Determining Formal Charge
advertisement

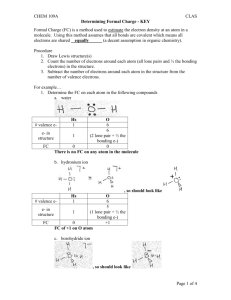
CHEM 109A CLAS Determining Formal Charge Formal Charge (FC) is a method used to estimate the electron density at an atom in a molecule. Using this method assumes that all bonds are covalent which means all electrons are shared (a decent assumption in organic chemistry). Procedure 1. Draw Lewis structure(s) 2. Count the number of electrons around each atom (all lone pairs and ½ the bonding electrons) in the structure. 3. Subtract the number of electrons around each atom in the structure from the number of valence electrons. For example… 1. Determine the FC on each atom in the following compounds a. water b. hydronium ion c. borohydride ion d. formic acid (HCOOH) e. nitrobenzene OR (instead of performing steps 2 & 3 above) you can learn to identify some common bonding patterns and the associated FC. Bonding Patterns & FC – reproduced from an Aue handout w/added examples. Most common patterns are in bold font. FC on… Carbon Nitrogen CH4 Oxygen NH3 H2 O Fluorine 1 bond 3 lp HF 2 bonds 2 lp 3 bonds 1 lp 4 bonds CH2CH2 N2H2 CHCH N2 H2CO formaldehyde 0 2 bonds 1 lone pair (lp) carbene (sextet = very unstable) 1 bond 2 lp 3 lp nitrene (sextet = very unstable) (sextet = very unstable) Page 1 of 2 CHEM 109A CLAS Determining Formal Charge 3 bonds CH3+ methyl cation 4 bonds (sextet = very unstable, but can be stabilized by hyperconjugation) NH4+ ammonium ion 3 bonds 1 lp H3 O+ hydroiunium ion 2 bonds 2 lp H2F+ fluoronium ion +1 5 bonds CH5+ 2 bonds 1 lp (exceeds octet = very unstable) 3 lp NH2+ (sextet = very unstable) F+ fluorenium ion (sextet = very unstable) 2 bonds 1 lp +2 -1 3 bonds 1 lp - CH3 methyl anion 2 bonds 2 lp NH2 - 1 bond 3 lp OH2+2 (sextet = very unstable) 4 lp HOhydroxide ion Page 2 of 2 Ffluoride ion