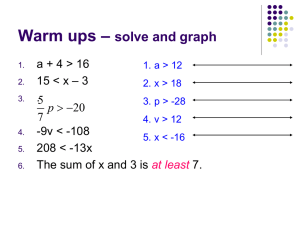
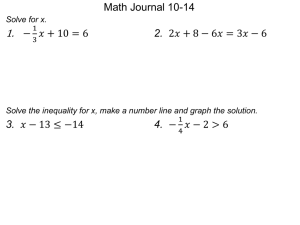
ALEKS PURPLE Solving a linear inequality: Problem type 4
advertisement

ALEKS PURPLE Solving a linear inequality: Problem type 4 Refer to Jolene’s Jottings #6 for additional detail on solving this type of problem. The process for solving linear inequalities involves seven steps: 1. Deal with fractions first. Multiply by the positive LCD or the denominator of the fraction to 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. EVERYTHING (every term) on BOTH sides of the inequality then simplify. Note that only fractions outside the parenthesis will be eliminated at this point. Deal with parentheses next. Whatever term is outside the parenthesis, distribute that to each term inside the parenthesis then simplify. Remember that if you only see a minus sign, that is a -1 that you need to distribute inside the parenthesis. Note that any fractions inside the parenthesis should be eliminated at this step of the process Combine like terms on each side of the inequality sign separately. "Move" all constant numbers (without a variable) to the right -- you "move" numbers by adding or subtracting them to BOTH sides of the inequality. "Move" all variables to the left -- again, you "move" variables by adding or subtracting them to BOTH sides of the inequality. Combine like terms on each side of the inequality sign separately. Isolate the variable by dividing by its coefficient on BOTH sides of the inequality. NOTE: If you are dividing by a negative number, reverse the sign of the inequality. Let’s do an example: Solving a linear inequality: Problem type 4 Solve the inequality 3y 9 5 y 3 for y. Simplify your answer as 3 much as possible. STEP ONE: Eliminate fractions. 5 y 3 3 Multiply both sides by 3 to eliminate the fraction: 3y 9 5 3 3y 3 9 3 y 3 3 3 9y 27 5y 9 STEP TWO: Deal with parenthesis next. There are no parenthesis in this problem so we’ll skip this step. STEP THREE: Combine like terms on each side of the inequality. There are no like terms on the same side of the inequality so we’ll skip this step. STEP FOUR: “Move” all constants to the right by adding or subtracting as appropriate. 9y 27 5y 9 Subtract 27 from both sides to "move" it to the right: 9y 27 27 5y 9 27 9y 27 27 5y 9 27 9y 5y 9 27 STEP FIVE: “Move” all variables to the left by adding or subtracting as appropriate. 9y 5y 9 27 Subtract 5y from both sides to "move" the variables to the left: 9y 5y 5y 5y 9 27 9y 5y 5y 5y 9 27 9y 5y 9 27 STEP SIX: Combine like terms on each side of the inequality sign (simplify): 9y 5y 9 27 4y 18 STEP SEVEN: Isolate the variable by dividing both sides by its coefficient. Switch the inequality sign if that coefficient of the variable is negative (ALWAYS switch the inequality sign when dividing by a negative number): 4y 18 Divide both sides by 4 to isolate (solve) the variable: 4y 18 4 4 18 y 4 Reduce the fraction (by the LCM of 2): y 9 4