Name: Date: Outcome 5: Earth History Pre
advertisement

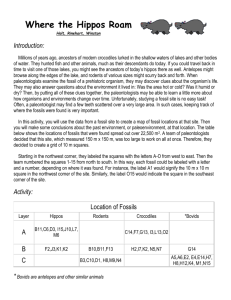
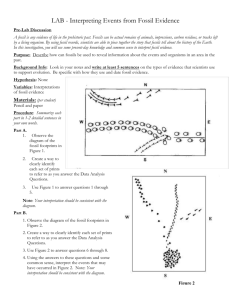
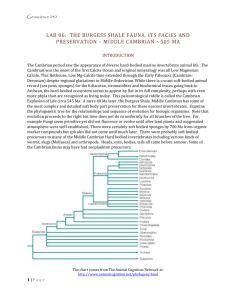
Name:_______________________________________ Date:________________ Outcome 5: Earth History Pre-Test 1. When did the dinosaurs disappear? Why did they go extinct? 2. How do we know how old the Earth is? 3. Why do some things turn into fossils and other things do not? What is required for fossilization? 4. Which radioactive substance would probably be used in dating the recent remains of a plant found in sedimentary deposits? (1) Carbon-14 (2) Potassium-40 (3) Rubidium-87 (4) Uranium-238 5. A fossil formed 11,400 years ago. Which percentage of the original amount of carbon-14 remains in the fossil? (1) 100% (2) 50% (3) 25% (4) 12.5% 6. The impacts of large asteroids on Earth are inferred to be associated with (1) free oxygen entering Earth’s atmosphere (2) seafloor spreading (3) the creation of subduction zones (4) global climatic changes 7. Which geologic event occurred in New York State at approximately the same time as the extinction of dinosaurs and ammonoids? (1) formation of the Queenston Delta (2) deposition of the sands and clays underlying Long Island (3) initial opening of the Atlantic Ocean (4) advance and retreat of the last continental ice sheet 8. Fossils of which type of animal would most likely be found in the surface bedrock of the Catskills? (1) reptiles (2) brachiopods (3) mammals (4) birds 9. The accumulation of water vapor, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen in Earth’s early atmosphere approximately 4 billion years ago resulted mainly from (1) outgassing from Earth’s interior (2) radioactive decay (3) photosynthesis by the earliest land plants (4) convection currents in Earth’s outer core Base your answer to question 10 on the geologic cross section of Earth’s crust below and on your knowledge of Earth science. Letters A through F identify rock units. Letter X identifies a fault. Wavy line YZ represents an unconformity. The locations of contact metamorphism and the map symbols for sedimentary rock layers B and E have been omitted. 10. Indicate the relative ages of geologic features B, E, F, and X, by listing the letters from oldest to most recent. Base your answer to question 11 on the data table and information below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The data table shows the radioactive decay of carbon-14 and the age of fossil remains, in years (y). Part of the table has been left blank. 11. The carbon-14 in the fossil remains of a mastodont has undergone five half-lives of radioactive decay. Calculate the age of these fossil remains. The diagram below represents three bedrock outcrops. The layers have not been overturned. Letters A through E identify different rock layers. Fossils found in the rock layers are shown. 12. Which fossil could be classified as an index fossil? 1. 2. 3. 4. Base your answer to questions 13 and 14 on the data table below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The data table shows information on six major mass extinction events that occurred many million years ago (mya) in Earth’s history. 13. Which event is generally accepted as the cause of the mass extinction that occurred 65.5 million years ago? (1) volcanic eruption (2) continental collision (3) asteroid impact (4) sea-level change 14. More than half of brachiopod species became extinct at the end of the (1) Devonian Period (2) Silurian Period (3) Ordovician Period (4) Cambrian Period The Burgess shale fossil discovery revealed unique Cambrian life-forms, most of which were not present in the previously known fossil record. Normally, soft body parts of dead organisms are destroyed by scavengers and bacteria on the ocean floor. However, in the deep-water depositional environment of the Burgess shale, oxygen was lacking and organisms were buried rapidly, preserving the unique community seen in the diagram. The soft-bodied organisms had previously been unknown. The Burgess shale fossils were originally found in a layer of bedrock in southwestern Canada. 15. Identify the number of one organism in the diagram that is most likely a trilobite 16. Explain why so many soft body parts of organisms were preserved in the Burgess shale. 17. During which epoch of the Cambrian Period were the Burgess shale organisms and sediments deposited? Base your answer to the questions 18-20 on the geologic cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents rock and sediment layers, labeled A through F. Each layer contains fossil remains, which formed in different depositional environments. Some layers contain index fossils. The layers have not been overturned. 18. The depositional environment during the time these layers and fossils were deposited (1) was consistently marine (2) was consistently terrestrial (land) (3) changed from marine to terrestrial (land) (4) changed from terrestrial (land) to marine 19. During which geologic epoch was layer F deposited? (1) Late Devonian (2) Middle Devonian (3) Early Devonian (4) Late Silurian 20. Which pair of organisms existed when the unconsolidated sediment in layer A was deposited? (1) birds and trilobites (2) dinosaurs and mastodonts (3) ammonoids and grasses (4) humans and vascular plants Answer Key 1. 2. 3. 4. (1) 5. (3) 6. (4) 7. (2) 8. (2) 9. (1) 10. Oldest → E, B, X, F → Most recent 11. 28,500 years 12. (3) 13. (3) 14. (3) 15. Answer: 4 or 5 or 7 or 9 16. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to: They were rapidly buried by sediment deposition. Oxygen was lacking. It was a deep-water environment. The soft parts did not decompose 17. Allow credit for Middle Cambrian Epoch. 18. (3) 19. (2) 20. (3)