Movement of subsances in and out of cells Questions and Answers
advertisement
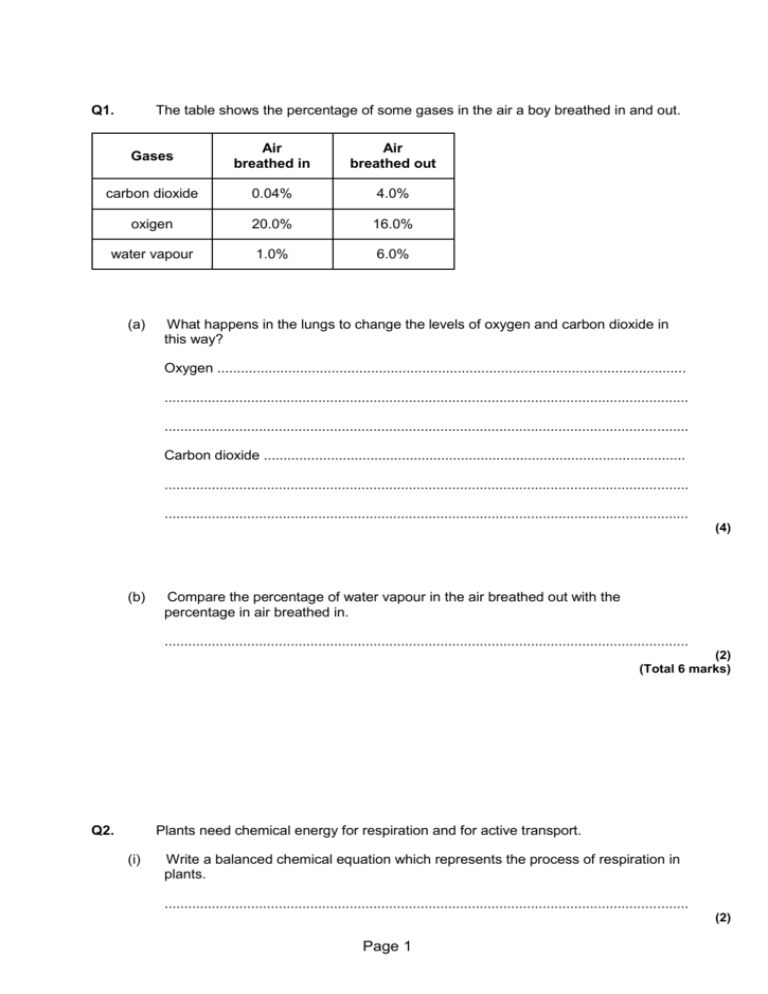
Q1. The table shows the percentage of some gases in the air a boy breathed in and out. Gases Air breathed in Air breathed out carbon dioxide 0.04% 4.0% oxigen 20.0% 16.0% water vapour 1.0% 6.0% (a) What happens in the lungs to change the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in this way? Oxygen ....................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Carbon dioxide ........................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) (b) Compare the percentage of water vapour in the air breathed out with the percentage in air breathed in. ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) Q2. Plants need chemical energy for respiration and for active transport. (i) Write a balanced chemical equation which represents the process of respiration in plants. ..................................................................................................................................... (2) Page 1 (ii) Describe the process of active transport in the root hair cells of plants. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 5 marks) Q3. Plant roots obtain some of their mineral salts from the soil by active transport. What is involved in active transport? ............................................................................................................................................... . ............................................................................................................................................... . ............................................................................................................................................... . ............................................................................................................................................... . ............................................................................................................................................... . ............................................................................................................................................... . Page 2 ............................................................................................................................................... . ............................................................................................................................................... . (Total 4 marks) Q4. (a) The diagrams show what happens to the shape of a plant cell placed in distilled water. (i) Explain why the cell swells and becomes turgid. Name the process involved. .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... (2) (ii) Give one feature of the cell wall which allows the cell to become turgid. .......................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Describe the change which will occur if a piece of peeled potato is placed in a concentrated sugar solution and explain why this change occurs. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Page 3 ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 6 marks) Q5. (a) The diagram shows a cereal crop. Complete spaces (i) and (ii). (2) (iii) What sort of weather may cause the cereal crop to wilt? ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Describe the process of transpiration in plants. Page 4 .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 6 marks) Q6. The diagram shows the human breathing system. (a) Complete the labels (i) and (ii). (2) (b) Complete the following sentence. When we breathe out, the mixture of gases which leaves the air sacs contains more .............................. and less ......................................... than the mixture of gases which enters the air sacs. (2) (Total 4 marks) Page 5 Q7. (a) The graph shows how the mass of oxygen you breathe in changes as you climb up a mountain. Describe, in as much detail as you can, how the mass of oxygen in one breath changes as you climb from sea level to 3000 m. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Page 6 ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (b) People who live high up in mountainous areas have more red blood cells than people who live at sea level. The graph below shows how the number of red blood cells changes with height above sea level. (i) How many more red blood cells does a person living at 3000 m above sea level have than someone living at sea level? Show clearly how you work out your answer. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... Increase in number of red blood cells = ....................................millions per m3 (2) (ii) What is the advantage of having more red blood cells? ........................................................................................................................... Page 7 ........................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 6 marks) Q8. The table shows the composition of blood entering and leaving the lungs. Gas Concentration in arbitrary units Blood entering lungs Blood leaving lungs Oxygen 40 100 Carbon dioxide 46 40 (a) Describe, in as much detail as you can, the changes that take place in the composition of blood as it passes through the lungs. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (3) (b) Which part of the blood: (i) transports most carbon dioxide; ..................................................................... (ii) transports most oxygen? ................................................................................ (2) (Total 5 marks) Page 8 Q9. A potted plant was left in a hot, brightly lit room for ten hours. The plant was not watered during this period. The drawings show how the mean width of stomata changed over the ten hour period. (a) Why do plants need stomata? ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Name the cells labelled X on the drawing. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) The width of the stomata changed over the ten hour period. Explain the advantage to the plant of this change. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 4 marks) Page 9 Q10. (a) The diagram shows four ways in which molecules may move into and out of a cell. The dots show the concentration of molecules. The cell is respiring aerobically. Which arrow, A, B, C or D, represents: (i) movement of oxygen molecules; .................... (ii) movement of carbon dioxide molecules? .................... (2) (b) Name the process by which these gases move into and out of the cell. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Which arrow, A, B, C or D, represents the active uptake of sugar molecules by the cell? ..................................................................................................................................... Explain the reason for your answer. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 5 marks) Page 10 Q11. The diagram shows part of the breathing system in a human. (a) Use words from the list to label the parts on the drawing. alveoli bronchiole bronchus diaphragm trachea (windpipe) (4) (b) Where in the lungs does oxygen enter the blood? ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Which process in cells produces carbon dioxide? ..................................................................................................................................... (1) Page 11 (Total 6 marks) Q12.A cook prepares a fresh fruit salad by cutting up a variety of fruits and placing them in a bowl with layers of sugar in between. After two hours the fruit is surrounded by syrup (concentrated sugar solution). Explain, as fully as you can, why syrup (concentrated sugar solution) was produced after two hours. .............................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................. (Total 4 marks) Q13. (a) The drawing shows some of the organs in the human thorax. Page 12 On the drawing, use guidelines to label: (i) the heart; (ii) a rib; (iii) the diaphragm; (iv) the trachea. (4) (b) The drawing shows a section through an alveolus. At A, oxygen moves from the air in the alveolus into the blood capillary. Explain, as fully as you can, how oxygen moves into the blood. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Page 13 ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) Q14. Some students set up an experiment using osmosis to find the concentration of sucrose solution in potato cell sap. They used discs of potato cut to the same size and weighing approximately 10 gms. The discs were put into each of five beakers. (a) (i) After two hours they reweighed the discs after carefully blotting them first. Why did the students blot the potato before weighing it? ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Their results are shown in the table below. Beaker 1 Beaker 2 Beaker 3 Beaker 4 Beaker 5 Final mass in g 13.0 12.2 9.0 7.9 7.3 Initial mass in g 10.0 10.6 10.0 10.1 10.4 The students calculated the % gain or loss in mass of potato. Complete this table of results for Beakers 2, 4 and 5. Page 14 Beaker 1 Beaker 2 13 – 10.0 = 3.0 Beaker 3 Beaker 4 Beaker 5 9.0 – 10.0 = –1.0 = –10% Gain in mass = 30% Loss in mass = 10% (3) (b) (i) Draw a graph of % Gain or Loss in mass against sucrose concentration. (3) Page 15 (ii) Use the graph to find the concentration of potato cell sap. Concentration of cell sap = ........................................... % sucrose solution (1) (iii) Explain in terms of osmosis how you chose this value. ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 10 marks) Q15. The diagram shows an enlargement of structure D. The arrows show the direction of the gases exchanged in this structure. Name gas X and gas Y. X ........................................................................................................................................... Y ........................................................................................................................................... (Total 2 marks) Page 16 Q16. Some students set up the following apparatus. The balances show the same mass at the start of the investigation. After 24 hours the mass of flask B was the same but the mass of flask A had changed. (i) Describe and explain the change to the mass of flask A. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (ii) Why did the students need to set up flask B? ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 4 marks) Page 17 Q17. Some students set up this experiment to investigate osmosis. They filled two pieces of dialysis [visking] tubing with different liquids and left them both in a beaker of 5% sucrose solution for an hour. (a) Describe and explain the likely results after one hour. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (6) (b) Describe two examples where osmosis is used in living things. Page 18 ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 8 marks) Q18. Some students set up the equipment below to investigate osmosis. (a) What is osmosis? .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (3) (b) (i) What will happen to the water level in the capillary tube during the investigation because of osmosis? Page 19 ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Use your knowledge of osmosis to explain why this happens. ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) Q19. The diagram shows a part of a lung that is involved in gaseous exchange in a human. (i) Draw and label, on the diagram, one arrow to show the direction of movement of oxygen between the alveolus and capillary. (1) (ii) Draw and label, on the diagram, one arrow to show the direction of movement of carbon dioxide, between the alveolus and capillary. (1) Page 20 (iii) Give the function of the red blood cell in this process. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 3 marks) Q20. The table gives information about a geranium plant and a cactus plant. The geranium grows in gardens in the UK. The cactus grows in hot deserts. Feature Geranium Cactus 5 15 1800 150 Percentage of water storage tissue in stem 50 85 Number of stomata per mm2 59 13 daylight at night 0.2 5 Thickness of waxy cuticle in micrometres Total leaf surface area in cm2 Time of day when stomata open Horizontal spread of roots in metres Using only information in the table, explain how the cactus is better adapted for living in hot, dry conditions. To gain full marks in this question you should write your ideas in good English. Put them into a sensible order and use the correct scientific words. ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... Page 21 ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... (Total 5 marks) Q21.Complete the table by writing the correct process next to its description. Choose your answers from the list in the box breathing diffusion digestion osmosis Description respiration Process Moving air in and out of the lungs The movement of particles of a substancefrom high to low concentration The release of energy from glucose (Total 3 marks) Q22. Four leaves were removed from the same plant. Petroleum jelly (a waterproofing agent) was spread onto some of the leaves, as follows: Page 22 Leaf A: on both surfaces Leaf B: on the lower surface only Leaf C: on the upper surface only Leaf D: none applied Each leaf was then placed in a separate beaker, as shown in diagram 1. Diagram 1 Each beaker was weighed at intervals. The results are shown in the graph. (a) Give evidence from the graph in answering the following questions. (i) Which surface (upper or lower) loses water most rapidly? ............................. Page 23 Evidence ........................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Is water lost from both surfaces of the leaf? .................................................... Evidence ........................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Diagram 2 shows the appearance of each surface of the leaf as seen through a microscope. Upper Surface of Leaf Lower Surface of Leaf Diagram 2 (i) Name space X and cell Y. X ................................................................... Y ................................................................... (2) (ii) Use information in diagram 2 to explain why the results are different for leaves B and C. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... Page 24 ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) Q23. The diagram shows an alveolus and a blood capillary in the lung. (i) During gaseous exchange, oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged across the wall of the alveolus. On the diagram, carefully draw two arrows to show the paths taken by oxygen and by carbon dioxide during this process. Label each arrow. (3) (ii) Name the process by which oxygen moves across the wall of the alveolus. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) Page 25 (iii) Each lung contains about 350 million alveoli. How does this help gaseous exchange? ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 5 marks) Q24. Emphysema is a disease of the lungs. People who smoke cigarettes are more likely to suffer from emphysema. The diagrams show lung tissue from a healthy person and lung tissue from a person with emphysema. The diagrams are drawn to the same scale. Lung tissue from a healthy person emphysema Lung tissue from a person with Explain how emphysema reduces the amount of oxygen which diffuses into the blood ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... (Total 2 marks) Page 26 Q25. The table shows the concentrations of some mineral ions in the cells of a pond plant and in the surrounding pond water. Concentration in mmol per dm3 Potassium Calcium Sulphate Plant cells 49.0 7.0 7.0 Pond water 0.5 0.7 0.4 (i) The plant cells would not have been able to absorb these mineral ions from the pond water by diffusion. Explain why not. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (ii) Suggest a process which would allow these ions to be absorbed from the pond water by the plant cells. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 3 marks) ## A runner might drink a special ‘sports drink’ at intervals during a marathon race. The table shows the substances present in a sports drink. Substance Percentage Water Sugar 5.0 Ions 0.2 Page 27 (a) Complete the table to show the percentage of water in the sports drink. (1) (b) The runner sweats and also breathes heavily during the race. (i) Why does the runner need to sweat? ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Which two substances in the table are lost from the body in sweat? ........................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) Which substance in the table is lost from the body during breathing? ........................................................................................................................... (1) (c) How does the sugar in the sports drink help the athlete during the marathon? ............................................................................................................................. ........ ............................................................................................................................. ........ (2) (Total 6 marks) Q27. The diagram shows the human breathing system. Page 28 (a) Place on the diagram: (i) a letter X where oxygen enters the blood; (1) (ii) an arrow showing the direction the diaphragm moves when we breathe in. (1) (b) List the following structures in the order the air passes through them when we breathe in. alveoli bronchi bronchioles trachea 1 .................................................................................. 2 .................................................................................. 3 .................................................................................. 4 .................................................................................. (1) (c) By what process does oxygen enter the blood? Draw a ring around your answer. diffusion digestion osmosis respiration (1) (Total 4 marks) Page 29 Q28. Long distance runners are advised to take several drinks during a race. The table gives the composition of two drinks, Isotonic and Cola. Drink Sugar concentration in grams per litre Sodium ion concentration in mmol per litre Chloride ion concentration in mmol per litre Isotonic 73 24 12 Cola 105 3 1 Explain why Isotonic would be the best drink for a long distance runner on a hot day. .............................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................. (Total 2 marks) Q29. A group of students looked at stomata on four different species of plants, A, B, C and D. They estimated the number of stomata per cm2 on the upper and lower surfaces of the leaves of the four species. Their results are shown in the table. Plant species Estimated number of stomata per cm2 of leaf surface Upper surface of leaf Lower surface of leaf A 4000 28 000 B 0 800 Page 30 C 8500 15 000 D 8000 26 000 (a) Which plant species probably lives in a dry region? Explain the reason for your answer. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (3) (b) All four species have more stomata on the lower surface of their leaves than on the upper surface. Suggest how this could help the plants to survive better. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 5 marks) Q30. A group of students looked at stomata on four different species of plants, A, B, C and D. They estimated the number of stomata per cm2 on the upper and lower surfaces of the leaves of the four species. Their results are shown in the table. Page 31 Plant species Estimated number of stomata per cm2 of leaf surface Upper surface of leaf Lower surface of leaf A 4000 28 000 B 0 800 C 8500 15 000 D 8000 26 000 (a) Which plant species probably lives in a dry region? Explain the reason for your answer. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (3) (b) All four species have more stomata on the lower surface of their leaves than on the upper surface. Suggest how this could help the plants to survive better. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 5 marks) Page 32 Page 33 ## (a) oxygen passes from the air/lungs into the body gains 1 mark but oxygen passes from the air/lungs into the blood gains 2 marks carbon dioxide passes from the body into the air/lungs gains 1 mark but carbon dioxide passes from the blood into the air/lungs gains 2 marks 4 (b) increased/5% more gains 1 mark but 6 times more (in air breathed out) gains 2 marks 2 [6] M2. (i) C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O energy is neutral 1 formulae all correct with no omissions / deletions correctly balanced credit 1 mark if the answer is the exact reverse of an incorrect answer for (a) 1 (ii) and three from Page 34 take up of (soluble) substances / ions against the concentration gradient or when the concentration (of the substance / ions) is greater inside the cell / cytoplasm than outside it through the (semi-permeable) (cell) membrane energy from mitochondria or energy from respiration not just energy 3 [5] M3. any four from molecules / ions do not credit mineral salts move(d) through / across the cell wall / membrane against (a / the) concentration gradient by a series of chemical reactions (because) diffusion cannot occur energy (required) (supplied by) respiration oxygen required for respiration (to occur) [4] M4. (a) (i) water (molecules) enter(s) (the cell) Page 35 or water (molecules) pass(es) through the (semi-permeable) cell membrane 1 by osmosis or because the concentration of water is greater outside (the cell than inside it the vacuole) accept because of the concentration gradient provided there is no contradiction 1 (ii) any one from (it is) elastic (it is) strong (it is fully) permeable (to water) or water can pass through it do not credit semi-permeable do not credit cell membrane is semi-permeable 1 (b) (the piece of) potato shrinks or loses its turgor or becomes flabby or becomes flaccid or plasmolysis occur or cytoplasm pulls away from the cell wall (because) concentration of sugar or because concentration of water 1 (solution) is greater than concentration inside the cell / vacuole inside the cell / vacuole is greater than concentration (of water) outside 1 water is drawn out of the cell 1 [6] Page 36 M5. (a) (i) photosynthesis 1 (ii) respiration do not credit combustion do not credit decay 1 (iii) dry accept hot or windy or drought 1 (b) any three from * evaporation (of water) or loss of water vapour * (mostly) from the leaf / leaves do not credit incorrect reference to leaves * through the stomata accept through each stoma accept through the stomas(sic) * causing a pull or causing an increase in osmotic potential (at the top of the plant) or causing an increase in water potential (at the top of the plant) or causing a decrease in osmotic pressure (at the top of the plant) * (so that) water moves up (through the plant) do not credit water vapour moves up through the plant * as the transpiration stream * water enters through roots (and goes up plants) 3 [6] Page 37 M6. (a) (i) trachea accept windpipe 1 (ii) (left) lung or lungs do not credit right lung 1 (b) carbon dioxide or water vapour do not credit just ‘water’ 1 oxygen answers in terms of used air or fresh air or of temperature differences are not acceptable 1 [4] M7. (a) falls 1 from 0.25 1 to 0.19 but by 0.06 gains two marks if neither figure given, accept steadily / at constant rate for one mark accept mass of oxygen inversely related / negative correlation to height above sea level for 2 marks 1 (b) (i) 1.8 accept correct readings from graph for (5 and 6.8) if subtraction incorrect for one mark allow one mark for correct subtraction from incorrect readings 2 (ii) (blood can carry) more oxygen Page 38 1 [6] M8. (a) any three from (concentration of) oxygen increases by 60 (units) allow oxygen more than doubles for 2 marks (concentration of) carbon dioxide decreases from 46 to 40 by 6 units allow ‘by a small amount’ N.B. usually the first 2 marks will be for the change in oxygen and carbon dioxide. The third mark will be for a quantitative comment on one of these changes 3 (b) plasma 1 red (blood) cell / haemoglobin / oxyhaemoglobin 1 [5] M9. (a) allow carbon dioxide to enter / gaseous exchange (oxygen neutral) (transpiration neutral) for one mark 1 (b) guard (cells) for one mark Page 39 1 (c) stops / reduces the rate of water loss / transpiration (reject if dark initiated) stops / reduces wilting / description e.g. drooping / maintains turgor for 1 mark each 2 [4] M10. (a) (i) (ii) B A for 1 mark each 2 (b) diffusion (reject osmosis) for one mark 1 (c) C because uptake against a concentration / diffusion gradient (reject osmosis) (if C not given, then idea of movement essential) for 1 mark each 2 [5] M11. (a) trachea / windpipe bronchus alveoli diaphragm for 1 mark each Page 40 4 (b) alveoli / air sacs (reject capillaries) for one mark 1 (c) respiration for one mark 1 [6] M12. ideas that sugar has dissolved in moisture (on surface of fruit) this solution more concentrated than solution inside fruit osmosis / diffusion movement of water out of fruit through partially permeable membrane (of fruit cells) any four for 1 mark each allow explanations in terms of concentrations of water molecules for full marks [4] M13. (a) correctly labelled structures (i – iv) each for 1 mark (allow labels as words or numbers: allow without guidelines if unambiguously labelled) 4 (b) ideas of diffusion greater concentration of oxygen in alveolus / high to low oxygen concentration membrane / alveolus permeability Page 41 any two for 1 mark each 2 [6] M14. (a) (i) change in weight was due to changes in potato or osmosis or not due to outside liquid ignore ‘to make fair test’ 1 (ii) beaker 2 = 15.1(%) gain allow 15% 1 beaker 4 = 21.8(5) loss not 21.7 allow –22% if no minus or no ‘loss’ check graph 1 beaker 5 = 29.8(%) loss allow –30% 1 (b) (i) both axes correct values and scales > ½ of each axis ignore lack of minus signs on vertical axis 1 points correct < ½ square allow answers in (a)(ii) 1 line correct allow curve of best fit which can miss 10, 15 or straight lines between points do not allow one straight line or sketched line bar graph zero marks 1 Page 42 (ii) point where line crosses axis (eg 15-16% sucrose) allow point from candidate’s graph ( 0.5%) 1 (iii) any two from: looking for understanding that water in equilibrium no change in mass not net movement of water or water entry and exit are equal because sucrose solution same concentration as cell sap or sucrose has same water potential as cell contents allow because the concentrations are the same (inside and out) 2 [10] M15. X – oxygen accept O2 Y – carbon dioxide accept CO2 [2] M16. (i) the mass got less accept it got lighter award 1 mark for water was lost from the plant 1 water was taken into the plant or roots absorbed water do not accept soaked into plant 1 Page 43 and lost through transpiration or the leaves or evaporated from the leaves or stomata 1 (ii) to check the effect of the plant or to act as a control or to show that it was not due to evaporation from water do not accept to keep it fair or to check that it was fair do not accept fair test 1 [4] M17. (a) award 3 marks per tube for each key idea for tube 1: expands or gets firmer or bigger or inflates it gains water because the concentration of water is less than its surroundings make sure answer is about water movement and not sucrose solution 3 for tube 2 gets floppy or flaccid or contracts it loses water because the concentration of water is greater than its surroundings 3 (b) any 2 from: uptake of water by root (hair) or movement from cell to cell within plant do not credit references to diffusion unless it is clear that the candidate is referring to the diffusion of water Page 44 guard cell function maintain turgor water absorption in the large intestine reabsorption of water from the nephron or collecting duct or in kidney or osmoregulation in kidney allow osmosis in other animals if some use is shown 2 [8] M18. (a) movement of water [1] from high concentration (of water) to low concentration (of water) or from (an area of) dilute solution to an area of concentrated solution [1] through a differentially or partially or selectively or semi permeable membrane [1] 3 (b) (i) it will rise 1 (ii) water enters visking tubing [1] because the concentration of water outside is greater than the concentration inside or because the concentration of salt or solute is greater inside the tubing than outside [1] or to equalise concentration water has to enter visking tubing [2] 2 [6] Page 45 M19. (i) oxygen into the blood stream arrow must start inside alveolus and finish outside the capillary 1 (ii) carbon dioxide out of the blood stream arrow must start inside the capillary and finish inside the alveolus 1 (iii) carries/takes up/releases oxygen or carbon dioxide accept forms oxyhaemoglobin 1 [3] M20. Quality of written communication for ideas given in a sensible order; comparison made for geranium and cactus for each feature(ie not just list for geranium followed by list for cactus) + linking of feature & explanation 1 any four features + explanations from: cactus has: accept converse points for geranium plant Feature Explanation thicker cuticle waterproof / keeps water in smaller surface area less water loss / less heat absorbed Page 46 fewer stomata less water loss stomata open at night / closed in day (closed when warmest) – so less water loss more widespread roots quickly absorbs water (after rain) / access to bigger area for absorbing water / absorb more water more water storage tissue little water available in environment / can survive drought / avoids dehydration 4 [5] M21. in correct sequence: breathing 1 diffusion 1 respiration 1 [3] M22. (a) (i) lower – B loses less (water / mass) than C or described in terms of petroleum jelly accept converse re Leaf C 1 Page 47 (ii) yes - B and C lose less than D or B and C lose more than A or D loses the most or A loses the least do not accept just ‘all leaves lose some weight’ 1 (b) (i) X = stoma accept stomata / stomatal pore do not accept air space 1 Y = guard cell 1 (ii) petroleum jelly blocks stomata / pores or petroleum jelly prevents water loss or petroleum jelly waterproofs allow pores are blocked in B 1 water (mainly) lost via stomata / pores / X or stomata on lower surface only 1 [6] M23. (i) On diagram: oxygen arrow to blood from air and CO2 arrow to air from blood 1 oxygen arrow to red blood cell 1 CO2 arrow from plasma 1 (ii) diffusion 1 (iii) large surface or large area do not accept space 1 [5] Page 48 M24. thicker surface 1 reduced surface area accept fewer alveoli 1 [2] M25. (i) in diffusion: material moves high to low concentration 1 here: concentration in cells > concentration in water or uptake is against the concentration gradient or by diffusion ions would move out 1 (ii) active transport / active uptake 1 [3] M26. (a) 94.8 1 (b) (i) to cool (the body) / maintain (body) temperature do not accept let out heat 1 (ii) water and ions 1 Page 49 (iii) water ignore CO2, and vapour 1 (c) any two from: used in respiration provides energy (energy) needed for movement / running / muscle action 2 [6] M27. (a) correctly labelled on diagram (i) ‘X’ on an alveolus centre of X on the alveolus wall or inside the alveolus not if the centre is outside 1 (ii) arrow pointing downwards accept anywhere but must point down 1 (b) in sequence 1 trachea 2 bronchi 3 bronchioles 4 alveoli 1 (c) diffusion accept positive indicator 1 [4] Page 50 M28. any two from: • more or most ions / sodium / chloride or replaces ions / sodium / chloride do not accept more ions / sodium / chloride for energy • lost in sweat • to keep blood concentration constant • less sugar therefore less chance of ‘sugar rush’ [2] M29. (a) B 1 (B has) low(est) number of stomata or no stomata on upper surface or only 800 (on lower surface) 1 less transpiration / evaporation / water loss owtte or water (vapour) is lost via stomata only allow zero water loss if linked to no stomata on upper surface / linked to leaf B upper surface ignore references to leaf surface area 1 (b) reduce loss / amount of water (vapour) accept converse or reduced transpiration (from upper surface) do not allow no water is lost 1 warmer above leaf accept converse or wilted leaf folds over lower surface Page 51 or lower leaf in shade ignore reference to dust or less light / heat / sun on lower side 1 [5] M30. (a) B 1 (B has) low(est) number of stomata or no stomata on upper surface or only 800 (on lower surface) 1 less transpiration / evaporation / water loss owtte or water (vapour) is lost via stomata only allow zero water loss if linked to no stomata on upper surface / linked to leaf B upper surface ignore references to leaf surface area 1 (b) reduce loss / amount of water (vapour) accept converse or reduced transpiration (from upper surface) do not allow no water is lost 1 warmer above leaf accept converse or wilted leaf folds over lower surface or lower leaf in shade ignore reference to dust or less light / heat / sun on lower side 1 [5] Page 52 Page 53






