Biogeochemical Cycles Packet
advertisement
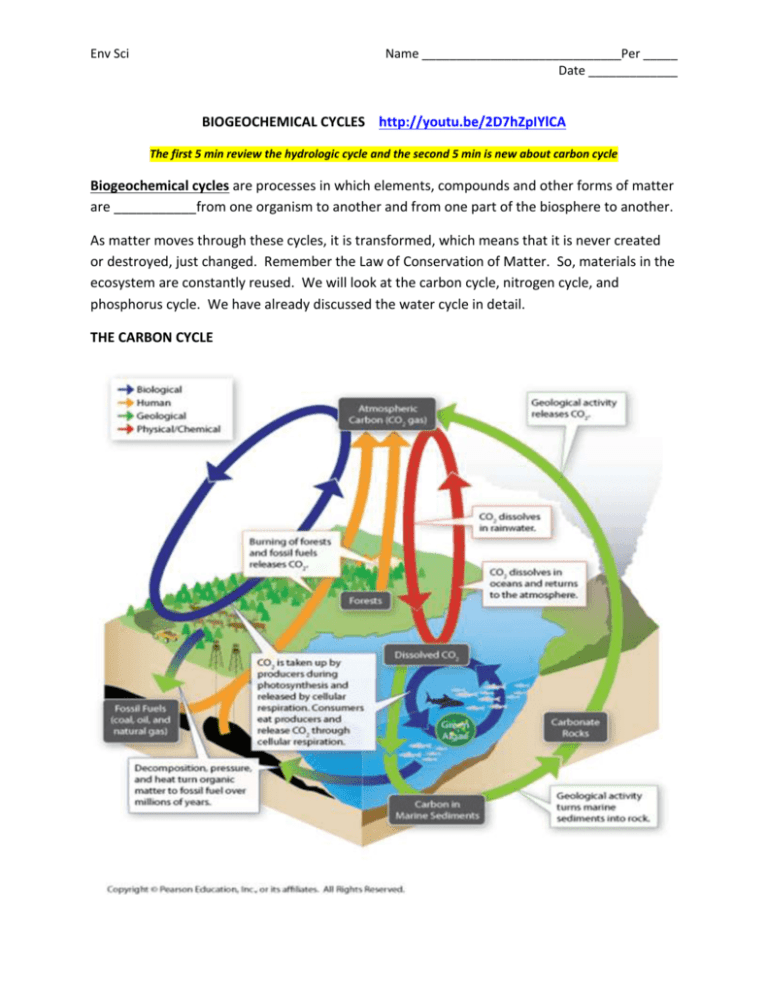
Env Sci Name _____________________________Per _____ Date _____________ BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES http://youtu.be/2D7hZpIYlCA The first 5 min review the hydrologic cycle and the second 5 min is new about carbon cycle Biogeochemical cycles are processes in which elements, compounds and other forms of matter are ___________from one organism to another and from one part of the biosphere to another. As matter moves through these cycles, it is transformed, which means that it is never created or destroyed, just changed. Remember the Law of Conservation of Matter. So, materials in the ecosystem are constantly reused. We will look at the carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, and phosphorus cycle. We have already discussed the water cycle in detail. THE CARBON CYCLE Env Sci Name _____________________________Per _____ Date _____________ As you know, carbon is an essential component of proteins, fats, carbohydrates and nucleic acids. The carbon cycle is the process where carbon is cycled between the atmosphere, land, water, and organisms. In the carbon cycle, carbon dioxide is continuously exchanged between the atmosphere, oceans, and living organisms through chemical and physical processes. Plants take in CO2 during photosynthesis and use it to build carbohydrates. These nutrients then pass through food webs to consumers. Many animals combine carbon with calcium and oxygen as they build their skeletons. Organisms release carbon in the form of CO2 gas by cellular respiration. When organisms die, decomposers break down the bodies releasing carbon to the environment. Geologic forces turn accumulated carbon into carbon-containing rocks or fossil fuels. CO2 is released into the atmosphere by volcanic activity and by human activities such as burning fossil fuels, as well as clearing and burning forests. Carbon cycle questions: http://youtu.be/dDBU0lg-HYE 1. Describe the 2 main processes of the carbon cycle (photosynthesis and cellular respiration). 2. How does burning fossil fuels affect the carbon cycle? Env Sci Name _____________________________Per _____ Date _____________ Match the term associated with the carbon cycle with the best description: a. photosynthesis b. cellular respiration c. fossil fuels 2. ____________ Carbon-containing compounds that were once part of ancient forests, marine organisms or other animals that have been buried and transformed into energy– rich fuels. 3. ____________ Plants use CO2 during this process and release O2 into the atmosphere. They also produce glucose during this process. 5. ____________ Organisms use glucose and oxygen and release CO2 during this process. 6. What are 3 types of fossil fuels http://youtu.be/cJ-J91SwP8w 7. What is a problem associated with humans burning too many fossil fuels? What gas does this release into the atmosphere in great quantities? What problem has this led to? http://youtu.be/jakJ-Tf79ac Env Sci Name _____________________________Per _____ Date _____________ THE NITROGEN CYCLE – fill all parts of the table with the video- (even the lines) http://youtu.be/372K0jyO0hQ Env Sci Name _____________________________Per _____ Date _____________ All organisms need nitrogen to build proteins and nucleic acids. Nitrogen makes up 78% of the gases in the atmosphere, but most organisms cannot use atmospheric nitrogen. It must be altered or fixed before organisms can use it. The only organisms that can fix atmospheric nitrogen into chemical compounds are a few species of bacteria known as nitrogen-fixing bacteria. All other organisms depend upon these bacteria to supply nitrogen. The nitrogen cycle is a process in which nitrogen is cycled between the atmosphere, bacteria and other organisms. Bacteria take nitrogen gas from the air and transform it into molecules living things can use. Nitrogen occurs in many different forms in the biosphere: Nitrogen gas (N2) – 78% Earth’s atmosphere Ammonia, nitrate ions, nitrite ions – found in soil, wastes produced by many organisms, and in dead and decaying organic matter. Dissolved nitrogen – in oceans and other large bodies of water Env Sci Name _____________________________Per _____ Date _____________ Important steps in the Nitrogen cycle: Nitrogen fixation – nitrogen fixing bacteria convert nitrogen gas into ammonia. Some of these bacteria live in the soil, while others live on the roots of certain plants called legumes (peanuts, peas, soybeans) Plants that do not have nitrogen fixing bacteria get their nitrogen from the soil Other bacteria in the soil convert the fixed nitrogen into nitrates and nitrites. Now, other plants use these nitrogen containing compounds to produce proteins and nucleic acids. Consumers eat these producers and reuse nitrogen to make their own nitrogencontaining compounds. Decomposers release nitrogen from waste and dead organisms as ammonia, nitrates and nitrites, that producers may take up again! Denitrification – In this process, other bacteria convert nitrates back into nitrogen gas, which is then released back into the atmosphere. Atmospheric nitrogen fixation – A relatively small amount of nitrogen gas is converted into usable forms by lightning. Humans add extra nitrogen to the biosphere through the manufacture and use of fertilizers. Excess fertilizer is often carried into surface water or ground water by precipitation. Nitrogen cycle questions: 1. All organisms require nitrogen to build _____________ and ________________ (which 2 groups of organic compounds – choose carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids) Match the term with the best description involving the nitrogen cycle: a. decomposers b. nitrogen fixation c. denitrification 2. ____________ The process in which certain types of bacteria convert nitrogen gas into ammonia. 3. ____________ These organisms release nitrogen from waste and dead organisms. 4. ____________ The process by which some bacteria convert nitrates into nitrogen gas which is released back into the atmosphere. Env Sci Name _____________________________Per _____ Date _____________ 5. Bacteria responsible for nitrogen-fixation are found in the roots of a. All plants b. certain plants such as legumes c. evergreen trees 6. Which statement about the nitrogen cycle is true? a. All nitrogen obtained by animals can be traced back to the eating of plants b. Plants fix nitrates into atmospheric gas c. Nitrogen atoms are continually created and destroyed 7. Which statement about this cycle is false? a. Plants but not animals are part of the nitrogen cycle b. The nitrogen cycle requires nitrogen-fixing bacteria c. Bacteria convert nitrogen gas into a form in which it can be used as a pant nutrient d. Bacteria and fungi break down dead plant and animal tissues into nitrates that plants can use. Env Sci Name _____________________________Per _____ Date _____________ 8. Organic compounds in dead organic matter and wastes are converted into ammonia as a result of________________ a. nitrogen fixation b. denitrification c. decomposition 9. Animals get their organic nitrogen compounds by______________ a. feeding b. breathing c. performing photosynthesis 10. Why is it so difficult for most organisms to use nitrogen gas from the atmosphere? a. Nitrogen is a non-reactive atom b. A strong triple covalent bond holds the molecule together. c. Oceans quickly absorb nitrogen gas, so not much is available in the air. 11. _____ are the primary organisms which drive the nitrogen cycle. a. Bacteria b. animals c. plants Go to the following website, and watch the animation about the nitrogen cycle. After you have watched it, write a brief description of the nitrogen cycle. In other words, summarize the nitrogen cycle in your own words. Try to include the main processes (nitrogen fixation, denitrification, decomposition) http://www.classzone.com/books/ml_science_share/vis_sim/em05_pg20_nitrogen/em05_pg20_nitrog en.swf Env Sci Name _____________________________Per _____ Date _____________ The Phosphorous Cycle - http://youtu.be/_IBx0zpNoEM The phosphorus cycle is the movement of phosphorus from the environment to organisms and then back to the environment. Phosphorus is part of many molecules that make up cells of living things. Phosphorus is needed to form bones and teeth in animals. Plants get the phosphorus they need from soil and water, while animals get it by eating plants or other animals that have eaten plants. This cycle is slow and does not normally include the atmosphere because phosphorus rarely occurs as a gas. Phosphorus enters soil and water in a few ways. When rocks erode, a little P dissolves as phosphate in soil and water. Plants absorb phosphates in the soil through their roots. P is added to soil and water when excess P is excreted in waste from organisms and when organisms die and decompose. Some P washes off land and eventually ends up in oceans. Many phosphate salts are not soluble in water, so they sink to bottom of ocean and accumulate as sediment. Env Sci Name _____________________________Per _____ Date _____________ How do humans affect phosphorus cycle? Fertilizer use! Fertilizers contain both N and P. If excessive amounts of fertilizer are used, the fertilizer can enter both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems through runoff. Excess N and P in aquatic ecosystems can cause rapid and overabundant growth of algae, which results in an algal bloom. An algal bloom is a dense, visible patch of algae that occurs near the surface of water. This can deplete the ecosystem of oxygen and other important nutrients. Acid Precipitation – when we burn fuel, nitric oxide is released into the atmosphere. Nitric oxide can combine with oxygen and water vapor in the atmosphere to form nitric acid. This dissolves in rain and snow and contributes to acid precipitation. Env Sci Name _____________________________Per _____ Date _____________ Questions: 1. Explain how the excessive use of fertilizer affects the nitrogen cycle and the phosphorus cycle. http://youtu.be/IndPs2XobLs http://www.answers.com/Q/How_does_the_use_of_fertilizer_affect_the_nitrogen_cycl e_and_phosphorus_cycle 2. What is one way that a person can help to reduce the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere? (hint: do you drive a car?) 3. Which organic macromolecules contain phosphorus? http://umm.edu/health/medical/altmed/supplement/phosphorus








