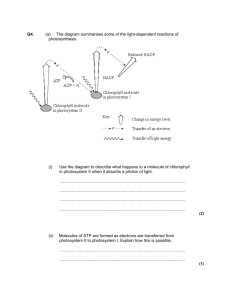
Linear Electron Flow
advertisement
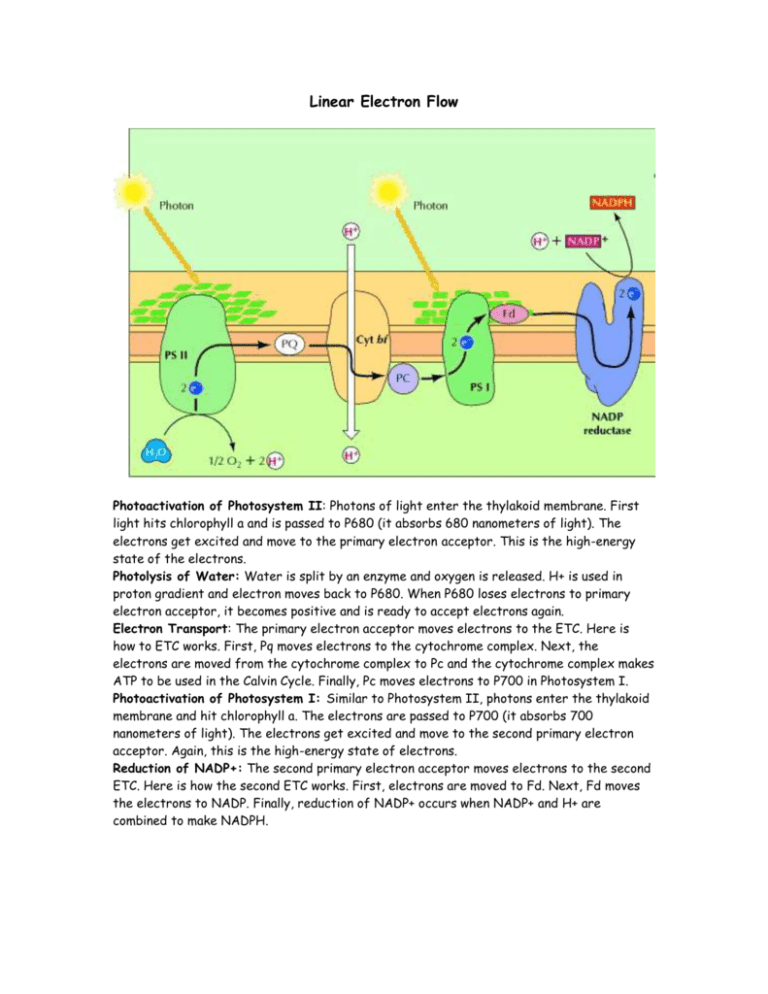
Linear Electron Flow Photoactivation of Photosystem II: Photons of light enter the thylakoid membrane. First light hits chlorophyll a and is passed to P680 (it absorbs 680 nanometers of light). The electrons get excited and move to the primary electron acceptor. This is the high-energy state of the electrons. Photolysis of Water: Water is split by an enzyme and oxygen is released. H+ is used in proton gradient and electron moves back to P680. When P680 loses electrons to primary electron acceptor, it becomes positive and is ready to accept electrons again. Electron Transport: The primary electron acceptor moves electrons to the ETC. Here is how to ETC works. First, Pq moves electrons to the cytochrome complex. Next, the electrons are moved from the cytochrome complex to Pc and the cytochrome complex makes ATP to be used in the Calvin Cycle. Finally, Pc moves electrons to P700 in Photosystem I. Photoactivation of Photosystem I: Similar to Photosystem II, photons enter the thylakoid membrane and hit chlorophyll a. The electrons are passed to P700 (it absorbs 700 nanometers of light). The electrons get excited and move to the second primary electron acceptor. Again, this is the high-energy state of electrons. Reduction of NADP+: The second primary electron acceptor moves electrons to the second ETC. Here is how the second ETC works. First, electrons are moved to Fd. Next, Fd moves the electrons to NADP. Finally, reduction of NADP+ occurs when NADP+ and H+ are combined to make NADPH. Linear Electron Flow: Analogy Photoactivation of Photosystem II: Represented by the first construction worker, photoactivation occurs when photons of light hit chlorophylls and excite the electrons. Photolysis of Water: Although not clearly shown in this diagram, the photolysis of water would occur in Photosystem II releasing H+ and oxygen. Electron Transport: The second construction worker, who takes electrons from the excited state and passes them to the ETC, shows electron transport. This mill that makes ATP in this diagram represents the cytochrome complex in the ETC, which makes ATP to be used in the Calvin Cycle. Photoactivation of Photosystem I: The third construction worker represents this stage because, like the first construction worker, it shows photons of light hitting the chlorophylls and exciting electrons. Reduction of NADP+: The fourth construction worker, who uses the gain of electrons to reduce NADP+ to NADPH, shows this. Websites: http://vcell.ndsu.edu/animations/photosystemII/first.htm http://vcell.ndsu.edu/animations/photosystemII/light.htm http://www2.mcdaniel.edu/Biology/botf99/photo/l4ightrx.html