears to be ‘lost’ from somewhere, it has been transferred somewhere else. Some ways we are attempting to use the energy from the sun are: photovoltaic cells, solar batteries and reflectors. Photovoltaic cells transform solar energy into electric energy. Solar reflectors are used to concentrate solar rays for industrial use and for the generation of electric current. One way to confine the solar energy is heating water by passing it through collectors and keeping it in isolated containers. In some cases it is possible to obtain enough hot water to satisfy a house needs during the day but conventional heaters are required at night. Energy from the sun far exceeds the Earth’s energy need, however, we have not found a way to efficiently capture and store it. 8.P.2.2 Some resources are not renewable or renew very slowly. Fuels already accumulated in the earth, for instance, will become more difficult to obtain as the most readily available resources run out. How long the resources will last, however, is difficult to predict. The preservation, management, and care of natural and cultural resources should be practice by all consumers. The ultimate limit may be the prohibitive cost of obtaining them. Energy from the sun (and the wind and water energy derived from it) is available indefinitely. The transfer of energy from these resources are weak and variable, systems are needed to collect, transport and concentrate the energy. This creates some advantages and disadvantages depending on location and the ability to collect. Essay Questions Project Ideas Technology Compare the forms of renewable resources. Which one do you believe is the most reliable? Why? If you lived in an area where fracking was occurring, how would you feel? Why? Create an ad for a type of renewable energy. Monitor the meter at your house to measure kilowatt usage. Complete an energy audit of your home. Research efficient (LEED) home designs - Create a floor plan/ model incorporating research US Department of Energy – Website http://energy.gov Energy Footprint www.earthday.net/footprint/index.asp www.energy4me.org Labs, Experiments, Activities, etc. Resources How to read an electric meter Home/School Audit Calculate Energy Savings – Energy Star Appliances Calculate Footprint Internet… great sites Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy http://www.eere.energy.gov/ Ways to save http://www.energysavers.gov/ Vehicles and Fuels http://www.energysavers.gov/your_vehicle/ Energy Basics: Different Technologies (solar/wind/hydro/etc) http://www.eere.energy.gov/basics/ Wind Power Animation http://www.eere.energy.gov/basics/renewable_energy/wind_animation.html Glossary of Terms http://www.eere.energy.gov/basics/glossary.html Building Strategies http://www.eere.energy.gov/basics/buildings/ Assessment Q/A Bell Work Quizzes Projects/Labs Test









