Waves
advertisement

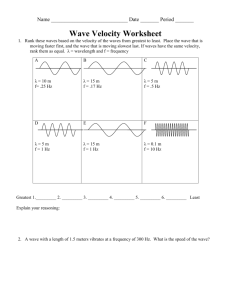
Waves... A wave is a traveling disturbance that transmits energy Waves transmit only energy (not matter) (when full wave cycles pass through a medium Periodic waves exhibit simple harmonic motion (a motion that is repeated over and over, with the same characteristics (shape, size and time). Kinds of Waves Electromagnetic Waves Mechanical Waves Wave Terms & Definitions Medium - The material through which the wave travels. Ex. Amplitude - How big, how bright (light), or how loud (sound) a wave is. Amplitude is proportional to energy. Wavelength (λ) - The length of one wave cycle. Wavelength is measured in meters (m). Period (T) - Time for one wave cycle to pass a specific point. Period is measured in seconds (s). Period is the inverse of frequency. Frequency (f) - How much of a wave cycle passes a point per second. Frequency is measured in waves/sec or Hertz (Hz). Differences in frequency are detected as different pitches (sound waves) or different colors (light waves). Frequency is the inverse of period. Wave speed (v) - How quickly a waves moves) through the medium. Wave speed (velocity) is determined by the medium and measured in meters per second (m/s). Wave speed is the distance of a wave cycle (wavelength) divided by the time of a wave cycle (period). Wave speed is also calculated by multiplying the wavelength times the frequency of the wave. Transverse Waves vs. Compression/Longitudinal Waves Sound Waves vs. Light Waves Why do you see lightning before you hear the thunder? If you got free tickets for the Subway Series, you may end up sitting in the nosebleed seats. As you are watching the game, you notice that you hear the crack of the baseball bat on the ball about 2.5 seconds after you see it. How are you from the action? (velocity of sound = 340 m/s) The "Mosquito" was marketed as an ultrasonic teenager repellent, an ear-splitting 17-kilohertz buzzer designed to help shopkeepers disperse young people loitering in front of their stores while leaving adults unaffected. 1. The range of human hearing is between 20 Hz and 20,000 Hz. What are the wavelengths of sound waves that can be detected by humans? (velocity of a sound wave at room temperature = 340 m/s) 2. What color is a laser with a wavelength of 680 nm (6.8 x 10 -7 m) ? 3. You shout at a cliff. It takes 5.4 sec for you to hear your echo. How far are you from the cliff? (vsound = 340 m/s) 4. How do you perceive different frequencies of light? How do you perceive different frequencies of sound? How are light and sound affected if the amplitude of the waves is changed? 5. In the diagram to the right, draw the interference pattern. At each vertical line, add the amplitudes of the waves together. Put a data point in that spot. Draw in the resulting wave pattern. 6. While waiting at a railroad crossing, you notice that the pitch of the train whistle changes as the train passes you. Why does this occur? 7. How can a specific frequency of sound break a wine glass? Wave Phenomena Waves behave in a predictable manner as they encounter obstacles, openings, other waves or changes in the medium. We observed these phenomena in the ripple tank lab. What is the difference between a wave pulse and a periodic wave? Reflection The energy of a wave is redirected when it hits an object. The wave bounces off the object in a different direction. Refraction - the bending of a wave as it moves from one medium to another. The speed and wavelength of the wave changes as the wave moves from one medium to another. Diffraction - The spreading out of a wave as it moves past an object or through a small opening. Interference - When two or more waves pass through the same medium at the same time, the amplitude of the waves adds together to form a new wave pattern. Doppler Effect - the name for a phenomenon in which the frequency of a sound or light source appears to change due to the motion of the source or the observer. Resonance - Amplification of a wave in an object caused by small amounts of energy delivered at the same frequency as the natural vibration of the object. Wave Practice Conceptual Physics For questions #1 to #4, refer to the diagram below. 1. What is the amplitude of the wave? 2. What is the wavelength? 3. The wave pattern shown above occurred in 10 seconds. What is the period? What is the frequency? 4. What is the velocity of the wave? 5. What is the period of a 256 Hz wave? If this wave is moving at 340 m/s, what is the wavelength of this wave? Is this wave a sound wave or a light wave? 6. What is the velocity of a 1.12 m (length) wave with a frequency of 32 Hz? 7. On the diagram below, wave A has a higher frequency than Wave B. Label wave A and wave B. With a ruler, measure the wavelength and amplitude of each wave. If the frequency of wave A is 150 Hz, determine the velocity of wave A. Wave B has the same velocity as wave A because it is moving through the same medium. What is the frequency of wave B? 8. A man tries to determine the distance to an island offshore by using his knowledge of physics and wave motion. He determines that its takes 56 seconds for a wave to go from his position to the island. He estimates the distance between wave crests to be 5 m. He notes that it takes 2 seconds for each successive wave crest to pass him. Knowing this information, how far away is the island?