Velocity and Momentum
advertisement

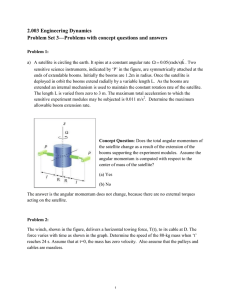
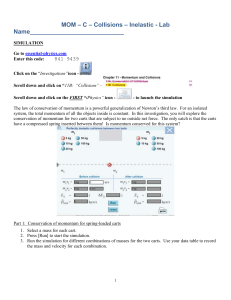
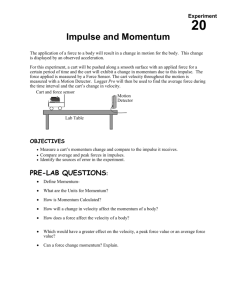
Velocity and Momentum Goals: To determine the cause and effect of net force on a cart. To relate momentum and velocity Materials: triple-beam balance, 100g mass, CPO ramp/stand/photo gate, 1.5m length of string, paper clips. Procedure: Part 1 (setup) Find the mass of the cart and record it at the top of the Data and Observations sheet. Place photo gate “A” (start) at the 5cm mark along the track. Photo gate “B” will change position during the experiment. Attach the paper clip to the eye hook in the front of the car and attach the string with the mass on it to the paper clip. The mass will hang over the edge of the ramp and you will drop it toward the floor during each trial. Part 2-Trials 1. Place photo gate “B” (finish line) at the 20cm mark along the ramp. Make sure both timer lights are lit and the timer is reset. 2. Allow thw mass to drop off the edge of the ramp and record the time at photo gate “B” into Data Table 7-1 3. Repeat the procedure for 3 trials. 4. Repeat the procedure, moving photo gate “B” to 40cm and 60 cm. You will complete 3 trials at each distance. Record all data into 7-1 Calculations 1. Calculate the average times for the cart to travel 20 cm, 40 cm, and 60 cm. Record these values in Table 7-2 in the Data and Observations section. 2. Calculate the average velocity for each distance by dividing distance traveled by average time. Record these values in Table 7-2. 3. Calculate the Final Velocity at each distance using this formula: Average velocity times 2. 4. Calculate the momentum of the cart at each distance by multiplying the mass of the cart by its final velocity. Record these values in Table 7-2. 5. Use Graph 7-1 in the Data and Observations section to make a graph of your data. Plot the average time on the x axis and the momentum on the y axis. Label the x axis Time (s) and the y axis Momentum (g·m/s). Analysis Questions 1. What force caused the car to accelerate? 2. Why was it necessary to have a constant force acting on the car? 3. What is the value of the momentum of the car before you released it? 4. What does your graph indicate about how momentum is related to the time that a constant force acts on an object? 5. Why does a shot-putter rotate through a circle before thrusting the shot?