Answer Scheme Midterm 2
advertisement
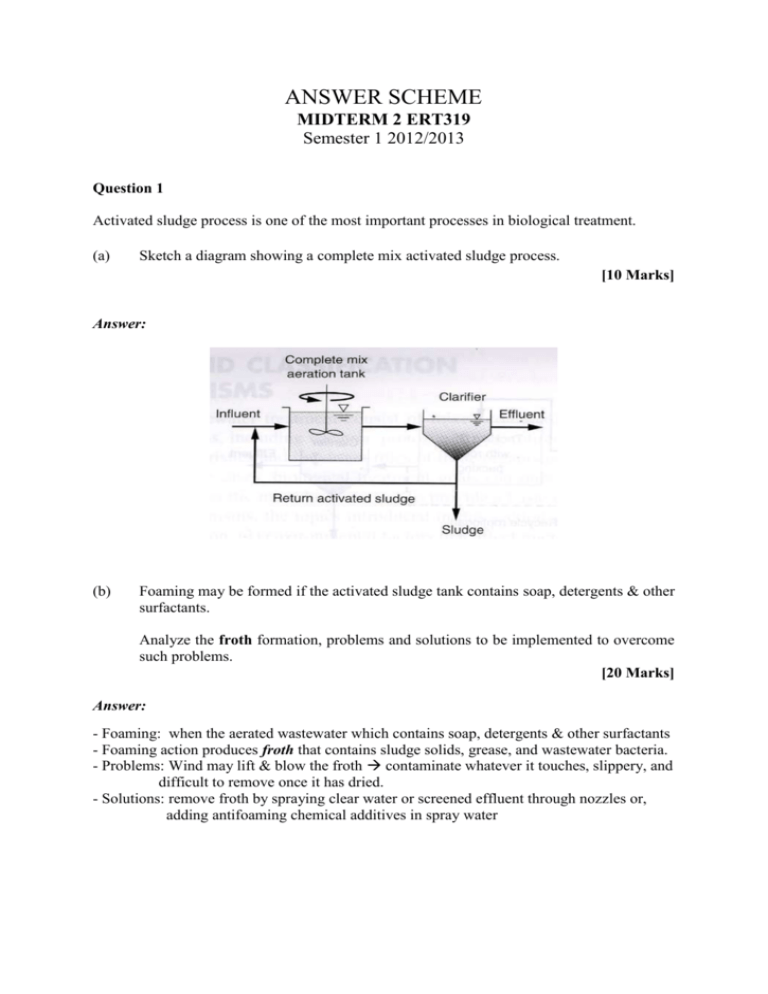
ANSWER SCHEME MIDTERM 2 ERT319 Semester 1 2012/2013 Question 1 Activated sludge process is one of the most important processes in biological treatment. (a) Sketch a diagram showing a complete mix activated sludge process. [10 Marks] Answer: (b) Foaming may be formed if the activated sludge tank contains soap, detergents & other surfactants. Analyze the froth formation, problems and solutions to be implemented to overcome such problems. [20 Marks] Answer: - Foaming: when the aerated wastewater which contains soap, detergents & other surfactants - Foaming action produces froth that contains sludge solids, grease, and wastewater bacteria. - Problems: Wind may lift & blow the froth contaminate whatever it touches, slippery, and difficult to remove once it has dried. - Solutions: remove froth by spraying clear water or screened effluent through nozzles or, adding antifoaming chemical additives in spray water Question 2 Figure 1 Figure 1 shows a diagram of a type of biological treatment unit operation. Propose a removal mechanism for this type of treatment. [20 Marks] Answer: - As the shaft rotates, the surfaces of rotating disks alternately come in contact with the microorganisms and organic content of wastewater and atmosphere. - During the rotation, the microbes get attached to the disks, and O2 from atmosphere is transferred to the wastewater to maintain aerobic condition. - The microbes attached to the disks surface grow in the form of biological film and consume organic content in the wastes. - After some times, as the bio-films thickens, an anaerobic condition develops nearer to the disks surface, then the slime layer gets washed out (sloughing) by incoming wastewater flow (the layer of microbes enters endogenous respiration and weaken the attachment to the films surface and easily washed-out by next wastewater flow). The sloughed bio-films is ultimately removed in the secondary clarifier before final disposal of treated effluent. Question 3 (a) Stabilization process of sludge is a process to reduce volume of waste, produce usable gas and improve the dewaterability of the sludge. Stabilization includes digestions and composting. Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of cylindrical anaerobic digestion. [20 Marks] Answer: Advantages Disadvantages (b) Figure 2 Figure 2 shows a schematic diagram of a waste dumping system. Analyze the functions of X and Y. [20 Marks] Answer: X: Leachate collection system - Consisting of a series of drainpipes or a drainage layer to collect leachate / avoid leachate from penetrating/ absorbing in the soil and contaminate the soil/ groundwater. - Easy to collect leachate for further treatment. Y: Primary barrier - Consisting of layer of clay, bentonite-enhanced soil or hydraulic asphalt. - Act as high-permeability layer to protect the leachate and landfill gas from contaminate the surrounding soil and groundwater. - Act as a barrier from which to separate and filter the leachate produced from contaminating the soil and groundwater.