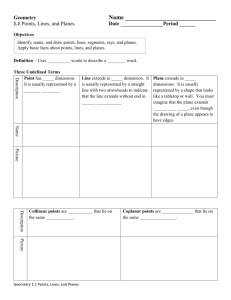
Projective geometry examples
advertisement
Projective geometry examples
These refer to exercises 3 and 4 on the handout and #10 on the Final Review. Specifically:
Given three lines in the projective plane, determine if they are concurrent. If they are concurrent, find the
point of intersection.
Geometrically (let’s visualize first): Recall that lines in P 2 are expressed as planes through the origin in R 3 :
ax by cz 0 . We express this as [a, b, c] for a line in P 2 . The projective line can be viewed as the intersection
of the plane with the plane z 1 (I’ll avoid planes parallel to z =1 in this discussion). Let’s take three distinct
projective “lines” (three planes in R 3 ).
Since they are distinct none are multiples of each other ( x y z 0 is the same line as 2 x 2 y 2 z 0 .
The three planes all go through the origin, but (0,0,0) is not a point in P 2 . We are trying to see if the
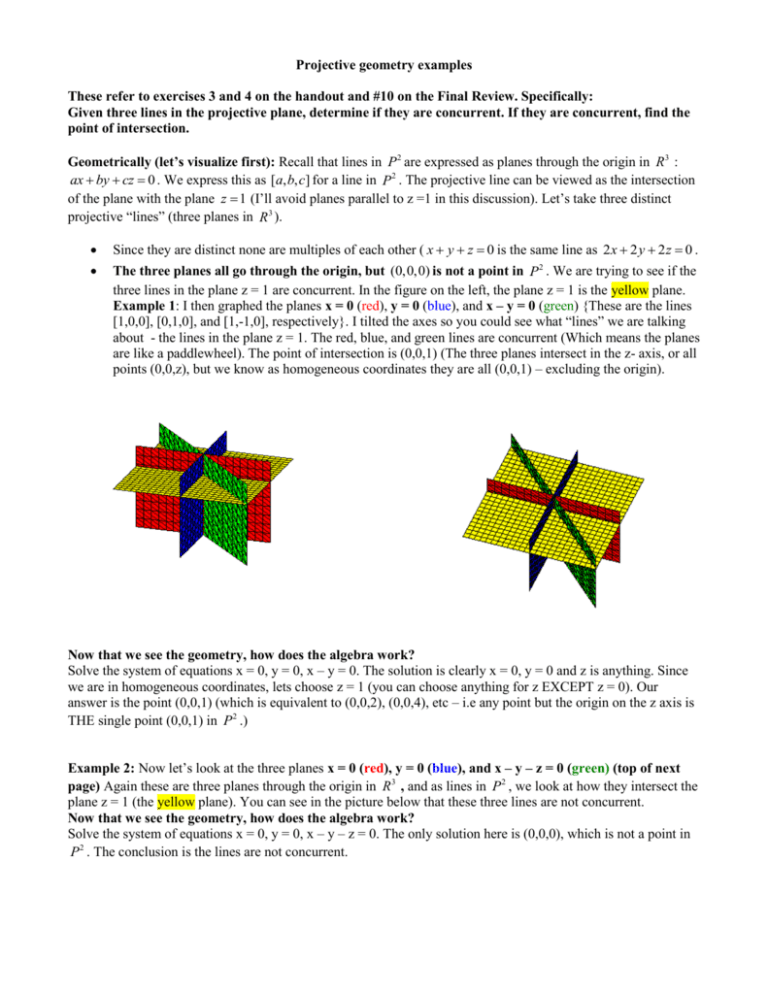
three lines in the plane z = 1 are concurrent. In the figure on the left, the plane z = 1 is the yellow plane.
Example 1: I then graphed the planes x = 0 (red), y = 0 (blue), and x – y = 0 (green) {These are the lines
[1,0,0], [0,1,0], and [1,-1,0], respectively}. I tilted the axes so you could see what “lines” we are talking
about - the lines in the plane z = 1. The red, blue, and green lines are concurrent (Which means the planes
are like a paddlewheel). The point of intersection is (0,0,1) (The three planes intersect in the z- axis, or all
points (0,0,z), but we know as homogeneous coordinates they are all (0,0,1) – excluding the origin).
Now that we see the geometry, how does the algebra work?
Solve the system of equations x = 0, y = 0, x – y = 0. The solution is clearly x = 0, y = 0 and z is anything. Since
we are in homogeneous coordinates, lets choose z = 1 (you can choose anything for z EXCEPT z = 0). Our
answer is the point (0,0,1) (which is equivalent to (0,0,2), (0,0,4), etc – i.e any point but the origin on the z axis is
THE single point (0,0,1) in P 2 .)
Example 2: Now let’s look at the three planes x = 0 (red), y = 0 (blue), and x – y – z = 0 (green) (top of next
page) Again these are three planes through the origin in R 3 , and as lines in P 2 , we look at how they intersect the
plane z = 1 (the yellow plane). You can see in the picture below that these three lines are not concurrent.
Now that we see the geometry, how does the algebra work?
Solve the system of equations x = 0, y = 0, x – y – z = 0. The only solution here is (0,0,0), which is not a point in
P 2 . The conclusion is the lines are not concurrent.
a1 x b1 y c1 z 0
Generalize: Given any three lines in P : a2 x b2 y c2 z 0 We know from the geometry (three plane through
2
a3 x b3 y c3 z 0
the origin) and from the algebra that (0,0,0) is a solution (plug it in). The only question to determine if the lines
are concurrent is if there is any other point besides (0,0,0) that is a solution. If there is more than one point then
there is a whole line where they intersect, which is our point in P 2 ). Note: can’t intersect in a plane if they are all
distinct.
Linear Algebra Fact: The above system of equations has a unique solution (meaning (0,0,0) only, meaning the
a1 b1 c1
lines are NOT CONCURRENT) if and only if the determinant a2 b2 c2 0 . This means that they are
a3 b3 c3
a1
concurrent if and only if a2
a3
b1
b2
b3
c1
c2 0 . (Check that this is true for the two examples above)This will tell us
c3
whether they are concurrent or not, but it will not give us the point of intersection – so you need to solve the
system of equations.
When are three distinct points collinear?
By duality, three points ( x1 , y1 , z1 ),( x2 , y2 , z2 ),( x3 , y3 , z3 ) collinear is exactly the same determinant condition except
replace the a, b, c with x, y, z in the matrices.
Example 1d (dual of above example 1): The points (1,0,0),(0,1,0),(1,-1,0) are collinear (you can check the
determinant is 0. Solving a = 0, b = 0, a – b = 0 we get (0,0,c) where c is any nonzero real. So [0,0,1] (using
square brackets for a line)or the line z = 0 is the line containing these three points (Note: This line is the ideal line
in P 2 (the xy-plane) so you can’t see it intersect the plane z = 1.
Example 2d: Dual of above example 2: The points (1,0,0), (0,1,0) and (1,-1,-1) are not collinear (check the
determinant is not 0. The solution is a = b = c = 0, but [0,0,0] is not a line in P 2 .