Place Value

Understanding by Design Template
5 th Grade – Place Value
Cox, Fox, Heredia
Stage 1 - Desired Outcome
Established Goals:
CCSS.Math.Content.5.NBT.A.1 Recognize that in a multi-digit number, a digit in one place represents 10 times as much as it represents in the place to its right and 1/10 of what it represents in the place to its left.
CCSS.Math.Content.5.NBT.A.2 Explain patterns in the number of zeros of the product when multiplying a number by powers of 10, and explain patterns in the placement of the decimal point when a decimal is multiplied or divided by a power of 10. Use whole-number exponents to denote powers of 10.
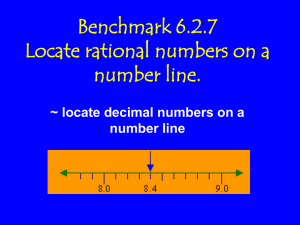
CCSS.Math.Content.5.NBT.A.3 Read, write, and compare decimals to thousandths.
CCSS.Math.Content.5.NBT.A.3a Read and write decimals to thousandths using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form, e.g., 347.392 = 3 × 100 + 4 × 10 + 7 × 1 + 3 ×
(1/10) + 9 × (1/100) + 2 × (1/1000).
CCSS.Math.Content.5.NBT.A.3b Compare two decimals to thousandths based on meanings of the digits in each place, using >, =, and < symbols to record the results of comparisons.
CCSS.Math.Content.5.NBT.A.4 Use place value understanding to round decimals to any place.
CCSS.Math.Content.5.NBT.B.5 Fluently multiply multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm.
CCSS.Math.Content.5.NBT.B.6 Find whole-number quotients of whole numbers with up to fourdigit dividends and two-digit divisors, using strategies based on place value, the properties of operations, and/or the relationship between multiplication and division. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
CCSS.Math.Content.5.NBT.B.7 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide decimals to hundredths, using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction; relate the strategy to a written method and explain the reasoning used.
Understandings:
Students will understand that:
The knowing the place value of a digit determines its value.
In comparing two whole numbers, the one with the most digits is always the greater number.
Essential Questions:
1. What patterns can we see in numbers?
2. How is our number system organized?
3. What can be generalized about place value?
4. How are decimals and whole numbers related?
Decimals follow the same pattern as whole numbers.
In decimals the number with the greatest number of digits is not always the greatest.
Students will know
Students will know and be able to
Read, write and identify the value of whole numbers to
1,000,000,000
Recognize digits in different places have different meanings (different values)
Order and compare whole numbers to
100,000,000.
Read, write and identify the value of decimals through ten-thousandths.
Compare and order decimals through thousandths.
Identify and write equivalent decimals.
Students will be able to……
1.
Recognize that in a multi-digit number, a digit in one place represents 10 times as much as it represents in the place to its right and 1/10 of what it represents in the place to its left.
2.
Explain patterns in the number of zeros of the product when multiplying a number by powers of 10, and explain patterns in the placement of the decimal point when a decimal is multiplied or divided by a power of
10. Use whole-number exponents to denote powers of
10.
3.
Read, write, and compare decimals to thousandths.
4.
Read and write decimals to thousandths using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form, e.g.,
347.392 = 3 × 100 + 4 × 10 + 7 × 1 + 3 × (1/10) + 9 ×
(1/100) + 2 × (1/1000).
5.
Compare two decimals to thousandths based on meanings of the digits in each place, using >, =, and < symbols to record the results of comparisons.
6.
Use place value understanding to round decimals to any place.
7.
Fluently multiply multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm.
8.
Find whole-number quotients of whole numbers with up to four-digit dividends and two-digit divisors, using strategies based on place value, the properties of operations, and/or the relationship between multiplication and division. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
9.
Add, subtract, multiply, and divide decimals to hundredths, using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction; relate the strategy to a written method and explain the reasoning used.
Stage 2 - Assessment Evidence
Performance Task:
1. Pre- assessment of Place Value
2. Formative Assessment – (Daily Activities, Question/Answer, Group activities,
Teacher/student mini-conferences, Exit Tickets)
3. Summative Assessment – (Paper/Pencil Test, Group Activities)
Stage 3 - Learning Plan
Learning Activities:
Create a place value chart that shows both large and small numbers, use color coding for periods and Ones, Tens, Hundreds sequence.
Ask questions about their chart. What did you notice? Is there a pattern?
Explain to you partner which place values determine large numbers, which small.
Do Place Value Activities – Use resource - http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/5th-gradenumber-activities.html
- These activities go over; comparing, multiplying and dividing by whole and decimal, representing decimals in different ways, comparing estimating, rounding, addition and subtraction of decimals
Tailor future activities to needs of students based on observations
1.
Ordering Numbers – number cards to order
2.
Number sorts – decimals/non decimals, by place value, etc.
3.
Build a Decimal – using base ten blocks
4.
Domino Digits – creating a decimal number with dominoes, reading, writing, comparing
5.
Decimal place value draw, spin or roll – creating decimal numbers, writing, comparing
6.
Number detectives – find examples of numbers of specific place value
Matching number forms – expanded notation, standard form, word form