HANDOUT: CH 10 pt 2 Study
advertisement

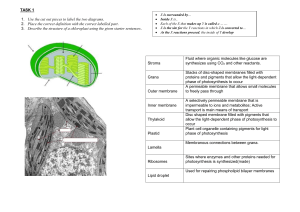
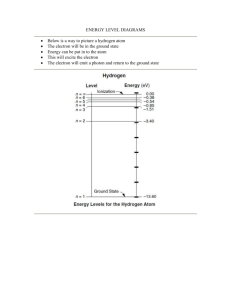
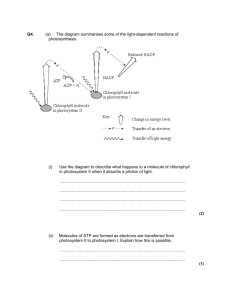
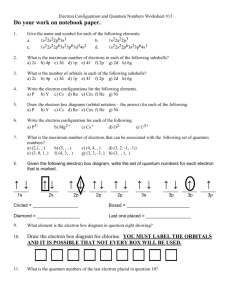
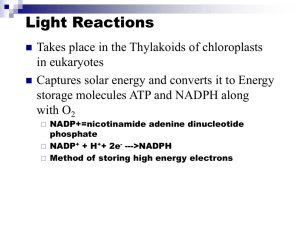
WLHS / AP Bio / Monson Name Date Per CHAPTER 10 STUDY ?’s (part 2): The Light Reactions (10.2; p. 189-197) **NOTE: Read ALL of the figure captions!!! 1a) What is the electromagnetic spectrum? 1b) Which segment of the spectrum is most important to life? Why? 2) A student performs an experiment in which she places 3 plants under 3 different colored lamps: blue, red, and green. Which color(s) of light will be best for the plant? Which color(s) will be the worst? Explain. 3) Explain the significance of the accessory pigments: -chlorophyll b: -carotenoids: 4) Summarize the experiments performed by Theodor Engelmann (see figure 10.10). According to his findings, which colors are most effective in driving photosynthesis? Which are least effective? WHAT is the EVIDENCE THAT SUPPORTS THIS??? 5a) What does it mean when a pigment molecule is described as being in its “ground state” versus its “excited state”? 5b) Generally, how long will pigments remain in their excited state? What happens to the excited electrons? 6) Compare and contrast chlorophyll solutions that are illuminated with light in the lab versus chlorophyll in an intact chloroplast. How and why is there a difference? 7) Explain how a photosystem harvests light energy. You may include a sketch of a photosystem to illustrate the process. 8) Create a chart in which you compare noncyclic (“linear”) electron flow with cyclic electron flow. Include in your chart: the components used; the inputs and outputs of each. 9a) Which energy molecules are produced in noncyclic electron flow? In cyclic electron flow? 9b) Why is there a difference? 10) How is NADPH concentration involved in feedback inhibition of noncyclic electron flow? (HINT: look ahead to figure 10.19!)