1.2.P. Single-phase half-wave rectifier with capacitive filter

SINGLE-PHASE RECTIFIERS WITH CAPACITIVE FILTER
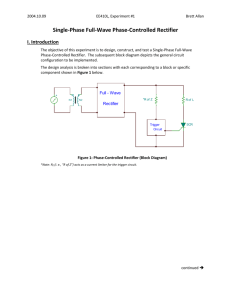
I. OBJECTIVES
a) To establish the dependence between the type of the rectifier (half-wave and full-wave) and the shape of the rectified voltage. b) The determination of the effects, which appear when the load resistor and the values of the filtering capacitor are modified, upon the rectified voltage. c) The deduction of the maximum reverse voltage and the maximum forward current through the rectifying diodes.
II. COMPONENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION
For the experiment you will use an experimental board with a transformer, four rectifying diodes, two electrolytic capacitors, a resistor and a potentiometer. In order to visualise the voltages you will use a dual channel oscilloscope, a voltmeter and an ammeter for the measurement of the average values of the voltage and current.
III. PREPARATION
1.P. SINGLE-PHASE HALF-WAVE RECTIFIER
1.1.P. SINGLE-PHASE HALF-WAVE RECTIFIER WITH RESISTIVE LOAD
How do the waveforms for v
S
, v
O
and i
O
look like for the circuit shown in Fig. 4.1.if n=22?
What is the average value (dc component) V
0
of the output voltage? How is it influenced by the value of the load resistor R
1
+R
2
+R
3
, where R
1
=800Ω, R
2
=220Ω şi R
3
What is the value of the maximum reverse voltage on the rectifying diode?
What is the value of the output voltage ripple ΔV
O
=100Ω?
(the difference between the maximum and minimum value)
For what combination of R
1
, R
2
and R
3 do you obtain the maximum average load current? What is the maximum instantaneous value of the current through the diode ( I
Fmax
)?
Notes: The sinusoidal voltage, which should be rectified in this experiment, is obtained from the transformer,
T r
, as you can see in the Fig. 4.1. The voltage source used as rectifier is a floating one. Because in the primary of the transformer is the voltage from the main network be careful not to touch this part of the transformer when it is plugged in, because you can be electrocuted.
1.2.P. SINGLE-PHASE HALF-WAVE RECTIFIER WITH CAPACITIVE FILTER
What is the difference between the circuits shown in Fig 4.1. and Fig 4.2?
How much does the C capacitor influence the voltages V s
(t), V
0
(t), i
0
(t)?
How is the DC component of V
0
modified for the circuit shown in Fig. 4.2. in comparison with the circuit shown in Fig.4.1. both having the same average value of the output current i
0
?
How does the value of the output voltage ripple ΔV
O
vary for the circuit in Fig. 4.2 when compared to the circuit in Fig. 4.1, for the same value of the output current.
What is value of the maximum reverse voltage, which might appear on D?
2.P. SINGLE-PHASE FULL-WAVE RECTIFIER
2.1.P. SINGLE-PHASE FULL-WAVE RECTIFIER WITH RESISTIVE LOAD
All the points below refer to the circuit shown in Fig. 4.3.
Which of the four diodes are in conduction for the positive alternance of the v s voltage?
How do the waveforms of v
S and v
O
look like?
What is the difference between the average value of the output voltage and the one at 1.1.P.?
What is the difference between the output voltage ripple when compared to the one obtained at 1.1.P ?
2.2.P. SINGLE-PHASE FULL-WAVE RECTIFIER WITH CAPACITIVE FILTER
How does the output voltage look likes for the circuit in Fig.4.4 (working in open circuit)?
Does the waveform of the v
O
voltage modify if the current is increased to 50mA? If so, how?
Which should be the value of the filtering capacitor (100μF or 1000μF) in order to obtain a higher average value of the output voltage for an output current of 50mA? But for an output current of 0mA?
IV. EXPLORATIONS AND RESULTS
1. SINGLE-PHASE HALF-WAVE RECTIFIER
1.1 SINGLE-PHASE HALF-WAVE RECTIFIER WITH RESISTIVE LOAD
Exploration
Build the circuit shown in Fig. 4.1.
With the dual channel oscilloscope, calibrated, set on Y-t mode, you will visualise v
S
and v
O
. With the dc miliammeter set on 200mA you will measure the dc component of I
O
(load current) and with a dc voltmeter you will measure the dc component of v
O
(output voltage) of the rectifier.
With a dc voltmeter you will measure the value of the dc component of V
O
.
For 3 configurations of the load resistors R
1
, R
2
and R
3
you will visualize v
O
(t), measure the dc component of v
O
and the output voltage ripple ΔV
O
.
D
Tr
+ mA
230V c.a.
~ v
S
810
R
1
220
R
2 v
O
100
R
3
Fig.4.1 Single-phase half-wave rectifier
Results
v
S
(t) and v
O
(t) for the values obtained for I
0
[mA] at 1.1.E.
How would you explain the shape of the voltage v
O
for I
O
=0mA ?
Is there any difference for the voltages at the previous point considering the increase of I
0
? How can you
explain this?
Write the values of I
O
, V
O
and ΔV
O
in Table 4.1.
Does the value of v
O
and ΔV
O modifies if I
O
modifies? Why?
What is the value of the maximum reverse voltage, which can be handled by the diode D? The voltage on D is the difference between v
S
and v
O
.
Which is the value of the maximum constant current through D, I
Fmax
?
2
I
O
[V]
V
O
[V]
ΔV
O
[V]
R
L
[Ω]
C [
F]
0
100
1000
0
100
1000
0
100
1000
Table 4.1
R
1
+R
2
+R
3
R
2
+R
3
R
3
1.2 SINGLE-PHASE HALF-WAVE RECTIFIER WITH CAPACITIVE FILTER
D
Tr
+ mA
230V c.a.
~ v
S
C
810
R
1
220
R
2 v
O
100
R
3
Fig. 4.2.
Single-phase half-wave rectifier with capacitive filter
Exploration
Build the circuit shown in Fig. 4.2. a) C=100μF
The experiment is done in the same way as for the experiment 1.1. b) C=1000μF
The experiment is done in the same way as for the experiment 1.1.
Results a) C=100μF
v
S
(t) and v
O
(t) for the values obtained for I
0
at 1.1.E.
How would you explain the shape of v
0
for I
0
=0mA?
How does the increase of I
O
influence the shape of v
O
? Why?
Write the values of I
For what value of I
O
,V
O
and ΔV
O
in Table 4.1.
O
does a maximum reverse voltage appear on D? What is its value? (you can use the waveforms v
O
and v
S
)
What is the relation between the maximum reverse voltage of the D and the amplitude of v
S
?
3
b) C=1000μF.
v
S
(t) and v
O
(t) for the values obtained for I
0
at 1.1.E.
How would you explain the shape of v
O
for I
0
=0mA?
Write the values of I
O
,V
O
and ΔV
O
What is the maximum value of the reverse voltage, which might appear across the diode D?
The waveforms for V
Rt
in Table 4.1.
and I
0
for P=0 (i o
= v
Rt
/R t
). What is the value of the maximum forward current through the diode D, I
Fmax
?
For what type of rectifier (with or without capacitive filter) is the diode D much more solicitated from the point of view of the maximum direct current?
For each value of I
0
from the table 4.1. compare the waveforms of v
O
obtained at the results of 1.2.a and
1.2.b. In which way is v
O
influenced by the value of the filtering capacitor?
How would you explain the big qualitative difference between the forms of ripple of v o
(t) obtained at the results of 1.1 and 1.2 ?
Using the values from table 4.1. how do the output characteristics of the half-wave rectifier look like v
O
(I
O
) in the next situations:
-rectifier with a filter;
-rectifier with a capacitive filter: - C=100μF
- C=1000μF
Draw these two characteristics on the same diagram.
Compare these diagrams from the point of view of the load current and the value of the filtering capacitor.
2. SINGLE-PHASE FULL-WAVE RECTIFIER
2.1 SINGLE-PHASE FULL-WAVE RECTIFIER WITH RESISTIVE LOAD
Exploration
Build the circuit shown in Fig. 4.3.
v
O
is visualised with the calibrated oscilloscope, which is set on Y-t mode.
The dc component of v
O
is measured using the dc voltmeter, and the dc component of I
O
is measured with the dc miliammeter.
v
O
(t) is visualised, dc component V
O
, dc component I
O
and te ripple ΔV
O
is measured for 3 combinations of the load resistors.
230V c.a.
~
Tr v
S
D4
D3
D1
+
D2
+ mA
-
0
810
R
1
220
R
2
100
R
3 v
O
Fig.4.3. Single-phase full-wave rectifier
Results
You will draw:
The Table 4.2 identically with the Table 4.1 where you will write the data for the single-phase full-wave rectifier.
The waveforms of v
0
for the values of I
0
at 2.1.E.
How would you explain the shape of v
O
(t)? Which is the difference between this one and the one obtained at the results from 1.1 ?
4
2.2 SINGLE-PHASE FULL-WAVE RECTIFIER WITH CAPACITIVE FILTER
Exploration
Build the circuit shown in Fig. 4.4
.
Tr D1
+ mA
230V c.a.
~ v
S
D4
+
D2 C
810
R
1
220
R
2 v
O
D3
100
R
3
Fig.4.4. Single-phase full-wave rectifier with capacitive filter a) C=100μF
The experiment is done in the same way as for the experiment 2.1. b) C=1000μF
The experiment is done in the same way as for the experiment 2.1.
Results a)
C=100μF
The waveforms for v
O
for the values of I
O
obtained at experiment 2.1
Why the shape of the output voltage is different compared with the one obtained in the experiment
2.1?
How does the shape of v o
influence the value of I o
obtained at experiment 2.1 ?
Write the values for I
O
, V
O
and ΔV
O
in Table 4.2. b)
C=1000μF
The waveforms for v
O
for the values of I
O
obtained at experiment 2.1
For the same value of I
O
compare the shape of the output voltage with the one obtained at paragraph a)
Write the values I
O
, V
O
and ΔV
O
in Table 4.2.
Using the values from Table 4.2 draw the output characteristics of the full – wave rectifier in the next situations:
rectifier with a filter
rectifier with a capacitive filter: C=100μF; C=1000μF
Compare these diagrams from the point of view of the load current and the value of the filtering capacitor.
Which type of rectifier (half or full – wave) supplies at the output a bigger dc voltage for the same values of the input voltage (v s
), load current and the filtering capacitance (C)?
If you consider the rectifier as a voltage source, which of the six situations studied so far is the most appropriate to be considered as an ideal voltage source?
Bring a few criterions based on which you could compare the half – wave rectifier with the full – wave rectifier. According to these criterions, which are the advantages and the drawbacks of each rectifier?
5