Plane Geometry - Chabot College
advertisement

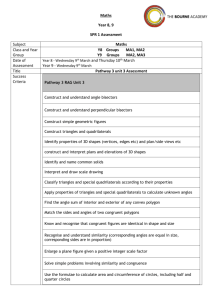
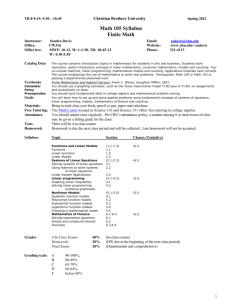
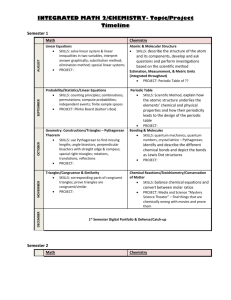
Chabot College Fall 2002 Replaced Fall 2010 Course Outline for Mathematics 57 PLANE GEOMETRY Catalog Description: 57 – Plane Geometry 3 units Topics in plane geometry. Includes congruence, similarity, parallel lines, and properties of polygons and circles. Prerequisite: Mathematics 65, Mathematics 65B or Mathematics 65L (all completed with a grade of C or higher) or an appropriate skill level demonstrated through the Mathematics Assessment process. 3 hours. [Typical contact hours: 52.5] Prerequisite Skills: Before entering the course the student should be able to: 1. write set theory notation; 2. apply order of operations to simplify algebraic expressions; 3. solve linear equations in one variable; 4. solve and graph linear inequalities in one variable; 5. graph linear equations in two variables by various methods; 6. add, subtract, multiply, and divide polynomials; 7. apply the formula for squaring a binomial; 8. factor special products, general trinomials, and polynomials with four terms; 9. add, subtract, multiply, divide and simplify rational expressions; 10. apply algebraic methods to solve word problems; 11. solve quadratic equations by factoring, using the principle of square roots, and using the quadratic formula; 12. solve systems of equations by graphing, substitution and elimination; 13. apply the properties of integral exponents; 14. solve formulas for any given variable; 15. solve rational equations; 16. find the slope of a line from the graph, from the definition and from the slope-intercept equation of the line; 17. find the equation of a line using the point-slope equation; 18. convert between scientific notation and standard notation. Expected Outcome for Students: Upon completion of the course the student should be able to: 1. define and/or illustrate: a. segment b. ray c. angle d. distance between points on a line e. perpendicular and parallel lines f. midpoint of a segment; 2. demonstrate: a. the elements of a formal proof b. the ability to utilize (1) above in the solution of problem material c. geometric inequalities d. the relation of arcs and angles formed by chords, secants and tangents to circles through proofs and problems e. the relation of circles and regular polygons, both inscribing and circumscribing; 3. form a conclusion based on mathematical logic; 4. compute areas and volumes of geometric figures; 5. do constructions with straight edge and compass. Chabot College Course Outline for Mathematics 57 Fall 2002 Page 2 Course Content: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Angles, congruent angles, angle bisectors Perpendiculars and parallels Distance between points on a plane Segments, congruent segments, midpoint of a segment Congruence of triangles, similarity of triangles Properties of triangles, medians, altitudes, bisectors of angles Polygons Surface areas and volumes Inequalities Logic Circles a. Properties b. Area c. Chords, tangents, secants 12. Constructions Methods of Presentation: 1. Lectures 2. Group discussion 3. Problem sessions Assignments and Methods of Evaluating Student Progress: 1. Typical Assignments a. Page 29 Do 1-12 all, 13- 29 odds, 31-34 all, 35, 37, 40, 41, 43, 45, 47-50 all, 51, 55, 61, 62, 63, 64 2. Methods of Evaluating Student Progress a. Midterms b. Quizzes c. Homework d. Final examination Textbook(s) Typical: Elementary Geometry, Alexander/Koeberlein, Houghton Mifflin Company, 1999 Special Student Materials: Ruler and compass C. Wieser Curriculum/math/57 Hps Css revised: 092000 Css revised: 05/05/01 Math 57.091501.rev1 MATH 57 Outline Fall 2002