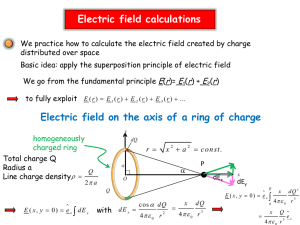
The vibrational spectra of 1- and 2-fluorofulvene molecule:Quantum
advertisement

المجلد الواحد والثالثون2008-المجلة القطرية للكيمياء National Journal of Chemistry,2008, Volume 31, 439-446 The Quantum Mechanical Calculations of the Vibration Spectra of the 1- Fluorofulvene and the 2-Fluorofulvene Molecules J.H. Ali, S.M. Haddawi , A. M. Bashi, and R. T. Haiwal Chemistry Dept., Science College, Kerbala Univ Kerbala-IRAQ. (NJC) (Received on 1/11 /2007) (Accepted for publication 9/6 /2008) Abstract The thirty fundamental vibration modes along with their corresponding IR absorption intensities for both of 1- and 2—fluorofulvene molecules were calculated using the method based on the MINDO/3-FORCES MO model .The assignments of all of these vibration modes were , also, carried out .The effect of the fluorine atom on the vibration spectra of the two molecules were studied. It was shown that there is an effect on the values of the frequencies and the corresponding IR absorption intensities of the fundamental vibration modes associated with the methylene group .In 1-fluorofulvene , any one of these normal modes has the higher frequency and, in some cases, the lower IR absorption intensity values than the corresponding one in the 2-fluorofulvene. In addition, the thermodynamic functions, Uo, Ho, So, Go , and Ao for the two molecules were calculated. Key words:MINDO/3-FORCES ,1- and 2-fluorofulvene molecules, vibration spectra. الخالصة امهت اززيممة امساسممية الثالثم ن برفقممة شممدد امتصمماا امشممحة تحممر الحم مراء المقابلممة ساسممت دا طريقممة احتمممد ت م حسمماا اماممما فلوروفممولن ن و لم-2 فلوروفممولن ن و-1 لهم ا اماممما أالهت اززيممة لكممم مممن الج مري ت ن وتمممر د ارسممة تمماث ر ر. أيضمما ت م تش م يا جميممه ه م ا اماممما امهت اززيممة.فورس م ز-3-علمما اسمملوا الم اممدو تأث ار علا قي التمرددار االهت اززيمة امساسمية وعلما ووجد إن هاا. النلور علا الط ف امهتزازي في الجزي ت ن فلوروفمولن ن أي واحمد-1 فمي جزي مة.شدد امتصاا امشحة تحر الحمراء المصاحسة لها في مجموعمة المثلم ن الحماالر شمد امتصماا امشمحة تحمر الحممراء o U, ت حساا الدوال الثرمودا امكية من ه ا اماما امعتيادية يمتل التردد امعلا وفي سحم اضافة ل ل. فلوروفولن ن-2 امقم مقاراة مه ما ااظرها في جزي ة . للجري ت ن الم كورت نHo, So, Go , Ao fluorosubstituted fulvenes is relatively common ligand in the organometalic ; the low-valent titanium-pentafulvene complexes have been prepared(7). The 1- and 2-fluorofulvene molecules, Fig.1, were studied theoretically(8) , but there is no reported study concerning their vibration spectra. Introduction Fulvenes are a crossconjugated molecules with some unique properties (1-3). Their structure and electronic distribution were investigated theoretically(4) and (5) experimentally . The halogenated substituted fulvenes were used to improve the octane quality of a fuel for an internal combustion engines(6) The 439 المجلد الواحد والثالثون2008-المجلة القطرية للكيمياء National Journal of Chemistry,2008, Volume 31, 439-446 H H 3 H H H 6 6 5 5 F 4 H 6 6 6 6 H H 4 1 2 3 H H 1 2 F a b Fig.1:- a ,1-fluorofulvene and b, 2-fluorofulvene molecules The aim of this study is to calculate the vibration spectra of the 1-and 2fluorofulvene molecules , investigate the effect of the fluorine on the fundamental vibration frequencies, and their corresponding IR absorption intensities, associated with the methylene group, and, finally, calculate the thermodynamic functions of these two molecules. The present study is based on MINDO/3-FORCES model(9) which was developed and applied to the treatment of organic molecules (10-12). Such treatment yields the equilibrium geometry and energy values of the molecules in addition to their fundamental vibration frequencies (3N-6) and IR absorption intensities. MINDO/3-FORCES model adopts the pulay forces method(13) to evaluate the force constants of molecules which are introduced then to the Wilson Secular equation of the following form(14), j L j ( F ij M ij ) 0 Results and Discussion The optimized geometric parameters of both of 1- and 2fluorofulvene molecules were listed along with their heats of formation, Hf , and with some other physical properties, table -1 .From this table, it was shown that the 2-fluorofulvene is slightly less stable than the other molecule. On the other hand, the character table shows that both molecules belong to Cs point group and the thirty fundamental vibration al frequencies are distributed among the following symmetry species, 21 A 9 A 30 Where 21A- are in-plane modes and 9A= are out of plane . Also, all these vibration modes are IR and Raman active. The thirty fundamental vibrations of each one of the two molecules were listed, tables 2 and 3. Among of these vibrations, seven modes are associated with the methylene group. These are the symmetric and antsymmetric CH2 st., the rocking and scissoring in plane bending , the wagging and twisting out of plane bending, and finally, the C=CH2 stretching vibration. In the absence of any experimental data, our calculated results were compared well with that obtained by the MINDO/3(15) and the scaled frequencies were ,in most cases, close to that of PM3 (16) ones, tables 2 and 3.The C-F frequency is not pure mode; it mixed slightly with the ring( CCC ) Solution of this equation yields vibration frequencies ( 4 2 2 C 2 ) and vibration mode eigen vector coefficients, L j .These coefficients are utilized in evaluating the atomic partial participation values (APP) (the partial contribution of each atom to the molecular vibration), the ir absorption intensities and in doing the graphical representation of each of vibration mode.(10-12). 440 المجلد الواحد والثالثون2008-المجلة القطرية للكيمياء National Journal of Chemistry,2008, Volume 31, 439-446 motion in 2-fluorofulvene and with ring( CH ) motion in the second molecule. Also, some of ring( CH ), ring( CH ), and ring( CCC ) modes , in both of the molecules, are coupled with the other vibration motions. The C-C st. vibrations are not completely pure and they localized along C-C bonds .On the others hand, the C-H vibrations are localized along the C-H bonds. In this study, we , also, investigated the effect of the fluorine atom on the values of the frequencies and their corresponding IR absorption intensities of the fundamental vibrations, associated with the methylene group, in the 1- and 2fluorofulvene molecules. The correlation of the fundamental vibrations, associated with the methylene group, in the two molecules, was listed in table-4. From this table, it was shown that each vibration mode, in the 2-fluorofulvene, has the lower frequency and, in some cases, the higher IR absorption intensity than the corresponding mode in the 1fluorofulvene.This may be attributed to the inductive effect caused by the withdrawing F substituent atom. Due to the closer of F atom to the methylene in the 1-fluorofulvene molecule, the inductive effect is the greater compared with that in the second molecule. The inductive effect causes to draw the electrons towards the F atom, so, this leads to increase the energy required for vibration transitions. The thirty fundamental vibration frequencies for each one of the two molecules along with the rotational constants A, B, and C , obtained in this study, were used to calculate the vibration and rotation contributions to the thermodynamic functions according to the following statistical thermodynamic equations, (17) , 30 RTX i o = , U vib xi 1 i 1 e U o rot =1.5RT X 30 S vib =R [ o i 1 e i X i 1 - ln(1-e 3 S rot =R[ 2 +ln 8 2 (8 3 I x I y I z )1 / 2 (kT ) 3 / 2 Xi )] o 3 ] 1.44 , =1 T These two contributions along with the others contributions, for the translation, electronic, and nuclear motions, were used to calculate Uo ,Ho ,So , Ao, and Go thermodynamic functions of the two molecules,table5.From this table it was obvious that the more stable molecule; Xi= o 1-fluorofulvene, has the lower S than that of the second molecule. There is no available experimental data in order o to compare our calculated S , (18) However the isomer fluorobenzene , which is more stable than the two molecules, Hf, =-90.643 kJ mol-1, has the value of 0.303 kJ mol-1.deg-1 for S 441 o National Journal of Chemistry,2008, Volume 31, 439-446 المجلد الواحد والثالثون2008-المجلة القطرية للكيمياء Table -1: The geometric parameters for 1- and 2-fluorofulvene molecules. Bond lengths in angstrom and bond angle in degree: See fig.1 Geometric parameter MINDO/3-FORCES* 1-fluorofulvene 2-fluorofulvene C1 – C2 1.353 1.353 C2 - C3 1.479 1.467 C3 - C4 1.360 1.358 C4 - C5 1.505 1.506 C5 - C1 1.497 1.507 C5 – C6 1.336 1.338 C3 – H3 1.094 1.086 C4 – H4 1.098 1.100 C6 – H5 1.101 1.101 C1 – F(C2-F) 1.365 1.370 99.7 103.1 C1 C5 C4 109.7 110.4 C5 C4 C3 111.5 107.0 C4 C3 C2 103.4 111.4 C3 C2 C1 115.5 107.8 C2 C1 C5 118.7 123.8 C5 C1F(C5C1H1) 122.4 123.2 C5 C4 H4 128.9 126.9 C1 C2 H2(C1C2F) 125.6 128.1 C4 C3 H3 130.4 128.4 C6 C5 C1 124.1 124.6 C5C6H6 110.2 110.5 H6C6H6 -1 Hf , kJ mol 71.156 72.180 Dipole moment, ( in Debye) 1.658 2.253 HOMO-LUMO, eV 8.556, 0.100 8.788,0.042 * calculated in this work 442 المجلد الواحد والثالثون2008-المجلة القطرية للكيمياء National Journal of Chemistry,2008, Volume 31, 439-446 Table: 2 The calculated thirty fundamental vibration frequencies ( in cm-1) along with the corresponding infrared absorption intensities (IR intensities in km. mol-1) , for the 1-fluorofulvene molecule. The scaled frequencies and the others calculated frequencies, for the molecule ,were ,also, shown. PM3 MINDO/3-FORCES* MINDO/3 Freq. ** No Freq, IR intensity, Freq. cm-1 Xi$ Assignments cm-1 -1 -1 cm ; km mol. Ref.15 Ref.16 a (in plane) V1 3586(3105) 10.28 3157 3585 14.997 ring (CH st.) V2 3547(3071) 27.05 3148 3545 14.833 CH2 as. st V3 3540(3066) 47.2 31.22 3539 14.809 ring(CH st.) V4 3528(2963) 17.37 3133 3527 14.312 CH2 s.st. V5 3518(3046) 20.52 3127 3517 14.713 ring (CH st.) V6 1854(1626) 30.02 1329 1853 7.854 C =CH2 st V7 1738(1524) 39.44 1875 1737 7.361 ring(C=C st.) V8 1671(1465) 28.44 1739 1670 7.076 ring(C=C st.) V9 1349(1349) 27.31 1518 1349 6.516 s CH2 + ring(C-C st.) V10 1353(1353) 7.611 1397 1332 6.535 ring (CCC st.) V11 1309(1309) 13.52 1345 1308 6.322 ring (C-C st.) + s CH2 V12 1181(1181) 6.79 1298 1179 5.704 ring ( CCC)+ring(C-F st.) V13 1091(1189) 2.54 1178 1091 5.743 ring( CH)(clockanticlockwise) 6.5 1.14 0.89 4.85 0.46 1102 1071 954 888 798 1067 1008 891 826 637 5.617 4.868 4.313 4.004 3.318 478(515) 0.2 621 473 2.487 ring( CH) ring( CH) +C-F st. CH2+ring( CCC) ring ( C-F)+ CH2 ring( CCC)(ring elongation) ring ( CCC) 352(379) 1.01 474 352 1.830 ring 280 189 0.922 ring ( CF) V14 V15 V16 V17 V18 1067(1163) 1008(1008) 893(893) 829(829) 637(687) V19 V20 V21 191(191) 1.99 = a (out of plane) V22 917(1010) 1.15 V23 824(898) 0.34 V24 757(825) 0.0 V25 738(804) 7.2 V26 645(645) 5.15 V27 575(575) 3.49 V28 408(408) 4.05 V29 265(265) 1.68 V30 139(196) 1.4 s: symmetric, st: stretching, : in 1039 918 4.878 CH2 975 824 4.337 ring ( CH.) 907 758 3.984 ring( CH.) 800 739 3.883 ring( CH.) 692 647 3.115 CH2+ ring ( CH.) 614 576 2.777 ring ( CH.)+ CH2 461 412 1.970 ring( CC.) 317 264 1.28 ring( C-F.)+ ring( CC) 161 140 0.946 CH2 tor. plane bending, as: antsymmetric, : out of plane bending, tor: torsion, :rocking, : wagging,: :twisting , $:Xi = 1.44 T * calculated in this work , ** The value between brackets is the scaled frequency(15) 443 المجلد الواحد والثالثون2008-المجلة القطرية للكيمياء National Journal of Chemistry,2008, Volume 31, 439-446 Table 3: The calculated thirty fundamental vibration frequencies ( in cm-1) along with the corresponding infrared absorption intensities (ir intensities in km mol-1) , for the 2-fluorofulvene molecule. The scaled frequencies and the others calculated frequencies, for the molecule ,were ,also, shown. PM3 MINDO/3-FORCES* Freq. MINDO/3 No Freq,** ir intensity, Xi$ Assignments -1 cm ref.15 -1 -1 cm ; km mol. Ref.16, a (in plane) V1 3581(3101) 7.37 3158 3579 14.978 ring (CH st.) V2 3569(3091) 20.76 3152 3568 14.930 ring (CH st.) V3 3542(3067) 32.08 3140 3541 14.814 CH2 as st.) V4 3527(2963) 18.02 3136 3526 14.312 CH2 s.st. V5 3516(3045) 24.23 3131 3515 14.708 ring (CH st.) V6 1836(1610) 13.10 1920 1835 7.776 C =CH2 st V7 1735(1521) 37.19 1872 1733 7.346 ring(C=C st.) V8 1673(1467) 3.330 1743 1672 7.086 ring(C=C st.) V9 1403(1230) 68.72 1524 1401 5.941 ring(C-C st.) V10 1330(1448) 0.590 1402 1330 6.994 s CH2 V11 1299(1299) 12.18 1343 1298 6.274 ring (C-C st.) V12 1162(1267) 12.82 1268 1161 6.119 ring ( CH) V13 1094(1192) 0.44 1184 1094 5.757 ring( CH) V14 1035(1128) 0.49 1084 1035 5.448 ring( CH) V15 968(1043) 5.82 1069 966 5.037 ring( CCC)(ring elongation) V16 946(946) 4.50 997 942 4.569 ring( CCC)+ring(C-F)st. V17 873(988) 1.49 927 873 4.772 CH2 V18 594(640) 0.64 726 594 3.091 ring( CCC)(ring elongation) V19 478(515) 1.32 620 473 2.487 ring ( CCC) V20 344(541) 0.46 463 V21 218(218) 1.88 307 = a (out of plane) V22 891(981) 2.46 1043 V23 826(900) 0.03 970 V24 782(852) 9.33 908 V25 711(711) 1.01 808 V26 607(607) 0.64 638 V27 571(571) 2.17 609 V28 498(498) 4.89 546 V29 243(243) 2.68 292 V30 134(134) 0.07 155 For abbreviations and symbols, see table 2. 444 344 2.613 ring 215 1.052 ring ( CF) 893 826 782 712 610 571 500 243 134 4.738 4.437 4.115 3.434 2.931 2.758 2.405 1.173 0.912 CH2 ring ( CH.) ring( CH.) ring ( CC.)+ CH2 CH2+ ring ( CC) ring ( CC)+ CH2 ring( CC)+ ring( C-F.) ring( C-F.)+ ring( CC) CH2 tor. المجلد الواحد والثالثون2008-المجلة القطرية للكيمياء National Journal of Chemistry,2008, Volume 31, 439-446 Table 4:-The correlation of the fundamental vibration frequencies, , cm-1 and their corresponding ir intensities, km mol-1 associated with the methylene group in 1-and 2-fluorofulvene molecules. Type of 1-fluorofulvene 2-fluorofulvene -1 -1 vibration , cm ( ir , km mol ) , cm-1 ( ir , km mol-1) mode v16, 893(0.89) v17, 873(1.49) CH2 v22,917(1.15) v22, 891(2.46) CH2 v26,645(5.15) v26 ,607(0.64) CH2 v9,1349(27.31) v10,1330(0.59) s CH2 CH2 as. st. v2,3547(27.05) v3,3542(32.08) CH2 s.st. v4,3528(17.37) v4,3527(18.02) C=CH2 st. v6,1854(30.02) v6,1836(13.02) CH2 tor. V30,139(1.4) V30,134(0.07) Table 5: The calculated standard thermodynamics functions at 298.12o K for 1and 2-fluorofulvene molecules Thermodynamics function Uo , kJ mol-1 Ho, kJ mol-1 1-fluorofulvene 2-fluorofulvene 15.801 18.279 16.298 18.776 So, kJ mol-1.deg-1 Go, kJ mol-1 Ao, kJ mol-1 0.430 -109.986 -112.464 0.435 -110.832 -113.311 Thanks for Prof. Dr. M. Shanshal for supplying us the MINDO/3-FORCES program 8- S.M. Khalil and H. M. Jarjis, Z. Naturforsch., 1990, 45a, 799-806 . 9a -S. M. Khalil and M. Shanshal. Theor. Chem.. Acta., 1977, 46, 23 . 9b-J. H. Ali and M. Shanshal, Z. Naturforsch., 2003, 58a, 1. 10-D. H, Abed and M. Shanshal, Arbeitsherich Des institüts Für theoretische Chemie, Stüttgart, 1990, 27, 389. 11-D. H. Abed, S. f. Al- Saidi and M. Shanshal, Chim. Acta Turc, 1995, 23, 7. 12a-R. M. Kubba, S. H. Rida and A. H. Hanoon, National Journal of chemistry,2005, 17, 60. 12b J.H. Ali, S.M. Haddawi , A. M. Bashi, Journal of Kerbala University, 5,1, 90-97, 2007 References 1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/fulvene 2-M. Neuenschwander, pure. Appl. Chem., 1986, 58, 55 . 3-O.Deep,S.Cogan,and S.Zillberg, Chemical Physics, 325, issues 2-3, 251, 2006. 4-T. Oicson and J. Sanstrom, Acta chem., Scand., 1982, B. 56, 23 . 5-Z. Yoshida, M. Shibata, A. Sakai and T. Sugimoto, J. Am. Chem. Soc ., 1984, 106, 6383 . 6http://www.freepatentsonline.com/ 4264336.html 7-A.Scherer,K.Kallak, A.Lutzen, M. Friedemann , D. Haase, W. Saak , R . Beckhaus ,European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, V 2005 , issue 6,1003-1010 ,2005. 445 National Journal of Chemistry,2008, Volume 31, 439-446 12c-H.R.Altaie,PH.D thesis, College of Science, Baghdad University, 2007 13-P. Pulay, Molec Phys., 1969, 17, 197. 14-E. B, Wilson, Jr. J. C. Decius, P. C, Cross, "Molecular Vibration", McGraw- Hill, New York, 1955. 15-M. J. S. Dewar and G. P. Ford, J. Am. Chem.. Soc, 1985, 1977, 99, 6. 16a-J. J. P. Stewart, J. Comput. Chem., 10, 1989, 209, 221. 16b-R. Leach Andrew, "Molecular Modeling Principles and Applications", 2nd ed., Prentice Hall, London , 2001 17- P.W. Atkins ,Physical Chemistry , sixth ed. Oxford University Press, 2001 18-D.H.Whiffen,J.Chem.Soc., 1956, 1350. 446 المجلد الواحد والثالثون2008-المجلة القطرية للكيمياء