Geometry Name: Date:______ Period:_____ WS 1.2
advertisement
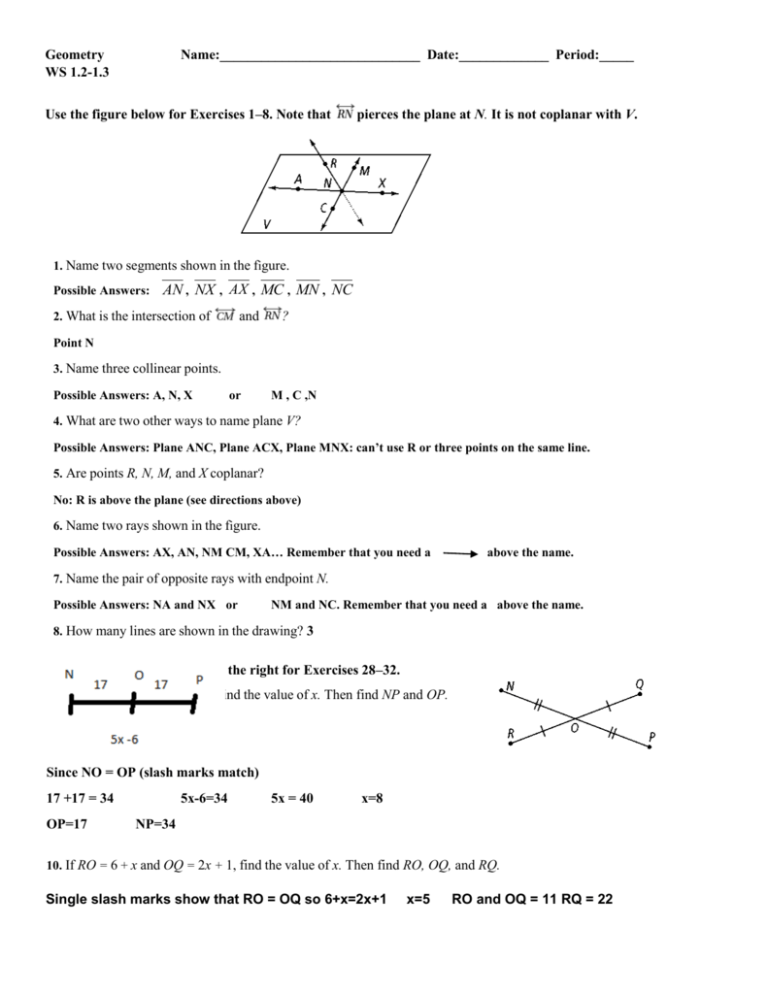
Geometry WS 1.2-1.3 Name:_____________________________ Date:_____________ Period:_____ Use the figure below for Exercises 1–8. Note that pierces the plane at N. It is not coplanar with V. 1. Name two segments shown in the figure. Possible Answers: AN , NX , AX , MC , MN , NC 2. What is the intersection of and ? Point N 3. Name three collinear points. Possible Answers: A, N, X or M , C ,N 4. What are two other ways to name plane V? Possible Answers: Plane ANC, Plane ACX, Plane MNX: can’t use R or three points on the same line. 5. Are points R, N, M, and X coplanar? No: R is above the plane (see directions above) 6. Name two rays shown in the figure. Possible Answers: AX, AN, NM CM, XA… Remember that you need a above the name. 7. Name the pair of opposite rays with endpoint N. Possible Answers: NA and NX or NM and NC. Remember that you need a above the name. 8. How many lines are shown in the drawing? 3 Algebra Use the diagram at the right for Exercises 28–32. 9. If NO = 17 and NP = 5x − 6, find the value of x. Then find NP and OP. Since NO = OP (slash marks match) 17 +17 = 34 OP=17 5x-6=34 5x = 40 x=8 NP=34 10. If RO = 6 + x and OQ = 2x + 1, find the value of x. Then find RO, OQ, and RQ. Single slash marks show that RO = OQ so 6+x=2x+1 x=5 RO and OQ = 11 RQ = 22 Geometry Name: ______________________ Date: ______________ Period: ______ WS 1.4-1.5 Use the figure at the right for Exercises 1-4. mFXH = 130 and mFXG = 49. 11. Name a pair of vertical angles. Look for letter x to be formed. < GXF and IXJ 12. Determine the measures of the missing angles. mFXH = 130 and mFXG = 49; m<GXH=81, m<HXI=50, m<IXJ=49, m<JXF=131 13. Name a linear pair. Find three points on a line like F,X, and I then another point off the line like H. Use the letters to name the angles <FXH and <HXI form a linear pair. Another one would be <GXH and <HXJ 14. Name a pair of adjacent angles that are not a linear Pair. Adjacent (side by side) that do not form a line. Possible answers include <GXH and <HXI; <FXG and <GXH; <HXI and <IXJ 15. Algebra If mRZT = 110, mRZS = 3s, and mTZS = 8s, what are mRZS and mTZS? <RZT is the large angle, <RZS and <TZS are the small angles. Add the two small ones together to get the big one. 8s+3s = 11s so 11s = 110 s=10 m<RZS=30 and m<SZT=80 16. Algebra mOZP = 4r + 2, mPZQ = 5r 12, and mOZQ = 125. What are mOZP and mPZQ? <OZQ is the large angle , <OZP and <PZQ are the small angles. 5r – 12 4r+ 2 9r – 10 = 125 9r = 135 r= 15 m<OZP=62 and m<PZQ = 63 Use the diagram below for Exercises 7 and 8. Solve for x. Find the angle. (Fill in diagram) 17. mAOB = 4x 1; mBOC = 2x + 15; mAOC = 8x + 8 <AOC is the large angle , <BOC and <AOB are the small angles. 4x - 1 2x + 15 6x + 14 = 8x+8 x=3 m<AOB=11 and m<BOC = 21 18. mCOD = 8x + 13; mBOC = 3x 10; mBOD = 12x 6 <BOD is the large angle , <COD and <BOC are the small angles. 3x - 10 8x + 13 11x +3 = 12x-6 x=9 m<COD=85 and m<PZQ = 63 19. ABC and EBF are a pair of vertical angles; mABC = 3x + 8 and mEBF = 2x + 48. What are mABC and mEBF? a. What does vertical mean (tell you to do with the angles)? Set them equal. b. Write and solve and equation for x. 3x+8=2x+48 x=40 c. Find the measure of the missing angles. 128 and 128 degrees 20. JKL and MNP are complementary; mJKL = 2x 3 and mMNP = 5x + 2. What are mJKL and mMNP? a. What does complementary mean (tell you to do with the angles)? Add up to 90 degrees b. Write and solve and equation for x. 2x - 3 5x + 2 7x – 1=90 7x=91 x=13 m<JKL=23 and m<MNP = 67 c. Find the measure of the missing angles. Bisects PQR. Solve for x and find mPQR. (Use for # 11 and 12) 21. mPQS = 3x; mSQR = 5x 20 P a. Draw and label a diagram. Look right 3x b. Write and solve an equation for x. c. Fin the mPQR. 60 degrees Q 5x-20 3x = 5x-20 -2x=-20 x=10 22. mPQR = 3x 12; mPQS = 30 R a. Draw and label a diagram. Look right b. Write and solve an equation for x. c. Fin the mPQR. 60 degrees 30+30=3x-12 60=3x-12 72=3x x=24 P 30 3x-12 S Q R