EMSE 3420 Course Outline FA09
EMSE 3420 Course Outline FALL 2009
KEAN UNIVERSITY
Union, New Jersey
FALL 2009
Basic Theory and Practice of Teaching English as A Second Language
Course Number:
Semester Hours:
EMSE 3420
Three
Prerequisites: None
Limitations on Enrollment: 20
Required: For Bilingual Education Majors and for Collateral Program in the
Teaching of English as A Second Language.
Catalog Description
Introduction to the linguistics methods, materials and techniques of teaching English as a Second
Language
N. B. In order to insure full class participation, any student with a disability condition requiring special accommodations (e.g., tape recorder, special adaptive equipment, special note taking or test procedures) is strongly encouraged to contact the professor at the beginning of the course. For the student’s convenience, both the professor office hours and telephone number will be listed on the syllabus.
KEAN UNIVERSITY
Union, New Jersey
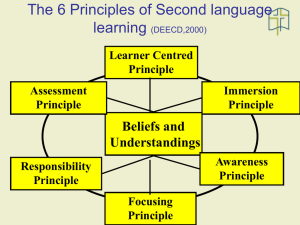
Theory and Practice of Teaching English as a Second Language
I. Course Objectives
Students will achieve growth toward becoming informed, dynamic professionals based on the
School of Education NCATE Spectrum Model as evidenced by demonstration of proficiency in
Knowledge (k), Skill (s), and Dispositions (d).
The student will be able to:
A.
describe and analyze the various English as A Second Language teaching
(k, d)
B.
identify and teach language skills according to the linguistic minorities’ needs and abilities (k, s)
C.
apply the techniques of second language teaching and present core and encore subject matter at levels appropriate to students (s)
D.
analyze instructional materials developed for the ESL environment
(k, d)
E. construct clear ESL goals and write ESL lesson plans (k, s)
E.
describe and interpret existing legal classifications of exceptional children
(k, d)
G. apply computer assisted instruction to second language teaching (s)
II. Course Content
A. Historical overview of language-teaching methodologies
1. Grammar translation
2. Immersion approach
3. Audio-Lingual
4. Cognitive code
B. Assessing the learner’s needs and setting priorities regarding
1. Native language proficiency
2.
Age
3.
Educational background
4. Learning style
2
C.
Organization and presentation of subject matter and techniques for teaching second language skills covering
1.
Organization and presentation of subject matter a.
Assessing students’ needs b.
Setting clear goals c.
Presenting information appropriate to students’ levels d.
Developing appropriate learning activities e.
Providing clear instruction and direction f.
Providing ample educational opportunities for students to make decisions. g.
Pacing and sequencing instruction h.
Using questioning techniques appropriate to students’ levels
2.
Techniques for teaching ESL a.
Teaching aural comprehension b.
Teaching pronunciation c.
Teaching vocabulary d.
Teaching structure e.
Teaching writing f.
Teaching reading g.
Teaching listening
D. Analyzing and using commercial and instructional materials
1. Survey available commercial ESL material
2. Identify select and evaluate ESL books
3. Finding and evaluating non-text material
E. Development of clear ESL goals and ESL lesson plans according to
1. Age
2. Group
3. Level of learner’s language proficiency
4. Skills to be taught
5.
Materials to be used
F.
Discussion and analysis of various classifications of exceptional children
1. Speech and language impaired
2. Mentally retarded
4.
Gifted and talented
G. The role of the computer in teaching English as a second language (ESL)
1.
Selection and discussion of computer assisted instruction programs in ESL
2.
Hands on experience with commercial and non- commercial computer software
3
III.
Methods of Instruction
1. Lectures and discussion
2.
Observation of ESL classes and of non-English proficient students in classes
conducted in English
3.
Practice in evaluating non-native speech (tapes prepared by non-native
speakers)
4. Evaluation of sample themes written by foreign students
5. Examination and evaluation of text and computer materials
6. Practice in use of audio equipment
7. Preparation of taped exercise for lab use by each student
IV. Methods of Evaluation
1. Tests (k)
2. Short papers (k, d)
3. Sample tapes (k, s)
4. Class and group discussion (k, d)
5. Supervised computer instruction (s)
6. Laboratory experiences and demonstrations (k, s, d)
V. Suggested Text(s)
Ovando, C.J., & Combs, M.C., Collier, V.P. (2006). Bilingual and ESL Classrooms: Teaching in Multicultural Contexts (4
/e
.). Boston: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-312649-7
VI. Bibliography
Allyn & Bacon Resources for Teaching English Learners, The Crosscultural, Language, and
Academic development Handbook , A complete K-12 Reference Guide, 4 th Edition ©2010
Chitester, Deborah Educator and Parental Resource Guide: Unlocking The Enigma of the
Second Language Learner . © 2007
Echevarria, Jana & Graves, Anne. Sheltered Content Instruction, Teaching English Language
Learners with Diverse Abilities. Third Edition ©2007
Freeman, Y. & Freeman, D. Academic Language for English Language Learners and Struggling
Readers. © 2008.
4
Freeman, Y., Freeman, D., & Ramirez, R. Diverse Learners in the Mainstream Classroom
©2008
Peregoy, Suzanne F. & Boyle, Owen F. Reading, Writing, And Learning in ESL, A Resource
Book for K-12 Teachers. Fourth Edition ©2005
Non-Print
ESL methodology videotapes. Developed and taped in Jersey City - IRC.
VHS 1400
VHS 1689
VHS 1150
VHS 815
VHS 35-40
M2-313
M2-498
Computer Software
Literacy Lost
Children of Poverty
Becoming Bilingual
Children of the Tribe
Effective Teaching Techniques
Forty four Sounds of English
Teaching Reading to Spanish Speakers
A, B, C. Omaha, NE. Merry Bee Communications.
Early Words. Omaha, NE. Merry Bee Communications.
Basic Inventory of Natural Language II. CA. CHECpoint Systems, Inc.
Grammar Mastery: Series B. N.Y. Regents/ALA Co.
Main Idea. Palo Alto, CA Etude Corporation.
Spelling Volume I. St. Paul. MN. MECC.
Story Machine. Cambridge, MA. Spinnaker Software Corporation.
Websites for Bilingual Teachers
1.
Bilingual Education/ESL Links http://latino.sscnt.ucla.edu/research/bieduc.
2.
Bilingual Education Resources on the Net http://www.estrellita.com/~karenm/bil.
3.
La Clase Bilingüe http://www.laclase.com/index.
4.
Parent Resources
5
http://www.indiana.edu/~eruc_rec/bks/ag45.html (/pi.html or /bi.html)
5.
Websites and Resources for Teachers (Lesson Plans) http://www.csun.edu/~vceed009/ http://www.ncbe.gwu.edu/classroom/lesssons. http://members.aol.com/Lingoteach/index.html http://www.sils.umich.edu/~jarmour/etc/etchome
6.
Bilingual Books for Kids/Multilingual Books and Tapes http:bilingualbooks.com
VII. Seminal Works
Auerbach, E. (1997). It’s not the English Thing: Bringing Reading Research into the ESL
Classroom. TESOL Quarterly , v. 31, n. 2, p. 237- 261.
Bello, T. (1997). Improving ESL Learners’ Writing Skills,
National Clearinghouse for ESL
Literacy Education . v. 3, p. 3-12, Washington, D.C.
Dougherty, B. (1996, October). The Write Way: A Look at Journal Writing in First-Year
Algebra.
Mathematics Teacher , 89, p. 556-560.
Fashola, Olatokunbo, Drum, P., Mayer, R. and Kang, S. (1996). A Cognitive Theory of
Orthographic Transitioning: Predictable Errors in How Spanish-Speaking Children Spell
English Words. American Equational Research Journal, 33 (4), p. 825-843.
Garcia, E. (2002). Student Cultural Diversity. Understanding and Meeting the Challenge.
Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company.
Gersten, R. (1996). The Double Demands of Teaching English Language Learners.
Educational
Leadership . p. 18-22.
Green, C.F. (1997). Developing Discussion Skills in the ESL Classroom. ELT Journal , v.5, n.2, p. 135-143.
Grujicic-Alatriste, L. (1997). Possible Effects of Pre Writing Oral Activities on the L
2
Process:
An SLA Perspective . http://www/surrey.ac.uk/ELI/alatriste.html
Hirsch, D. (1997). Goal Setting for ESL Lessons. The English Teacher . v. 6, p. 23-28.
Jimenez, R.T., Garcia, G.E., & Pearson, P.D. (1996). The Reading Strategies of Bilingual/
Latina/o Students who are Successful English Readers: Opportunities and Obstacles.
Reading Research Quarterly , v. 31, n.1, 90-108.
Korber, J. (1997). One World, One People-ESL Lessons. English Language Center . v. 2, n1,
6
p. 18-27.
Nelson, D. (1997). ESL Lessons, Games, Ideas & Links.
English Language Center. TESOL
Quarterly , v. 31, n.1, p. 9-37.
Owen, B. (1996). On the Effectiveness of Formal Instruction in the ESL Classroom. A case study in Hong Kong . http://www/surrey.ac.uk/ELI/owenb.html
Pica, T. (1997). Tradition and Transition in Second Language Teaching Methodology. Working
Papers in Educational Linguistics , v. 13, n.1, p. 1-22.
Riozi, A. (1996). Observing ESL Writing Instruction’s A Case Study of Four Teachers. Journal of Intensive English Studies , v. 10, p. 19-30.
Schleppegrell, M. (1997). Problem Posing in Teacher Education. TESOL Journal v.6, n.3, p. 8-12.
Shannon, S. (1996 November). English in the Barrio: Quality of Content among Immigrant
Children. Hispanic Journal of Behavioral Science . v. 12, p. 256-276.
Taylor, A. (1997). Motivation in the Adult ESL Classroom . http://www/surrey.ac.uk/ELI /taylora.html
7