AM122 - Rogue Community College
advertisement
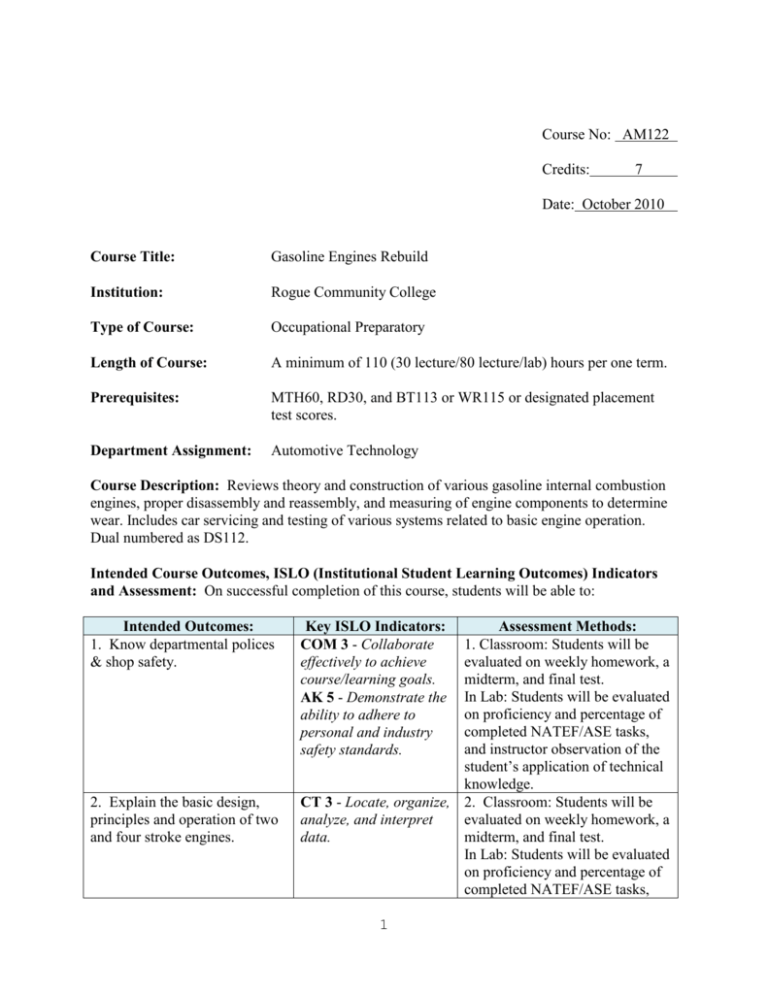
Course No: AM122 Credits: 7 Date: October 2010 Course Title: Gasoline Engines Rebuild Institution: Rogue Community College Type of Course: Occupational Preparatory Length of Course: A minimum of 110 (30 lecture/80 lecture/lab) hours per one term. Prerequisites: MTH60, RD30, and BT113 or WR115 or designated placement test scores. Department Assignment: Automotive Technology Course Description: Reviews theory and construction of various gasoline internal combustion engines, proper disassembly and reassembly, and measuring of engine components to determine wear. Includes car servicing and testing of various systems related to basic engine operation. Dual numbered as DS112. Intended Course Outcomes, ISLO (Institutional Student Learning Outcomes) Indicators and Assessment: On successful completion of this course, students will be able to: Intended Outcomes: 1. Know departmental polices & shop safety. 2. Explain the basic design, principles and operation of two and four stroke engines. Key ISLO Indicators: COM 3 - Collaborate effectively to achieve course/learning goals. AK 5 - Demonstrate the ability to adhere to personal and industry safety standards. Assessment Methods: 1. Classroom: Students will be evaluated on weekly homework, a midterm, and final test. In Lab: Students will be evaluated on proficiency and percentage of completed NATEF/ASE tasks, and instructor observation of the student’s application of technical knowledge. CT 3 - Locate, organize, 2. Classroom: Students will be evaluated on weekly homework, a analyze, and interpret midterm, and final test. data. In Lab: Students will be evaluated on proficiency and percentage of completed NATEF/ASE tasks, 1 Intended Outcomes: 3. Explain the purpose and methods of engine lubrication and cooling. 4. Research and use specifications to inspect, diagnose, and measure engine parts to determine causes of wear or failure. 5. Use specifications for inspection and procedures necessary for parts ordering. 6. Use the proper hand tools and precision measuring and machining tools to repair and rebuild components to usable condition. Key ISLO Indicators: Assessment Methods: and instructor observation of the student’s application of technical knowledge. CT 3 - Locate, organize, 3. Classroom: Students will be evaluated on weekly homework, a analyze, and interpret midterm, and final test. data. In Lab: Students will be evaluated on proficiency and percentage of completed NATEF/ASE tasks, and instructor observation of the student’s application of technical knowledge. 4. Classroom: Students will be AL 5 - Use evaluated on weekly homework, a technological tools to midterm, and final test. research new In Lab: Students will be evaluated information, solve on proficiency and percentage of problems, and communicate effectively. completed NATEF/ASE tasks, and instructor observation of the student’s application of technical knowledge. CT 3 - Locate, organize, 5. In Lab: Students will be evaluated on proficiency and analyze, and interpret percentage of completed data. AK 3 - Apply knowledge NATEF/ASE tasks, and instructor observation of the student’s and skills through a application of technical global perspective with an awareness of context, knowledge. personal assumptions, and worldview. AK 1 - Demonstrate ability to transfer learning in familiar and unfamiliar contexts in order to complete tasks. AL 5 - Use technological tools to research new information, solve problems, and communicate effectively. 2 6. Classroom: Students will be evaluated on weekly homework, a midterm, and final test. In Lab: Students will be evaluated on proficiency and percentage of completed NATEF/ASE tasks, and instructor observation of the student’s application of technical knowledge. Intended Outcomes: 7. Assemble the components of the engine to operating condition. Key ISLO Indicators: AK 2 - Integrate previous and new learning, along with practical skills, to solve problems. AK-5 - Demonstrate the ability to adhere to personal and industry safety standards. Assessment Methods: 7. In Lab: Students will be evaluated on proficiency and percentage of completed NATEF/ASE tasks, and instructor observation of the student’s application of technical knowledge Typical Required and Recommended Text(s): Hadfield, Christopher. Today’s Technician – Automotive Engine Repair and Rebuilding 4th Ed. Classroom & Shop Manual, Delmar Publishers. Erjavec, Jack. Engine Repair, NATEF Standards Job Sheets, Test A1, Delmar Publishers. Typical Required and Recommended Equipment and Materials: Each student is required to keep a notebook for handouts and notes and personal hand tools for laboratory procedures. Refer to department tool list for required tools. Assessment Methods: Successful completion of these competencies and skills will be judged by the following criteria: Attendance, participation, homework, exams, work habits, and laboratory projects completed. 3 TYPICAL COURSE OUTLINE: I. Engine Preparation & Classification II. Engine Operation III. Engine Measuring and Evaluation IV. Repair & Machining Operations V. Engine Construction, "upper end" VI. Servicing the "upper end" VII. Engine Construction, "lower end" VIII. Servicing the "lower end" IX. Servicing the Engine Block X. Engine Balancing XI. Sealing the Engine XII. Assembling the Engine XIII. Engine Lubrication & Oils XIV. Starting the Engine XV. Cooling Systems XVI. Engine Systems, Ventilation, Emissions, Exhaust XVII. Diesel Engine Design and Characteristics 4