" CHAPTER 8 Bonding: General Concepts i"1
advertisement
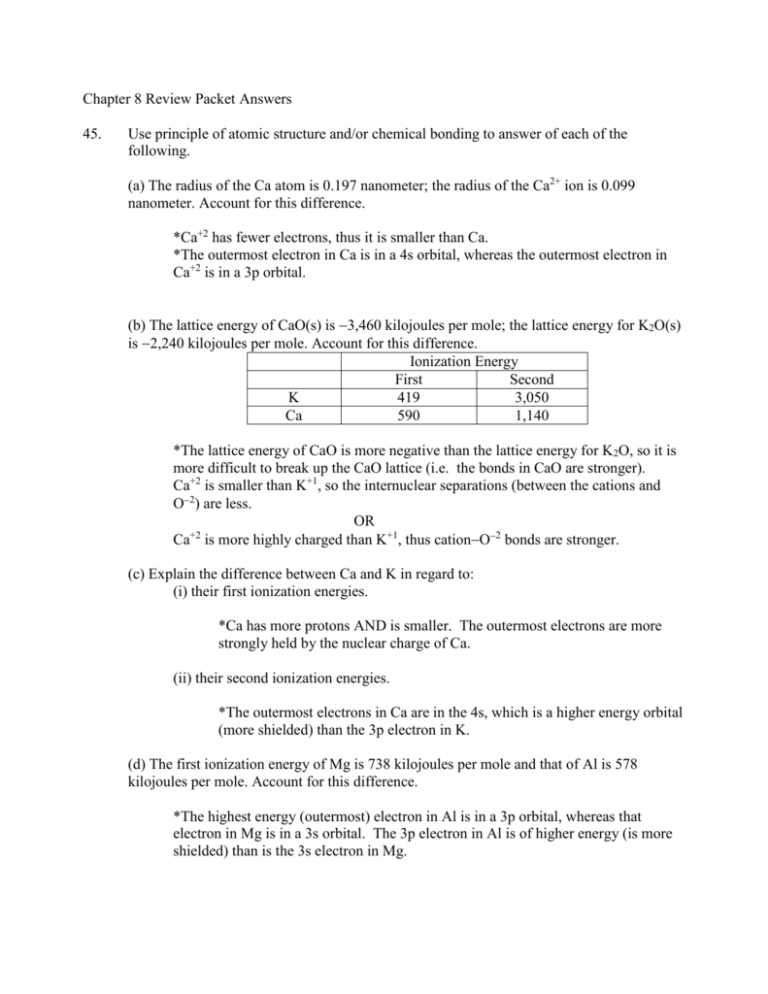
Chapter 8 Review Packet Answers 45. Use principle of atomic structure and/or chemical bonding to answer of each of the following. (a) The radius of the Ca atom is 0.197 nanometer; the radius of the Ca2+ ion is 0.099 nanometer. Account for this difference. *Ca+2 has fewer electrons, thus it is smaller than Ca. *The outermost electron in Ca is in a 4s orbital, whereas the outermost electron in Ca+2 is in a 3p orbital. (b) The lattice energy of CaO(s) is 3,460 kilojoules per mole; the lattice energy for K2O(s) is 2,240 kilojoules per mole. Account for this difference. Ionization Energy First Second K 419 3,050 Ca 590 1,140 *The lattice energy of CaO is more negative than the lattice energy for K2O, so it is more difficult to break up the CaO lattice (i.e. the bonds in CaO are stronger). Ca+2 is smaller than K+1, so the internuclear separations (between the cations and O2) are less. OR +2 Ca is more highly charged than K+1, thus cationO2 bonds are stronger. (c) Explain the difference between Ca and K in regard to: (i) their first ionization energies. *Ca has more protons AND is smaller. The outermost electrons are more strongly held by the nuclear charge of Ca. (ii) their second ionization energies. *The outermost electrons in Ca are in the 4s, which is a higher energy orbital (more shielded) than the 3p electron in K. (d) The first ionization energy of Mg is 738 kilojoules per mole and that of Al is 578 kilojoules per mole. Account for this difference. *The highest energy (outermost) electron in Al is in a 3p orbital, whereas that electron in Mg is in a 3s orbital. The 3p electron in Al is of higher energy (is more shielded) than is the 3s electron in Mg. 46. The lattice energy of LiH is 858 kJ/mol whereas that for MgH2 is 2790 kJ/mol. Account for the large difference in these two quantities. Lattice energy is based on the charge of the atom and the size of the atom. The greater lattice energy (more exothermic) will be associated with: first, the highest-charged electrons and second, the smaller ions. **The effect of the charge is greater than the effect of the size. Mg+2 has a greater charge than Li+1 but Li+1 is smaller than Mg+2. Since the effect of the charge has a greater impact than size, MgH2 should have a greater lattice energy than LiH. 47. The three species, NH21, NH3, and NH4+1 have H N H bond angles of 105, 107, and 109 respectively. Explain this variation in bond angles. If the lone pair(s) on the nitrogens are considered, all are variations of a tetrahedral shape. The bond angles in a tetrahedral shape are 109.5. Lone pair electrons take up more room than bonding electrons so each additional lone pair will cause the bond angle to decrease. 48. How can the concept of resonance be used to explain that all six CC bonds in benzene are equal in length? The actual structure is a resonance structure. It is an average of the two structures. The idea of resonance means that all bonds are identical. The actual bond length will be between the lengths of the bonds that make up the resonance structure. 49. Use bond energy values to calculate H for the reaction in which isopropanol is oxidized to form 2-propanone. (Hint: There is one reactant and one product.)