Water Pollution Worksheet
advertisement

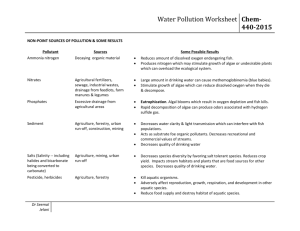
Water Pollution Worksheet Name_______________________________ WATER POLLUTION 1. Which of the following are sometimes considered pollutants if found in water? (Place an "x in front of those that are). ____ ammonia ____ chlorides ____ iron ____ sulfides ____ nitrates ____ copper ____ carbon dioxide ____ phosphates ____ chromium ____ silica ____ lead ____ cyanide 2. Name one possible source of excess nitrogen in a body of surface water. ___________________________________________________ _____________ 3. What could be a possible source of sulfates found in a supply of drinking water? ___________________________________________________ _____________ 4. What is one possible result of a low amount of dissolved oxygen in body of surface water? ___________________________________________________ _____________ 5. In a body of surface water polluted with chromium, where would the chromium be located? Why would it be located there? ___________________________________________________ _____________ ___________________________________________________ _____________ 6. Classify each of the following as a "point source" or "non-point source" of pollution by placing a "p" or "np" in the blank provided. ____ outflow pipe from a factory emptying wastes into a stream ____ snow melt carrying dissolved solids into a river ____ excess pesticide carried by rainfall into an irrigation ditch ____ hot water from a nuclear cooling system being dumped into a river 7. Classify each of the following pollutants as organic, inorganic, toxic, or thermal by placing an "o", "i", "t", or "th" on the blank provided. ____ sodium chloride from urban streets where it was used to melt ice ____ hot water from a nuclear cooling system ____ suspended clay from agricultural run-off ____ nitrogen resulting from breakdown of manure dumped in a pond ____ lead from mining operations dumped in water ____ insecticide from agricultural run-off 8. Define water pollution. ___________________________________________________ ___________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________ Appendix G Water Pollution Worksheet Answers Name______Name_______________________ WATER POLLUTION 1. Which of the following are sometimes considered pollutants if found in water? (Place an "x in front of those that are). _x___ ammonia _x___ chlorides _x___ iron _x___ sulfides _x___ nitrates _x___ copper _x___ phosphates _x___ chromium _x___ lead _x___ cyanide _x___ carbon dioxide _x___ silica 2. Name one possible source of excess nitrogen in a body of surface water. ammonia, nitrate, nitrite, fertilizer, sewage, manure, other organics_______ 3. What could be a possible source of sulfates found in a supply of drinking water? mining, industrial runoff___________________________________________ 4. What is one possible result of a low amount of dissolved oxygen in body of surface water? fish kill, growth of anaerobic bacteria_________________________________ 5. In a body of surface water polluted with chromium, where would the chromium be located? Why would it be located there? It would be located on /under the bottom; because it is a heavy metal which would sink to the bottom and become covered with sediment._____________ 6. Classify each of the following as a "point source" or "non-point source" of pollution by placing a "p" or "np" in the blank provided. __p__ outflow pipe from a factory emptying wastes into a stream __np__ snow melt carrying dissolved solids into a river __np__ excess pesticide carried by rainfall into an irrigation ditch __p__ hot water from a nuclear cooling system being dumped into a river 7. Classify each of the following pollutants as organic, inorganic, toxic, or thermal by placing an "o", "i", "t", or "th" on the blank provided. __i__ sodium chloride from urban streets where it was used to melt ice __th__ hot water from a nuclear cooling system __i__ suspended clay from agricultural run-off __o__ nitrogen resulting from breakdown of manure dumped in a pond __t__ lead from mining operations dumped in water __t__ insecticide from agricultural run-off 8. Define water pollution. Water pollution is the decreased usefulness of water due to the increase of substances in the water_______________________________________________ ____________________ NON-POINT SOURCES OF POLLUTION & SOME RESULTS5 Pollutant Ammonia nitrogen Sources Decaying organic material Some Possible Results Reduces amount of dissolved oxygen endangering fish. Produces nitrogen which may stimulate growth of algae or undesirable plants which can overload the ecological system. Nitrates Agricultural Large amount in drinking fertilizers, sewage, water can cause industrial wastes, methemoglobinemia (blue drainage from babies). Stimulate growth of feedlots,farm algae which can reduce manures & legumes dissolved oxygen when they die & decompose. Phosphates Excessive drainage Eutrophication. Algal blooms from agricultural which result in oxygen areas depletion and fish kills. Rapid decomposition of algae can produce odors associated with hydrogen sulfide gas. Sediment Agriculture, forestry, Decreases water clarity & urban run-off, light transmission which can construction, mining interfere with fish populations. Acts as substrate foe organic pollutants. Decreases recreational and commercial values of streams. Decreases quality of drinking water. Salts (Salinity -- Agriculture, mining, Decreases species diversity by including halides urban run-off favoring salt tolerant species. and bicarbonate Reduces crop yield. Impacts being converted stream habitats and plants to carbonate) that are food sources for other species. Decreases quality of drinking water. Pesticide, Agriculture, forestry Kill aquatic organisms. herbicides Adversely affect reproduction, growth, respiration, and development in other aquatic species. Reduce food supply and destroy habitat of aquatic species. Bioaccumulate in tissues of plants, macroinvertebrates and fish. Some are carcinogenic and/or mutagenic. Decrease photosynthesis inaquatic plants. Reduce recreational and commercial activities. Polycyclic urban runoff Bioaccumulate, biomagnify, aromatic and are toxic to aquatic life. hydrocarbons Can produce carcinogenic (PAHs) metabolites when digested. Polychlorinated urban runoff, landfills Toxic to aquatic organisms; biphenyls (PCBs) can bioaccumulate, biomagnify and be stored in fat deposits. Adsorb to sediments. Persist in environment longer than most chlorinated compounds. Petroleum urban runoff Water soluble components hydrocarbons can be toxic to life. Portions may adsorb to particulate organic matter, be deposited in sediment and may adversely affect biological functions. Silica decomposition of Forms hard, dense scale alumina silicate (which is resistant to heat minerals in the transfer) in boilers. Causes drainage basin loss of turbine efficiency due through which the to deposit of insoluble silica water flows deposits on turbine blades. Sulfates mining, industrial Lower pH in streams which run-off stresses aquatic animals and leaches toxic metals out of sediment and rocks. High acidity and concentrations of Sulfides sewage, industrial run-off, paper manufacturing Radionuclides mining / ore processing, nuclearpowerplant wastes, commercial & industry heavy metals can be lethal to aquatic organisms and eliminate entire aquatic communities. In the form of hydrogen sulfide, cause noticeable odor. Hydrogen sulfide is toxic; acts as a respiratory depressant in humans and fish. Some are toxic, carcinogenic, or mutagenic. Some degenerate into other substances (e.g., radium and lead) which are toxic and carcinogenic to aquatic organisms. When ingested, they can bioconcentrate in tissues, bones and organs where they emit radiation for a long time. Appendix I Table of Common Indicators Drinking Water Standards (Established by the U.S. Public Health Service unless otherwise noted) www.che.wsu.edu/.../dishon/sipaper_wsu.htm NON-POINT SOURCES OF POLLUTION & SOME RESULTS5 Pollutant Sources Ammonia nitrogen Decaying organic material Nitrates Agricultural fertilizers, sewage, industrial wastes, drainage from feedlots,farm manures & legumes Phosphates Excessive drainage from agricultural Some Possible Results Reduces amount of dissolved oxygen endangering fish. Produces nitrogen which may stimulate growth of algae or undesirable plants which can overload the ecological system. Large amount in drinking water can cause methemoglobinemia (blue babies). Stimulate growth of algae which can reduce dissolved oxygen when they die & decompose. Eutrophication. Algal blooms which result in oxygen areas depletion and fish kills. Rapid decomposition of algae can produce odors associated with hydrogen sulfide gas. Sediment Agriculture, forestry, Decreases water clarity & urban run-off, light transmission which can construction, mining interfere with fish populations. Acts as substrate foe organic pollutants. Decreases recreational and commercial values of streams. Decreases quality of drinking water. Salts (Salinity -- Agriculture, mining, Decreases species diversity by including halides urban run-off favoring salt tolerant species. and bicarbonate Reduces crop yield. Impacts being converted stream habitats and plants to carbonate) that are food sources for other species. Decreases quality of drinking water. Pesticide, Agriculture, forestry Kill aquatic organisms. herbicides Adversely affect reproduction, growth, respiration, and development in other aquatic species. Reduce food supply and destroy habitat of aquatic species. Bioaccumulate in tissues of plants, macroinvertebrates and fish. Some are carcinogenic and/or mutagenic. Decrease photosynthesis inaquatic plants. Reduce recreational and commercial activities. Polycyclic urban runoff Bioaccumulate, biomagnify, aromatic and are toxic to aquatic life. hydrocarbons Can produce carcinogenic (PAHs) metabolites when digested. Polychlorinated urban runoff, landfills Toxic to aquatic organisms; biphenyls (PCBs) can bioaccumulate, biomagnify and be stored in fat deposits. Adsorb to Petroleum hydrocarbons urban runoff Silica decomposition of alumina silicate minerals in the drainage basin through which the water flows mining, industrial run-off Sulfates Sulfides sewage, industrial run-off, paper manufacturing Radionuclides mining / ore processing, nuclearpowerplant wastes, commercial & industry sediments. Persist in environment longer than most chlorinated compounds. Water soluble components can be toxic to life. Portions may adsorb to particulate organic matter, be deposited in sediment and may adversely affect biological functions. Forms hard, dense scale (which is resistant to heat transfer) in boilers. Causes loss of turbine efficiency due to deposit of insoluble silica deposits on turbine blades. Lower pH in streams which stresses aquatic animals and leaches toxic metals out of sediment and rocks. High acidity and concentrations of heavy metals can be lethal to aquatic organisms and eliminate entire aquatic communities. In the form of hydrogen sulfide, cause noticeable odor. Hydrogen sulfide is toxic; acts as a respiratory depressant in humans and fish. Some are toxic, carcinogenic, or mutagenic. Some degenerate into other substances (e.g., radium and lead) which are toxic and carcinogenic to aquatic organisms. When ingested, they can bioconcentrate in tissues, bones and organs where they emit radiation for a long time.