PastProv - Electrostatics
advertisement

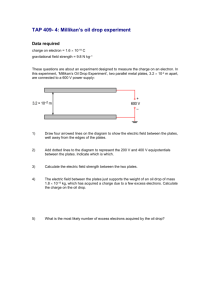
Electrostatics 4. Release 07/08 1. Three point charges are arranged as shown. What are the magnitude and direction of the electric force on the -15 µC charge due to the other two point charges? (a) 4.6 N left (c) 49 N left 2. 3. (b) 4.6 N right (d) 49 N right Each diagram shows two points X and Y in the electric field near a positive charge. In which case is the difference in the magnitudes of the electric field strengths for the two points the greatest? Which of the following correctly shows the electric field between two oppositely charge plates? A proton travelling at 1.40 x 106 m/s enters the region between two charged parallel plates as shown. What voltage applied to the second plate would result in the proton just reaching this plate (vf = 0 at the second plate) and what is the direction of the electric field between the two plates? (a) 9 030 V; right (c) 11 400 V; right (b) 9 030 V; left (d) 11 400 V; left Release 06/07 5. Which diagram best represents the path of an electron travelling between charged parallel plates? 6. Three identical positive charges are arranged as shown. What is the direction of the electric force on Q2? 7. What is the electric force on an electron in the region between parallel plates that are 4.0 cm apart with a 250 V potential difference? (a) 0 N (b) 1.6 x 10-18 N -15 (c) 1.0 x 10 N (d) 6.3 x 103 N 8. A small sphere with an electric charge may be moved in four different ways near a fixed electric charge. Which displacement requires the most work? 11. A proton is moved 3.0 cm in the electric field between parallel plates. (Diagram not to scale). How much work was done on the proton? (a) 1.2 x 10-19 J (c) 4.0 x 10-18 J (a) 1 (c) 3 9. (b) 2 (d) 4 (b) 2.7 x 10-18 J (d) 6.0 x 10-18 J 12. A proton and an electron, initially at rest as shown, are accelerated across parallel plates. Which of the following best describes the final kinetic energies and speeds of the two particles? An electric charge accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 250 V reaches a speed of 9.4 x 106 m/s. What speed will this same charge reach if it is accelerated by a potential difference of 125 V? (a) 4.7 x 106 m/s (b) 6.6 x 106 m/s 6 (c) 9.4 x 10 m/s (d) 1.3 x 107 m/s Release 05/06 10. What are the magnitude and direction of the electric force on charge Y due to charge X? 13. In the cathode ray tube shown, plates M and X are charged positively. Which of the following shows the resulting position of the beam as seen on the screen? (a) 3.9 x 10-8 N left (c) 5.2 x 10-8 N left (b) 3.9 x 10-8 N right (d) 5.2 x 10-8 N right 18. What is the magnitude of the electric field at point P in the diagram below? (1 μC = 1 x 10-6 C) Release 04/05 14. Which diagram best illustrates the electric field between oppositely charged parallel plates? (a) 22 N/C (c) 41 N/C (b) 31 N/C (d) 50 N/C 19. A positive charge Q is located several metres from a fixed positive charge as shown in the diagram below. You are told to move charge Q a distance of 1.0 m so as to cause the greatest increase in its electrical potential energy. In which direction do you move it? 15. Three charges of identical magnitude are arranged as shown. What is the direction of the electric force on Q2? (a) 1 (c) 3 (b) 2 (d) 4 June 04 16. Identical 12 μC charges are placed at the ends of a metre stick. What is the electric potential at point P at the 60 cm mark on the metre stick? (a) 9.0 x 104 V (c) 4.5 x 105 V (b) 3.8 x 105 V (d) 9.8 x 105 V January 04 17. What does an electric field line indicate? (a) The direction of the electrostatic force on a positive charge. (b) The direction of the electrostatic force on a negative charge. (c) The magnitude of the electrostatic force on a positive charge. (d) The magnitude of the electrostatic force on a negative charge. 20. Which of the following is equal to the work required per coulomb to move a positive charge from one position to another in an electric field? (a) Ep, electrical potential energy (b) ΔEp, change in electrical potential energy (c) V, electric potential (d) ΔV, electric potential difference 21. The diagram below shows a positive charge located near a smaller (in magnitude) negative charge. In which region is there a point where the electric field due to the two charges is equal to zero? (a) I (c) III (b) II (d) IV 26. At what speed will a proton, accelerated from rest, hit the plate at the right? August 04 22. The magnitude of the force experienced by any charged object, q, when placed in an electric field is equal to which of the following? (a) V/q (b) Ep/q (c) ΔV·q (d) E·q 23. The electric field at point P in the diagram below is 8500 N/C directed to the right. What is the size and polarity of charge q2? (a) 2.2 x 105 m/s (c) 3.1 x 105 m/s (b) 2.4 x 105 m/s (d) 4.4 x 105 m/s 27. Two views of a cathode ray tube are shown below. (a) + 6.2 μC (c) + 14 μC (b) - 6.2 μC (d) - 14 μC 24. A proton is made to travel in a straight line near a fixed positively charged object as shown in the diagram below. What is happening to the proton’s electric potential energy as it travels from A to B? (a) (b) (c) (d) It is increasing. It is decreasing. It is increasing then decreasing. It is decreasing then increasing. August 03 25. Which of the following shows how electric potential varies with distance from a positive point charge: The beam is then adjusted to Position 1 as shown below. In order to change the electron beam from Position 1 to Position 2, a student can (a) make plate x2 more positive (b) make plate x4 more positive (c) increase the accelerating voltage (d) decrease the accelerating voltage June 03 28. Which of the following is a possible electric field configuration? 29. What is the electric potential at point P midway between the two point charges shown below? (1 μC = 1 x 10-6 C) (a) 0 V (c) 1.4 x 104 V (b) 6.8 x 103 V (d) 5.4 x 104 V 30. A proton is moving at 5.0 x 106 m/s when it is 8.0 m from a fixed 1.5 x 10-5 C charge Q. What is the speed of the proton when it is 2.0 m from the fixed charge Q? (a) 2.5 x 106 m/s (b) 3.6 x 106 m/s 6 (c) 3.9 x 10 m/s (d) 4.5 x 106 m/s January 03 31. Which of the following represents the electric field between two opposite point charges of different magnitudes? 32. What are the magnitude and direction of the electric field at point P? (a) 2.4 x 104 N/C left (c) 3.0 x 104 N/C left (b) 2.4 x 104 N/C right (d) 3.0 x 104 N/C right 33. A proton moving at 5.0 x 105 m/s enters a series of charged parallel plates. What is the impact speed on the last plate? (a) 9.1 x 105 m/s (c) 1.1 x 106 m/s (b) 9.8 x 105 m/s (d) 1.3 x 106 m/s Written 34. During an electrostatics experiment to investigate Coulomb’s Law, a positive point charge, q, is moved gradually closer to a 10 µC charge that is fixed to a table top. The electrostatic force, Fq, experienced by q1 at several separation distances, r, from the 10 µC fixed charge is recorded. It is possible to use such data to create a linear graph and obtain a slope. In the box on the graph, write the function (include units) of the separation distance, r, that must be used on the horizontal axis to produce a linear relation from this data. Explain how you can use the slope of the graph to determine the unknown charge, q1. (Release 07/08) 35. A small negatively charged sphere with a mass of 4.5 x 10-6 kg is suspended electrostatically between oppositely charged horizontal parallel plates as shown in the diagram. A potential difference of 360 V is required across the plates to hold the charged sphere stationary. Calculate the magnitude of the charge on the sphere. (6 marks) (Release 06/07) 39. A 1.0 x 10-3 kg Styrofoam ball carrying 50 μC of charge is released from rest from position A as shown in the diagram below. (Aug 04) (a) Determine the change in electric potential energy of the ball as it moves from position A to position B. (b) What is the speed of the ball as it reaches position B? (vi = 0 at A) (a) A sphere with a smaller mass carrying an equal but opposite charge is now placed between the plates. Using principles of physics, explain the changes that must be made to the plates to keep the new sphere stationary. 36. A proton at rest 1.0 m from a fixed 5.0 μC charge is released as illustrated. Calculate the speed of the proton when it is 3.0 m from the fixed charge. (release 05/06). 37. Alpha particles with a mass of 6.6 x 10-27 kg and a charge of 3.2 x 10-19 C are fired towards each other from a great distance. If they each have a speed of 2.5 x 106 m/s to start with, what will be their minimum separation distance? (release 04/05) 38. How much work would it take to move a -15 μC charge from point P to a position infinitely far away? (June 04) 40. Two protons are initially held at rest 2.5 x 10-10 m apart. If one of the protons is released as shown below, what is its speed when it is 8.0 x 10-10 from the fixed proton? (August 03) (7 marks) 41. An electron with a speed of 3.3 x 107 m/s is directed between charged parallel plates as shown. (June 03) (a) What are the magnitude and direction of the electrostatic force on the electron while it is between the plates? (5 marks) (b) What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the electron while it is between the plates? (2 marks) 42. A proton, accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 1.2 x 104 V, is directed at a fixed 5.0 x 10-6 C charge. (January 03) a. b. . What is the speed of the proton as it leaves the parallel plates? ( 4 marks) What is the distance, d, from the fixed charge when the proton is stopped? (3 marks) Answers: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. A D D D D D C C B C B B B D D C A C D D 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. D D B C 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 1/r2 (m-2) 4.9 x 10-9 C 2.4 x 106 m/s 2.2 x 10-14 m 0.81 J -5.4 J, 1.0 x 102 m/s 2.75 x 104 m/s