Waves Study Guide Key
P. Sci. Waves
Key
Put all answers on a separate sheet of notebook paper.
1.
Mechanical waves need a _ medium _ through which to transport energy.
2.
The particles in a surface water wave move _ in a circle (back-&- forth / up & down) .
3.
Waves in which the particles of medium move at right angles to the direction of the wave are _ transverse _ waves.
4.
The _ wavelength _ of a wave is measured from the crest of one wave to the crest of the next.
5.
If the wavelength of a given wave decreases, you know that its frequency will _ increase _
6.
Two waves have the same frequency and wavelength, but the first wave has a greater amplitude. The energy of the first wave _ greater than _that of the second.
7.
Wave A has a greater frequency than wave B, but the amplitude of the two waves is the same. The energy of wave A is _ equal to that of wave B.
8.
The unit for frequency is the _ hertz _.
9.
A wave will travel only as long as it has _ energy _ to carry
10.
When you squeeze together the coils of a spring and then release them, you are creating a _ compressional _ wave
11.
Waves in which the particles of the medium move only in the same direction as the motion of the wave are _ compressional _ waves
12.
You are creating a wave on a spring. If you start shaking the spring more slowly, the wavelength of the resulting wave will _ increase _.
13.
If you are lying on a raft, and you notice that the number of waves that go past the raft increases, you also find that the distance between each crest __ decreases __.
14.
Wave A carries more energy than wave B. Wave B has a smaller _ amplitude _ than wave A
15.
The energy a wave carries is measured by its __ amplitude _.
16.
For a given wave, if the frequency doubles, the wavelength _ is halved _.
17.
When a wave passes from a less dense medium to a more dense medium, the _ speed _ may change
18.
Repeating disturbances that transfer energy through matter or space are _ waves _
19.
The two types of mechanical waves are __ transverse _ and
_ compressional (longitudinal) _
20.
If the frequency of a water wave changes, its _ wavelength _ must also change
21.
The symbol
(lambda) stands for the __ wavelength _.
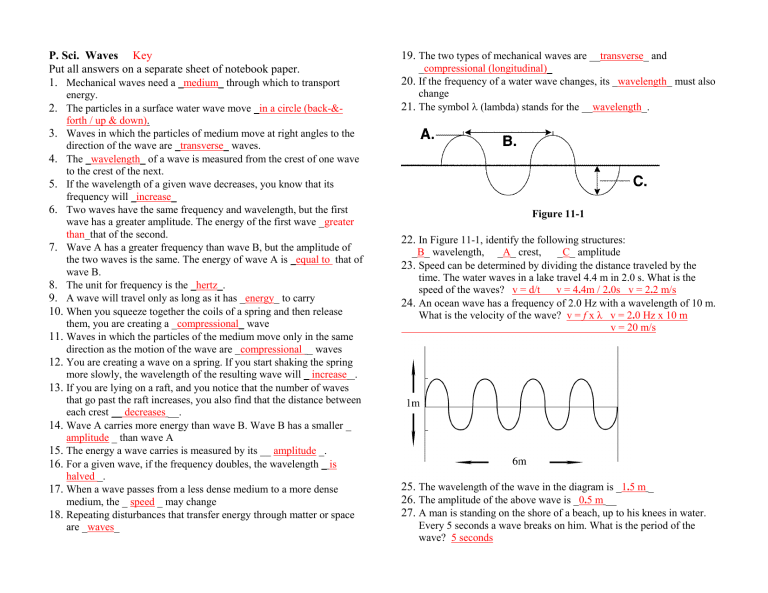
Figure 11-1
22.
In Figure 11-1, identify the following structures:
_ B _ wavelength, _ A _ crest, _ C _ amplitude
23.
Speed can be determined by dividing the distance traveled by the time. The water waves in a lake travel 4.4 m in 2.0 s. What is the speed of the waves? v = d/t v = 4 .
4m / 2 .
0s v = 2 .
2 m/s
24.
An ocean wave has a frequency of 2.0 Hz with a wavelength of 10 m.
What is the velocity of the wave? v = f x λ v = 2 .
0 Hz x 10 m v = 20 m/s
25.
The wavelength of the wave in the diagram is _ 1 .
5 m _
26.
The amplitude of the above wave is _ 0 .
5 m __
27.
A man is standing on the shore of a beach, up to his knees in water.
Every 5 seconds a wave breaks on him. What is the period of the wave? 5 seconds
28.
A child is sending pulses down a stretched rope at a rate of 2 pulses per second. The distance between the pulses is 5 meters. What is the speed of the wave? 10 m/s
29.
A train of waves is moving at a speed of 30 m/s. The frequency of the waves is 10 Hz. What is the wavelength? 3 m
30.
A person is standing still and listening to a siren sounding an alarm.
The frequency of the sound is 500 Hz. The person begins running toward the sound at a rate of 20 m/s. The frequency of the sound the person hears will__ increase _
31.
Which type of electromagnetic wave has the greatest wavelength?
visible light , microwaves, radio waves , X rays
32.
A wave with a frequency of 0.5 Hz and a speed of 10 m/s has a wavelength of _ 20 m _
33.
A(n) _ wave _ is a disturbance that transmits energy through matter or space.
34.
The matter through which a wave travels is called the __ medium _.
35.
A(n) _ mechanical wave _ is defined as a wave that requires a medium.
36.
A(n) _ electromagnetic wave _ consists of changing electric and magnetic fields and does not require a medium.
37.
A wave that causes the particles of the medium to vibrate perpendicularly to the direction the wave travels is called a(n)
_ transverse wave _.
38.
A wave that causes the particles of the medium to vibrate parallel to the direction the wave travels is called a(n) _ longitudinal _.
39.
The highest point of a transverse wave is called the _ crest _.
40.
The lowest point of a transverse wave is called the __ trough _.
41.
The _ amplitude _ is the greatest distance that particles in a medium move from their normal position when a wave passes.
42.
The _ period _ is the time required for one full wavelength to pass a certain point.
43.
The __ frequency _ is the number of vibrations that occur in a 1-second time interval
44.
The frequency of a sound wave determines _ the pitch of the sound _
45.
How loud a sound is depends on _ the amplitude of the waves _
46.
The difference between visible light and X rays is that _ the frequency of X rays is greater _
47.
The color of light is determined by _ the frequency _ of the light waves.
48.
The bouncing back of a wave as it meets a surface or boundary is called _ reflection _.
49.
The bending of a wave as it passes an edge or an opening is called
_ diffraction _.
50.
The bending of waves as they pass from one medium to another is called _ refraction __.
51.
_ Interference __ occurs when two or more waves exist in the same place at the same time.
52.
In _ destructive interference __, waves combine so that the resulting wave is smaller than the largest of the original waves.
53.
In __ constructive interference _, waves combine so that the resulting wave is bigger than the largest of the original waves.
54.
A(n) _ standing wave _is a wave form caused by interference that appears not to move along the medium and that shows nodes and antinodes.
55.
Explain the difference between mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves. Mechanical waves require a medium in which to travel. Electromagnetic waves do not
56.
Explain the relationship between vibrations and waves. Most waves are caused by a vibrating object. Mechanical waves are caused by the vibrating particles of the medium. Electromagnetic waves may be caused by vibrating charged particles
57.
Why does sound travel faster in solids than in liquids, and faster in liquids than in gases? When a particle of a medium is disturbed, it will cause a neighboring particle to be disturbed. The closer the particles are and the more tightly they are bound, the faster the disturbance will travel through the medium. The particles of solids are very close together, the particles of liquids are not as close, and the particles of a gas are relatively far away from each other
58.
Suppose ocean waves are hitting a shore at a frequency of 20 waves per minute. Two swimmers are in the water. One swimmer says the frequency is 25 waves per minute and the other says the frequency is
15 waves per minute. How can the Doppler effect explain this apparent difference? One swimmer is swimming out to sea and is moving against the direction the waves are traveling, which causes the swimmer to encounter a wave 25 times per minute. The other swimmer is swimming toward shore in the same direction the waves are traveling, so that swimmer encounters waves less frequently
59.
Compare and contrast refraction and reflection. Both refraction and reflection occur when a wave traveling through a medium encounters a different medium. Reflection involves the wave bouncing back into the original medium, while refraction involves the wave changing direction as it passes into the new medium
60.
What happens when two waves are in the same place at the same time? A wave is not an object but a disturbance that is propagated through a medium. For this reason, it is possible for two different waves to occupy the same space at the same time. When they do, a single wave is formed. This is called interference
61.
What determines whether the interference between two waves is constructive or destructive? If the motion of the particles of the two waves are in the same direction at a given point, the motions will add up and there will be constructive interference. Otherwise, there will be destructive interference
62.
Explain how two sound waves of slightly different frequencies produce beats When the two different sound waves are added together, there is alternating destructive and constructive interference.
Constructive interference causes the loudness of the sound to increase and destructive interference causes the loudness to decrease





